Shop by Category
Engine
312 products
Showing 1 - 24 of 312 products
The Heart of the Machine: Exploring the Wonders of Car Engines
When you turn the key or press the ignition button, the magic happens. The hum of the engine springs to life, propelling your vehicle forward with power and efficiency. Car engines are the mechanical hearts that drive our automobiles, combining innovation, precision, and raw power. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of car engines, exploring their components, working principles, and the advancements that make them more efficient and environmentally friendly.The Basics: Internal Combustion Engines:
The majority of cars on the road today are powered by internal combustion engines. These engines convert the chemical energy stored in fuel into mechanical energy, which propels the vehicle. They operate on the principle of controlled explosions within cylinders. The two primary types of internal combustion engines are gasoline engines and diesel engines.Engine Components:
Car engines consist of various interconnected components that work in harmony to generate power. Some key components include:a) Cylinders: These cylindrical chambers provide the space for the combustion process to occur. The number of cylinders can vary, with most cars having four, six, or eight cylinders.
b) Pistons: Pistons move up and down inside the cylinders, creating the necessary pressure for combustion. They are connected to the crankshaft, which converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotational motion.
c) Valves: Valves regulate the flow of air and fuel into the cylinders and the expulsion of exhaust gases. They open and close at specific times to ensure the smooth operation of the engine.
d) Fuel Injection System: This system delivers fuel into the cylinders in a controlled manner. Modern engines often employ electronic fuel injection systems, which optimize fuel efficiency and performance.
e) Ignition System: The ignition system ignites the air-fuel mixture in the cylinders to create combustion. In gasoline engines, spark plugs provide the ignition spark, while diesel engines use compression ignition.
Working Principles:
Internal combustion engines follow a four-stroke cycle known as the Otto cycle. The four strokes are:a) Intake Stroke: The piston moves downward, drawing in a mixture of air and fuel into the cylinder through the intake valve.
b) Compression Stroke: The piston moves upward, compressing the air-fuel mixture, which increases its temperature and pressure.
c) Power Stroke: At the top of the compression stroke, the spark plug ignites the compressed mixture. The resulting explosion drives the piston downward, generating power.
d) Exhaust Stroke: The piston moves upward again, pushing out the exhaust gases through the open exhaust valve.
Advancements and Future Trends:
Car engines have evolved significantly over the years, driven by the pursuit of improved performance, fuel efficiency, and reduced emissions. Some notable advancements include:a) Turbocharging and Supercharging: These technologies force more air into the cylinders, resulting in increased power output without sacrificing fuel efficiency.
b) Direct Injection: Modern engines employ direct fuel injection, which delivers fuel directly into the combustion chamber. This method allows for better control of fuel atomization, enhancing efficiency and reducing emissions.
c) Hybrid and Electric Powertrains: The rise of hybrid and electric vehicles has revolutionized the automotive industry. Hybrid powertrains combine internal combustion engines with electric motors, offering improved efficiency and reduced emissions. Electric vehicles (EVs) rely solely on electric motors, eliminating tailpipe emissions altogether.
d) Alternative Fuels: Researchers and manufacturers are exploring alternative fuels, such as hydrogen and biofuels, to reduce the environmental impact of car engines further.
Showing 1 - 24 of 312 products
Display
View
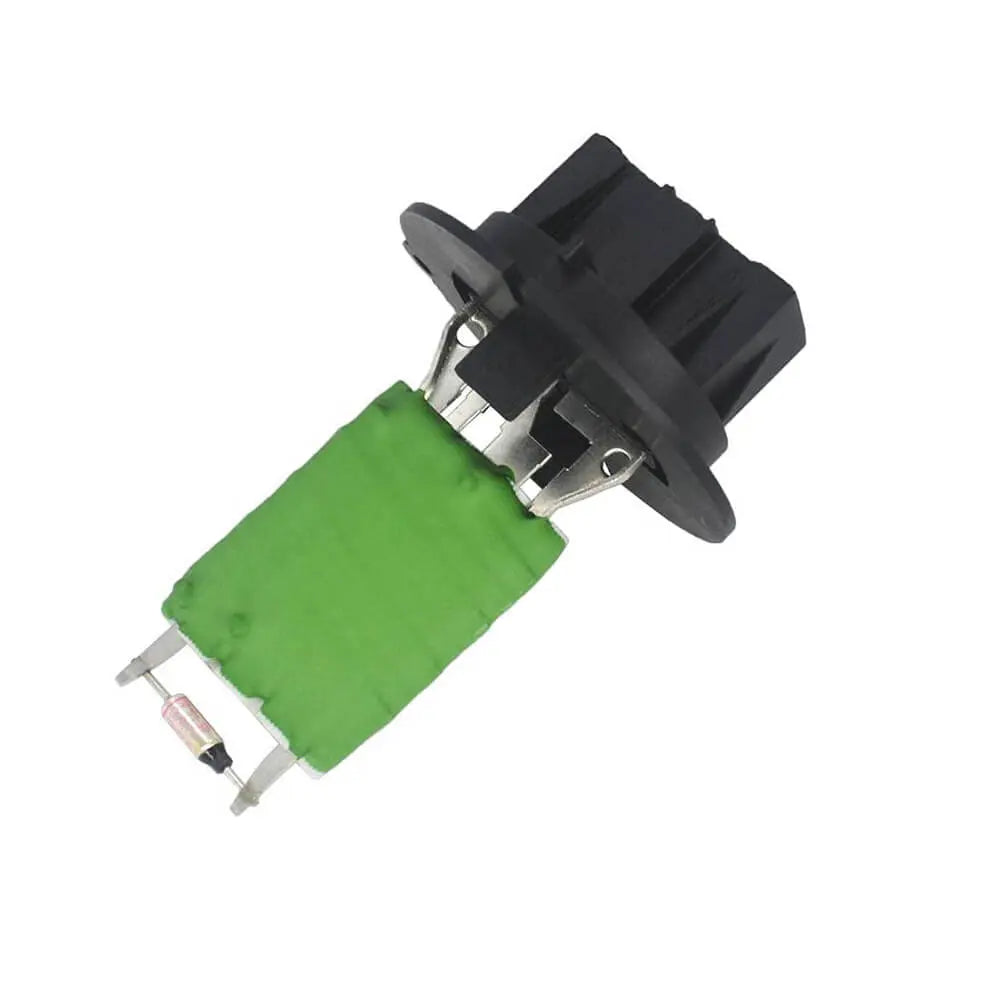


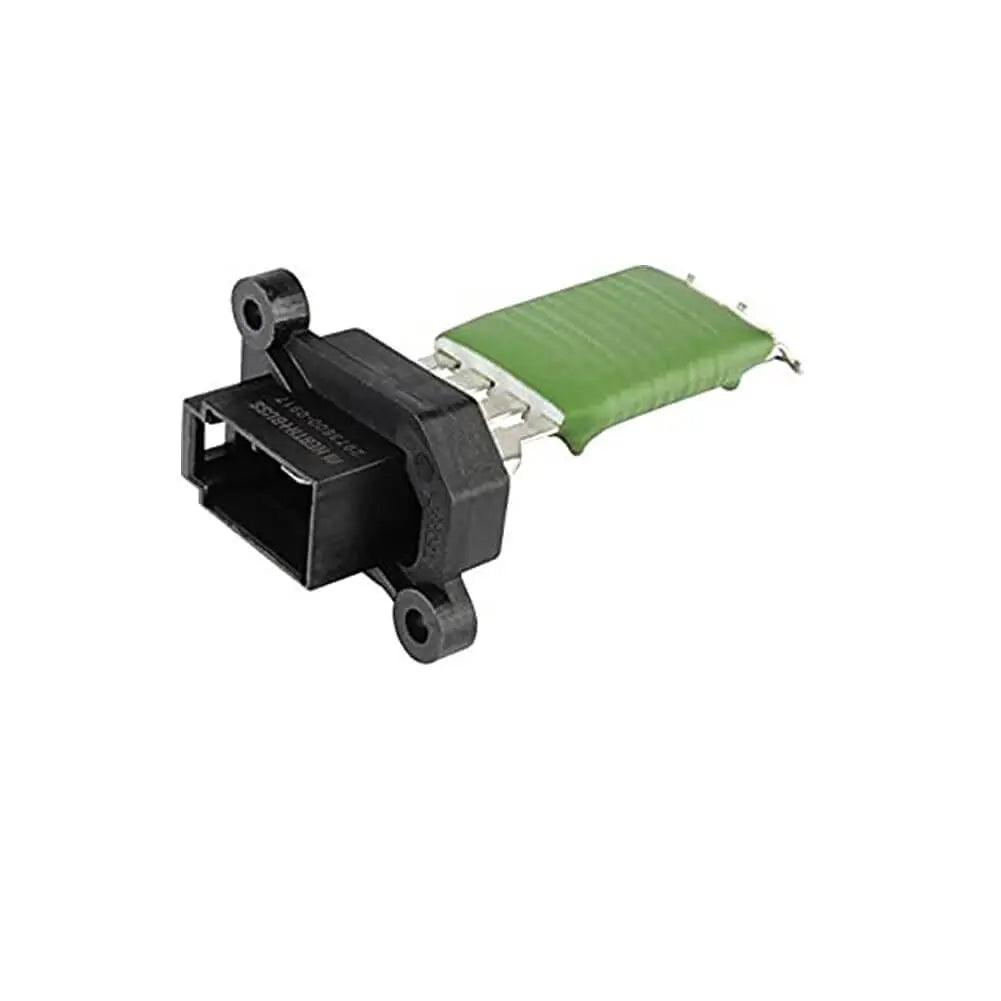
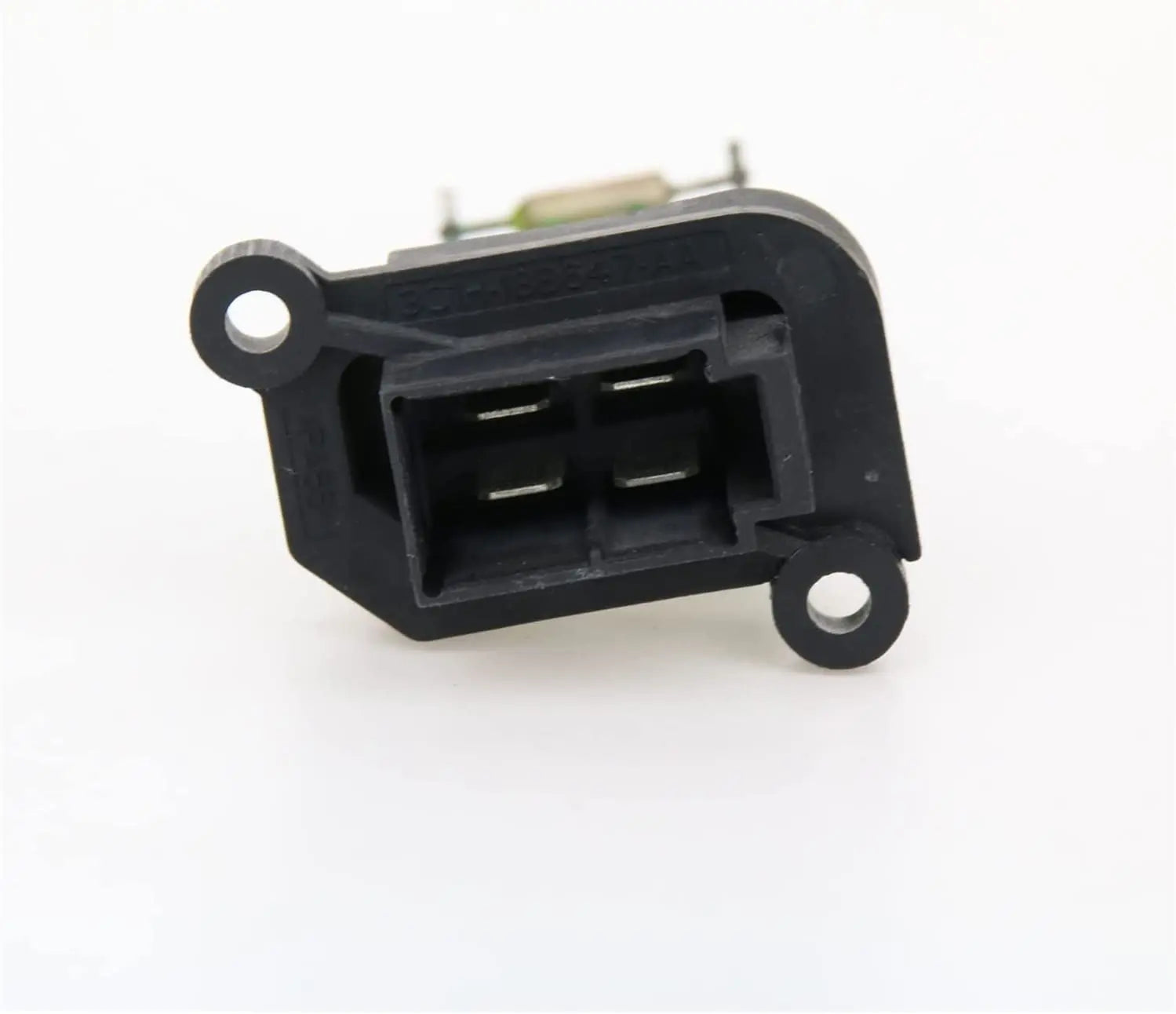
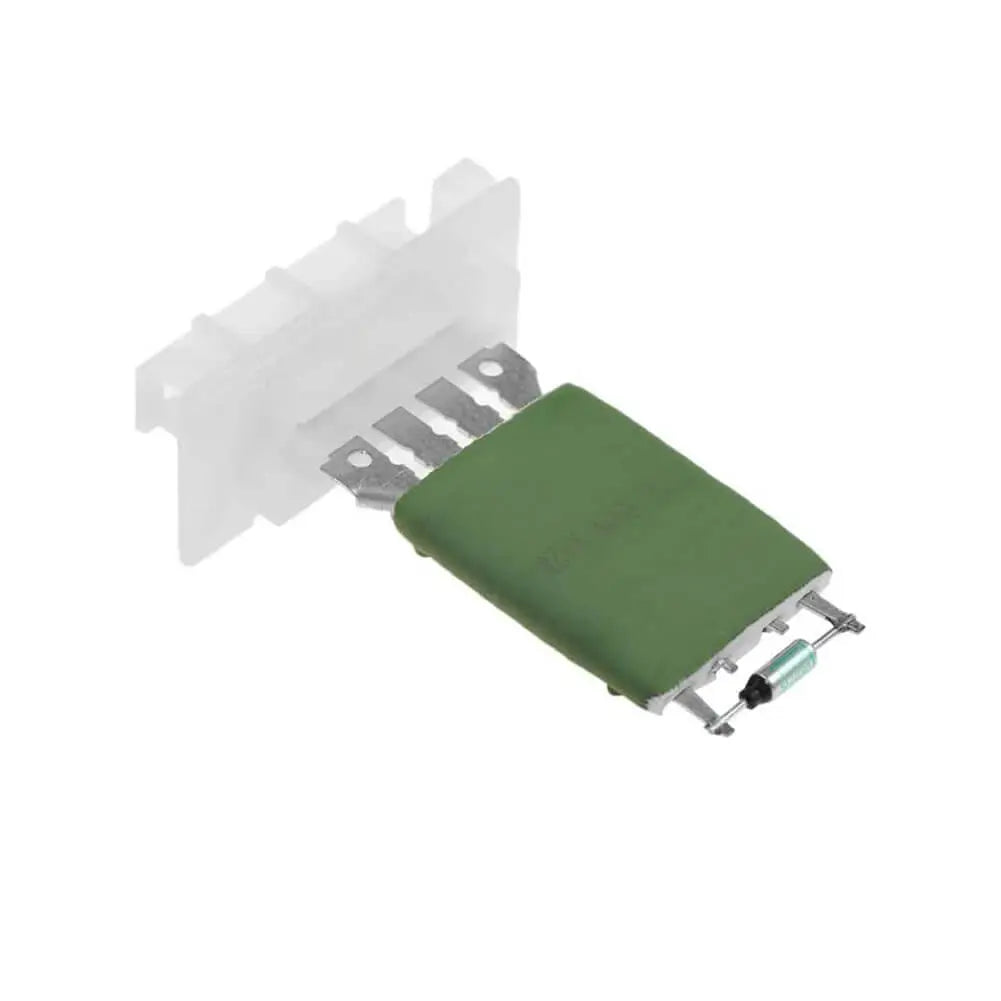
Heater Blower Motor Fan Resistor For Peugeot 206 307 HB, Saloon, Van, Estate, CC - 6450JP, 6450.JP
Sale price£12.90
No reviews
In stock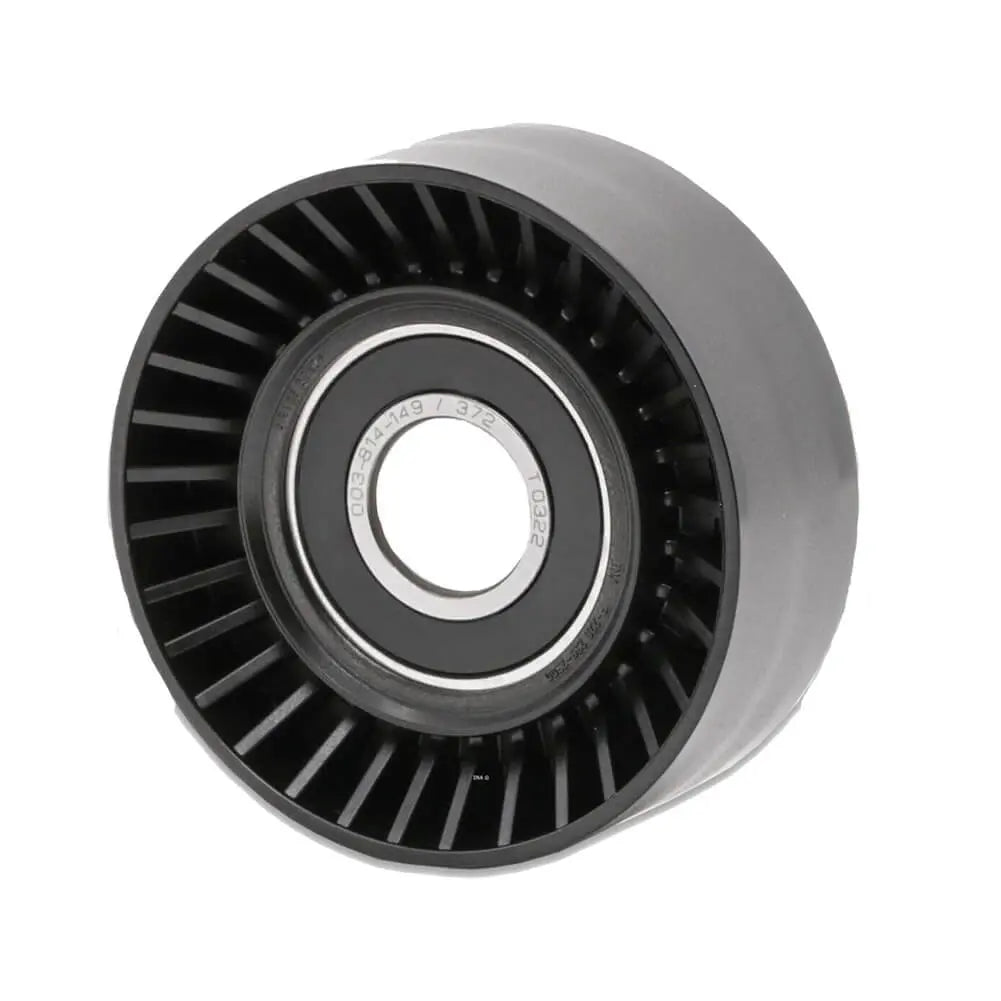
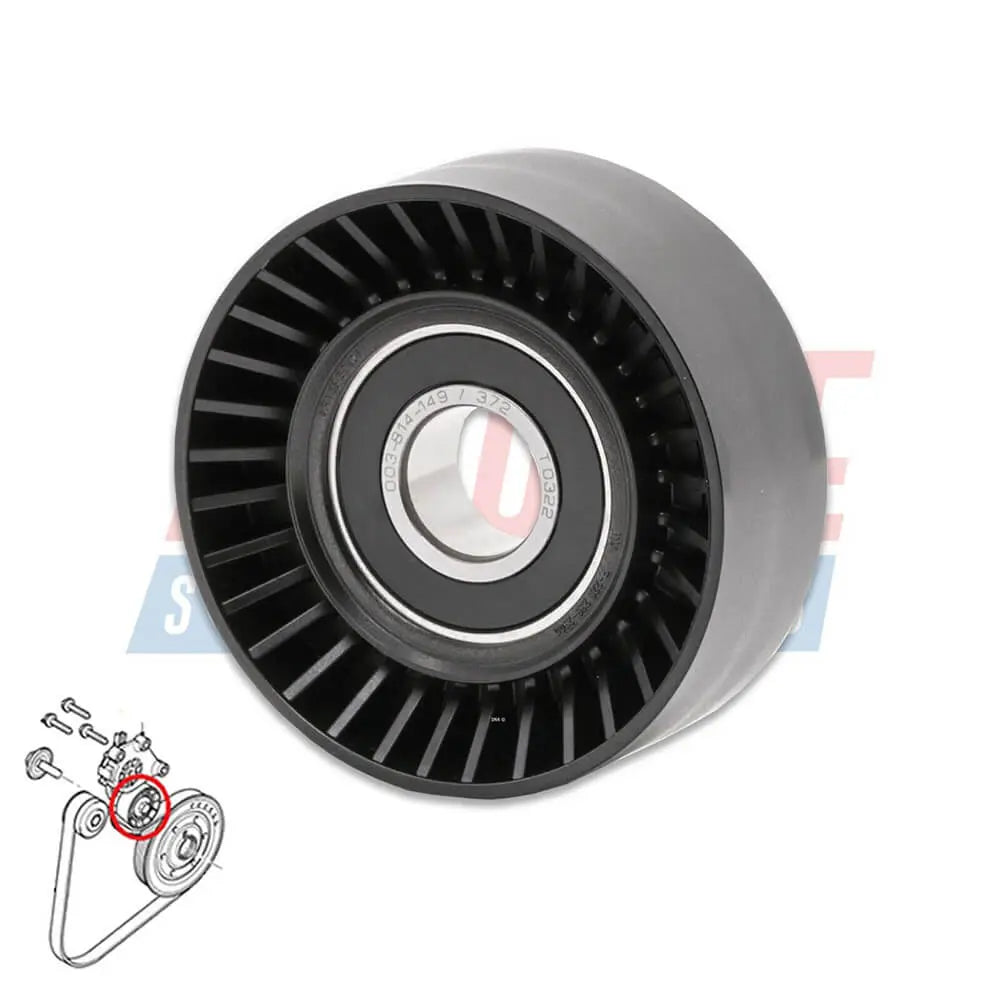

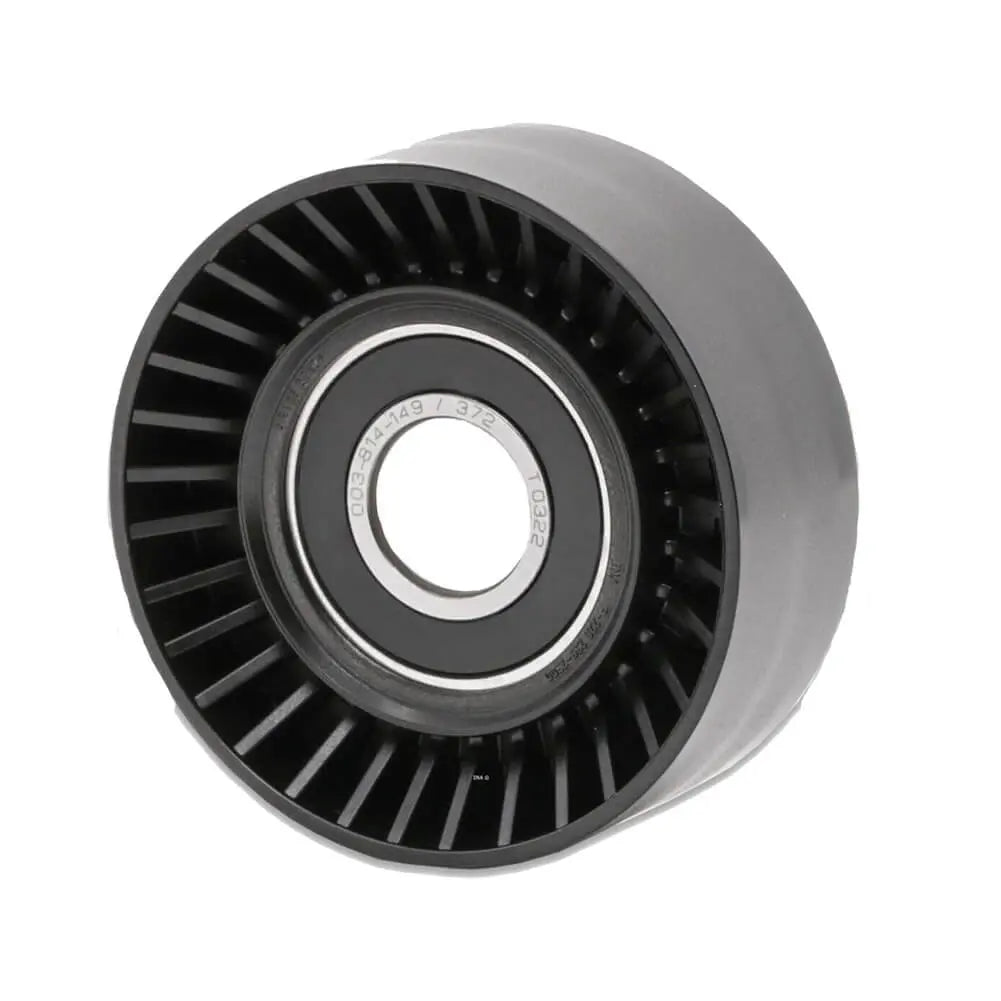
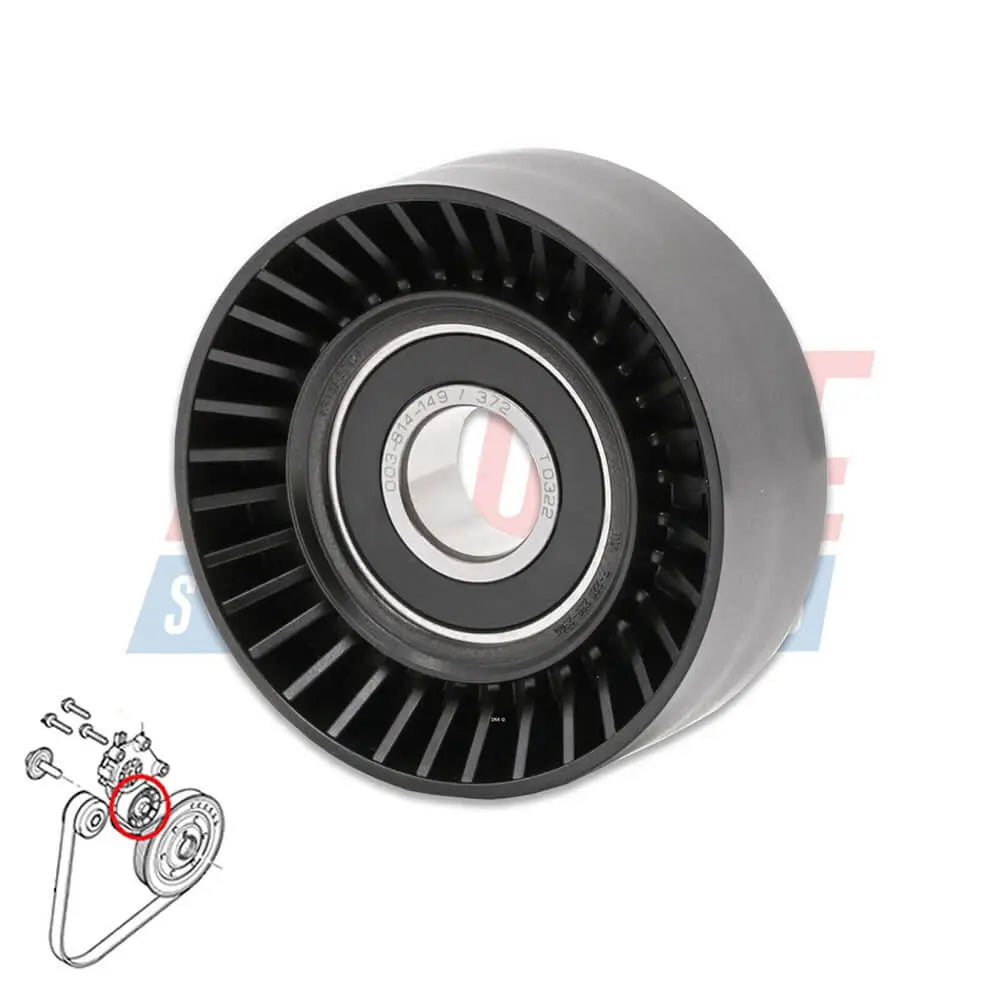
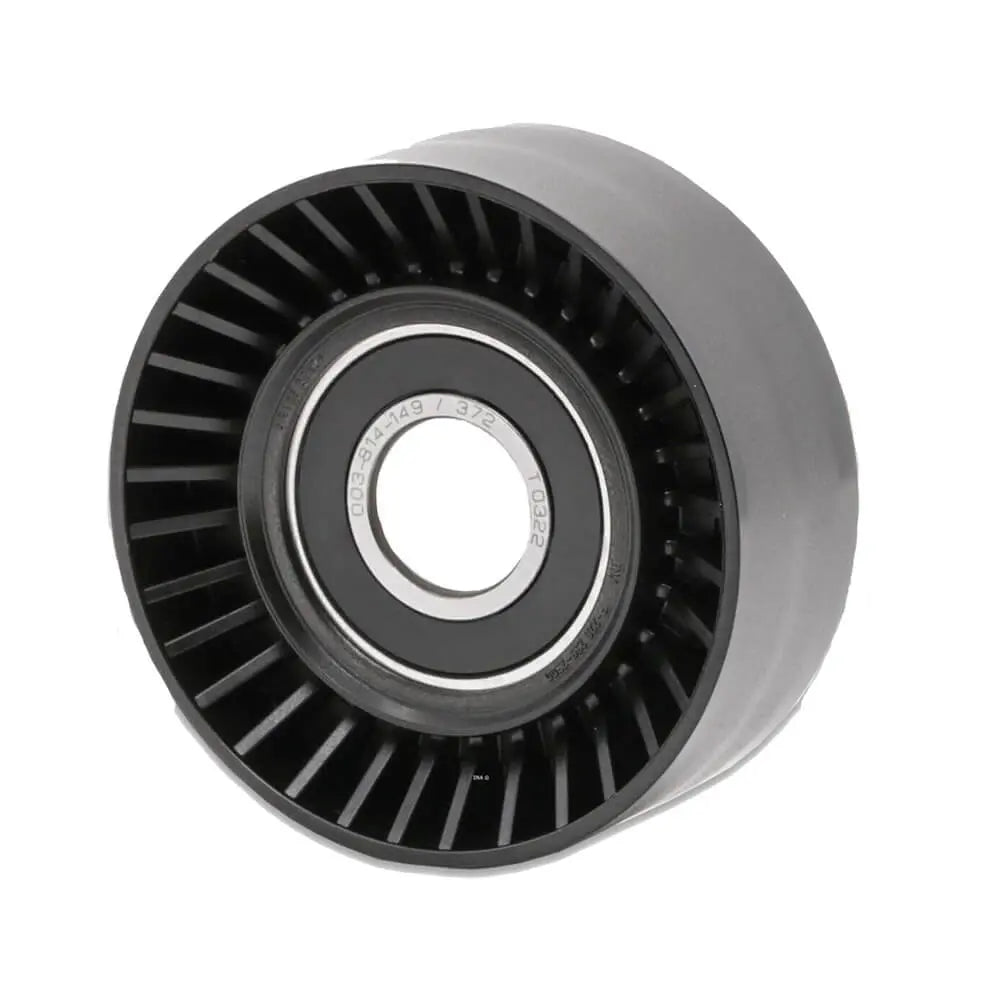
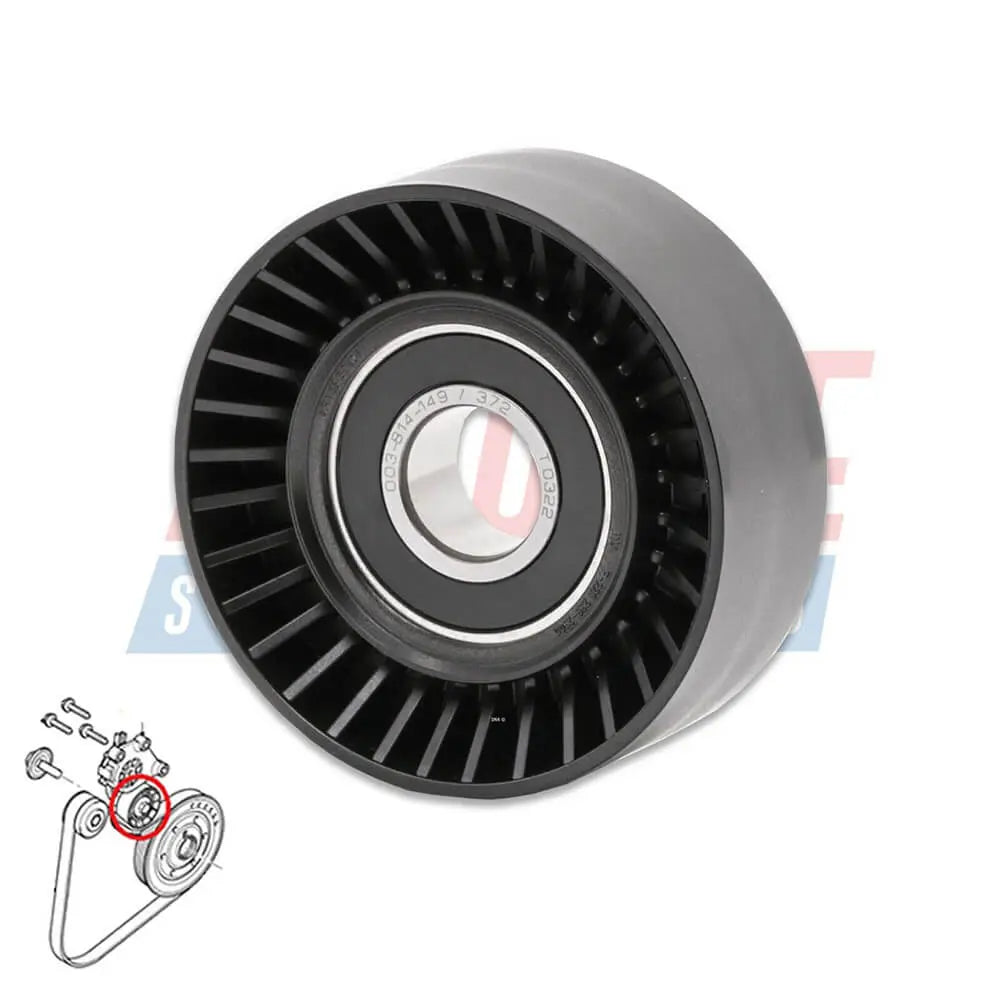
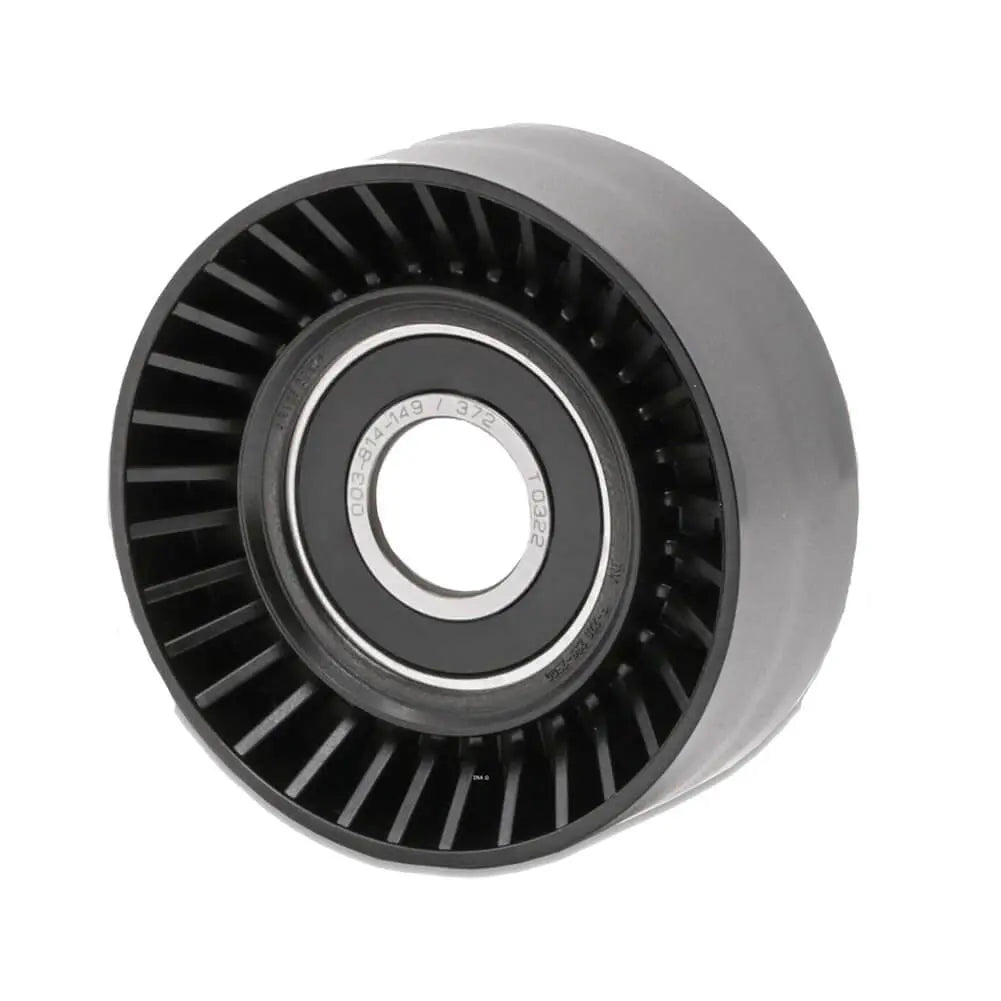
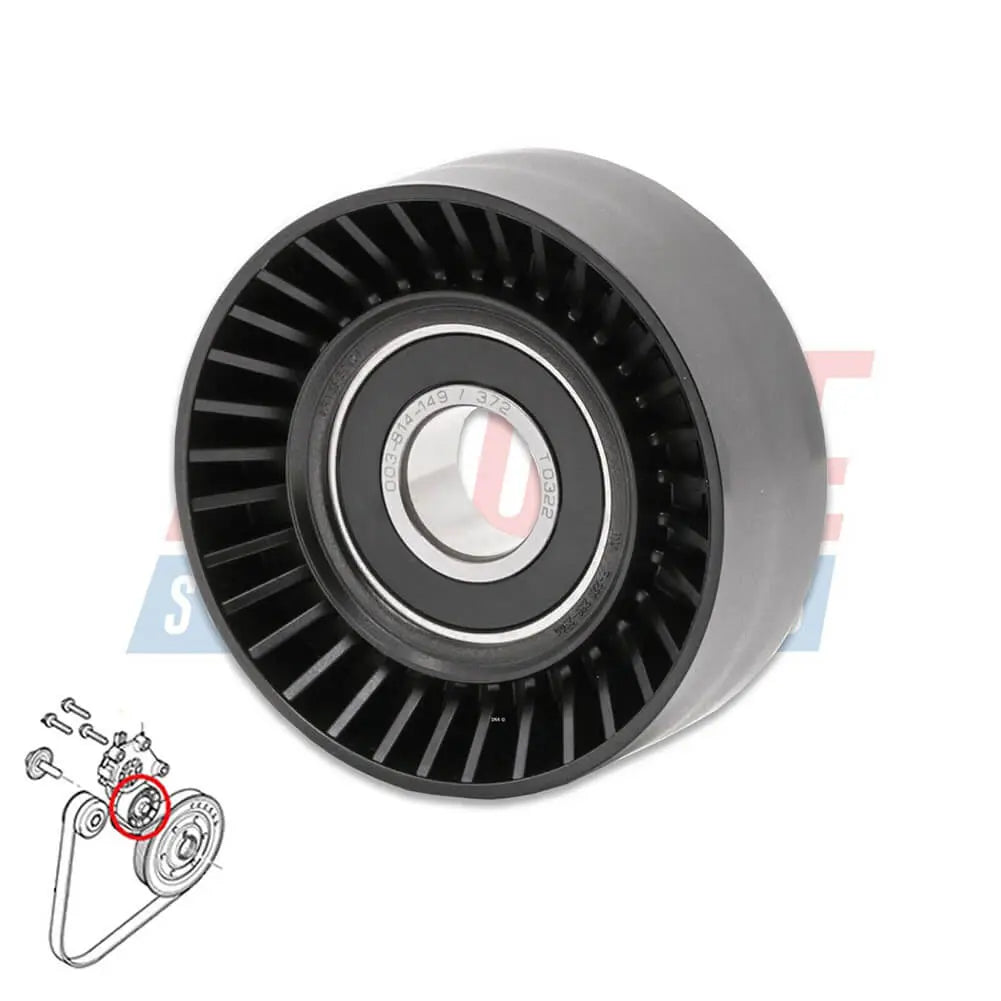
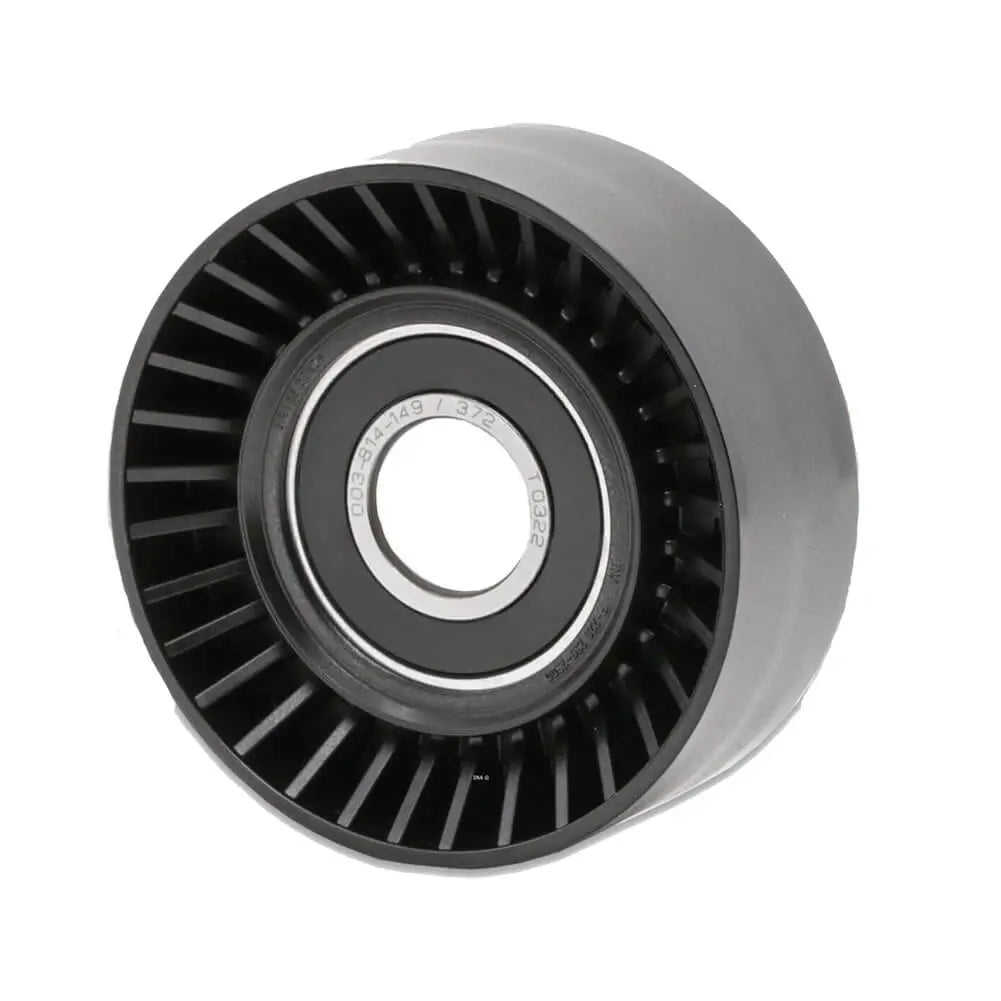
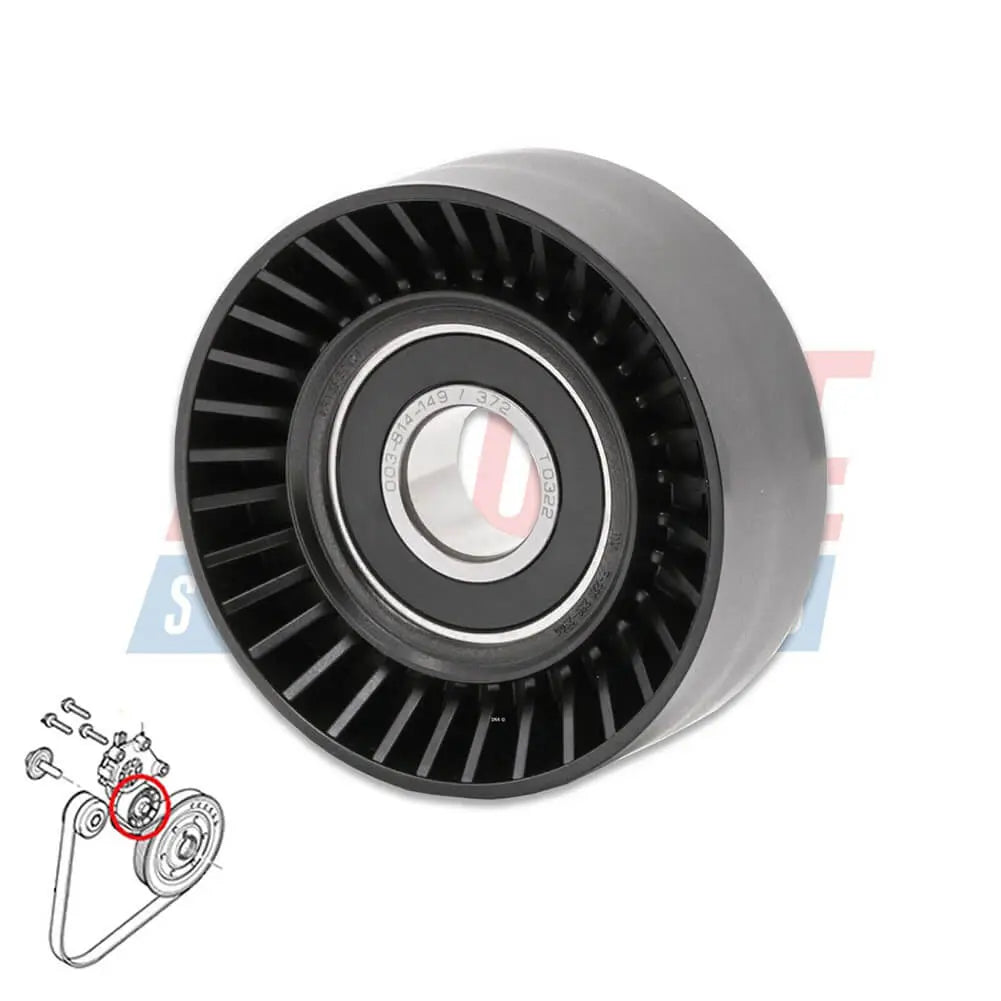
Ribbed Belt Tensioner Pulley For Volvo C30 S40 S80 V50 V70 - 31251129, 30731765, 575186
Sale price£8.90
No reviews
In stock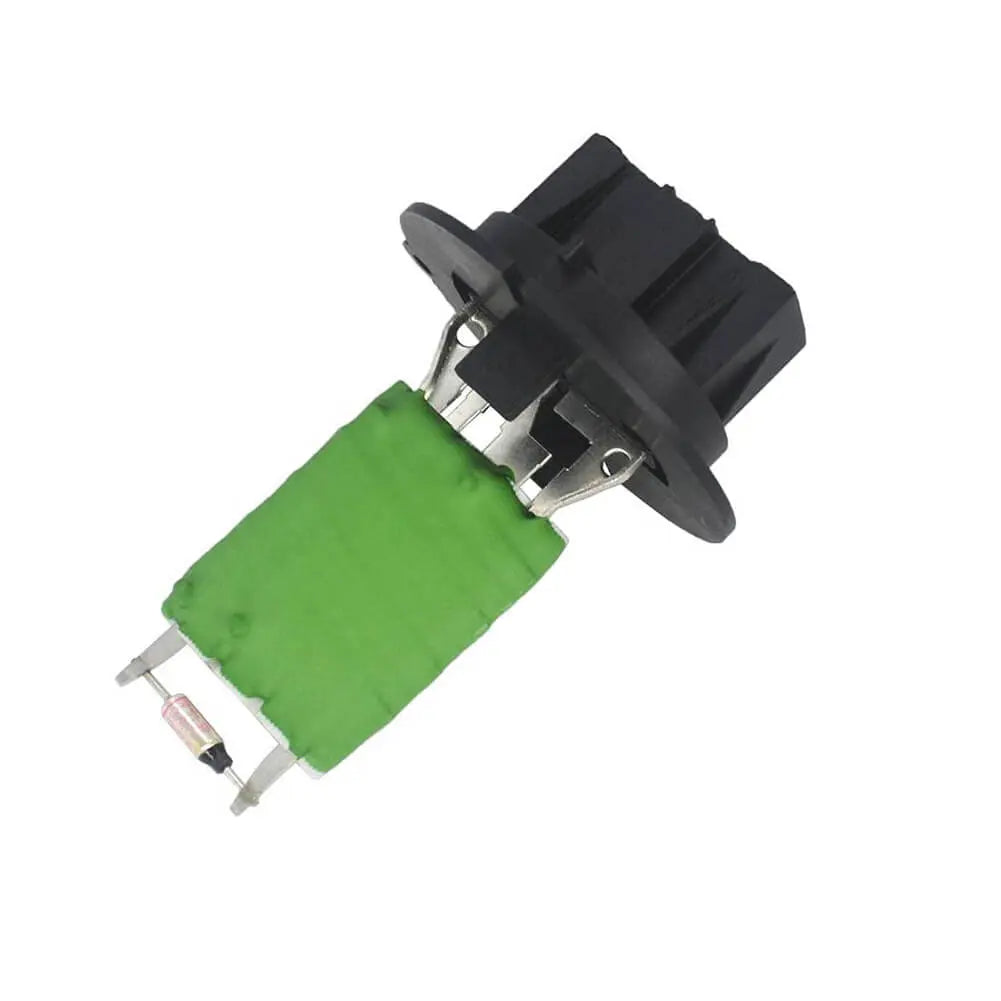
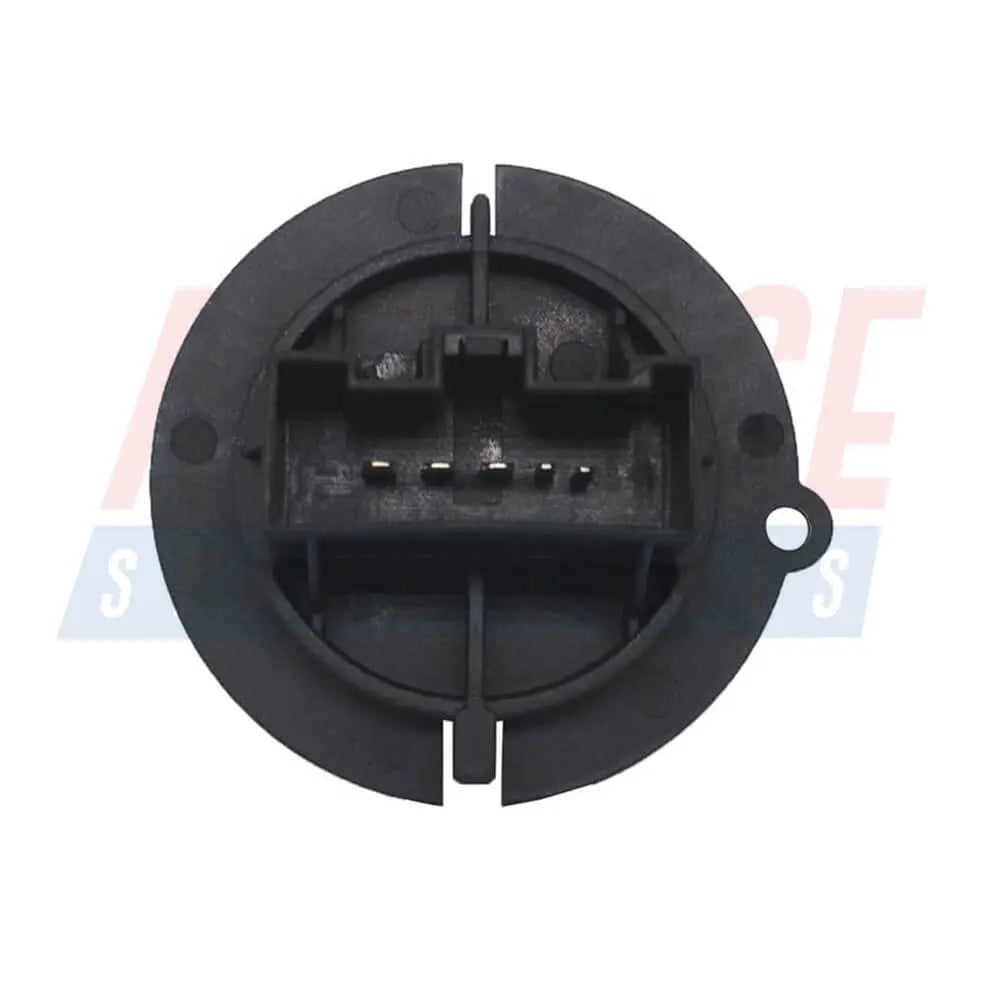

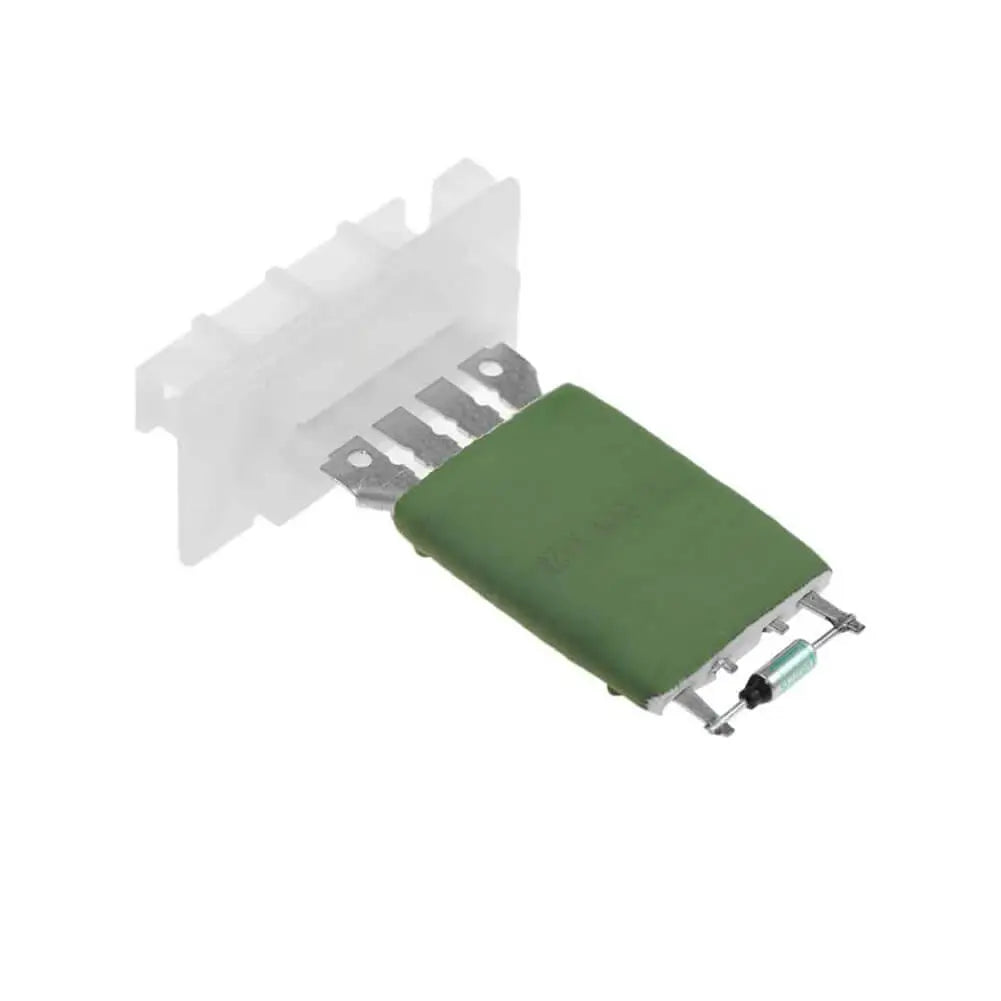
Heater Blower Motor Fan Resistor For Citroen C3 (FC, FN) Xsara Picasso (N68) 6450JP, 6450.JP
Sale price£12.90
No reviews
In stock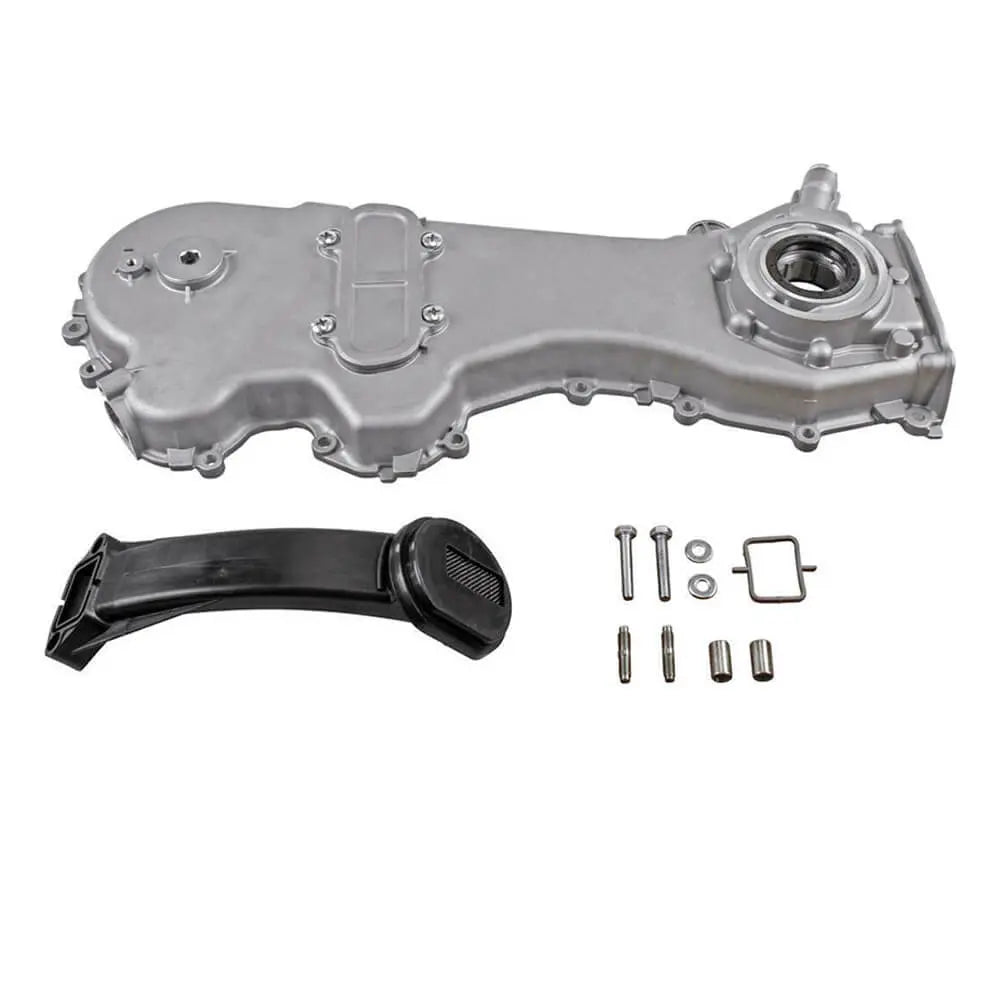
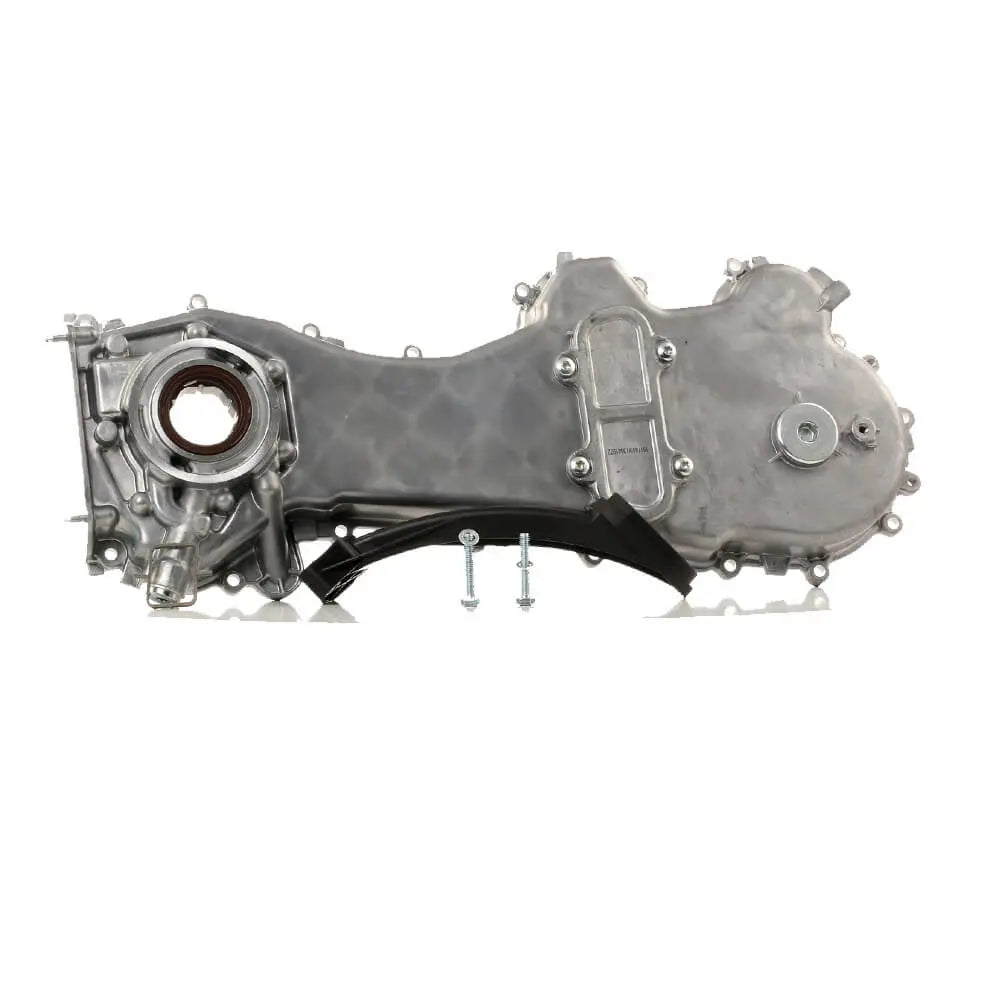

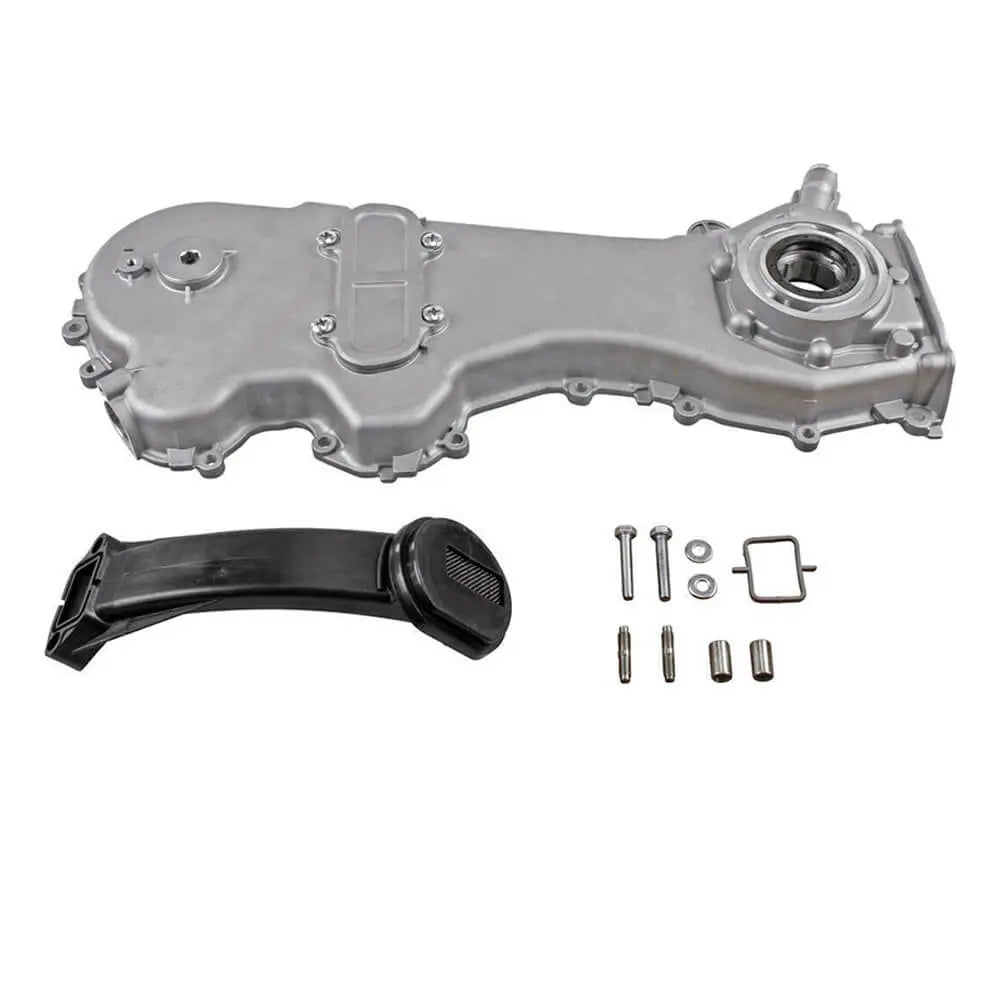
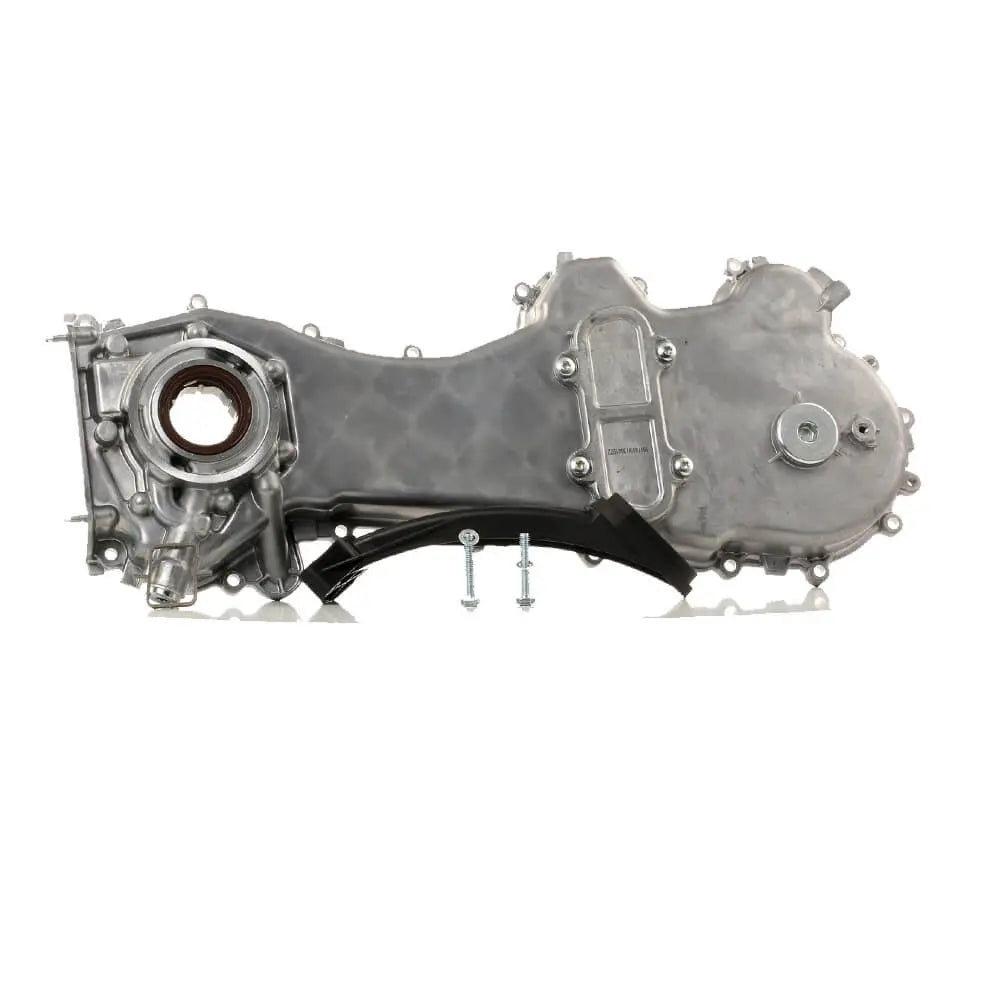
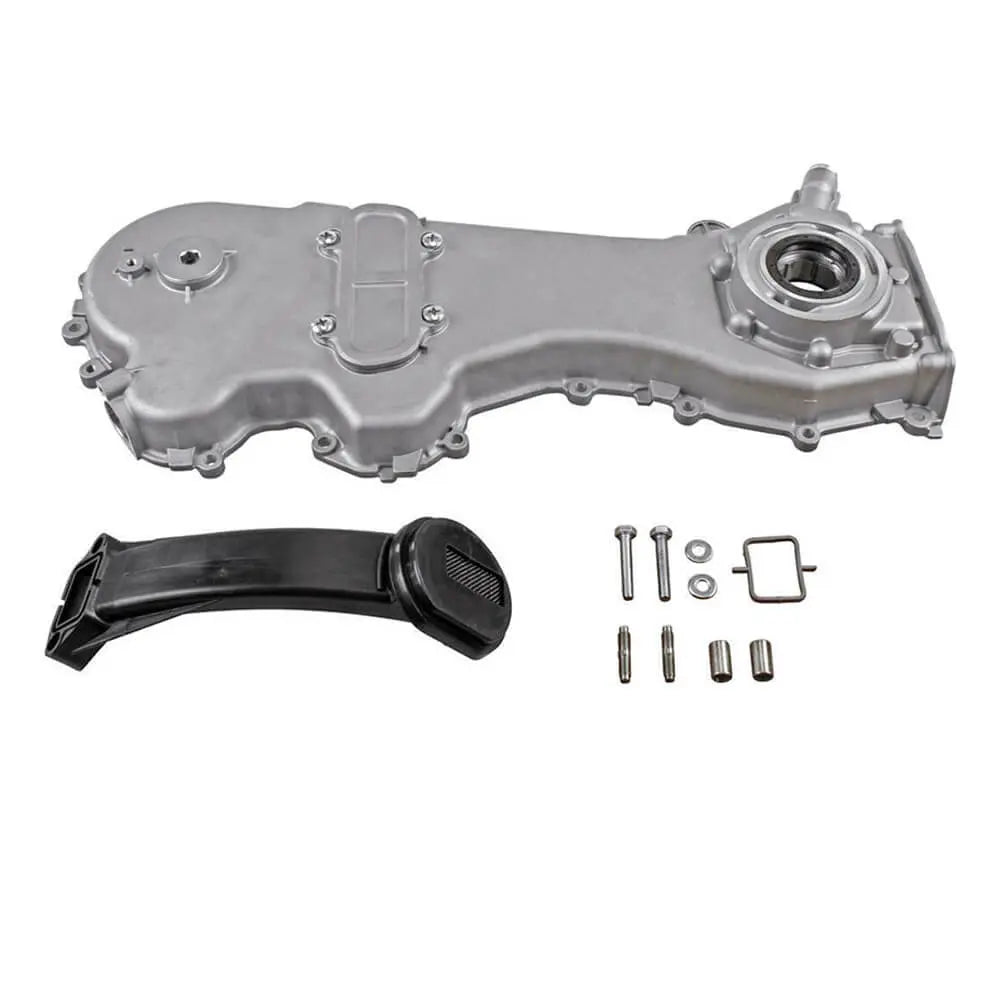
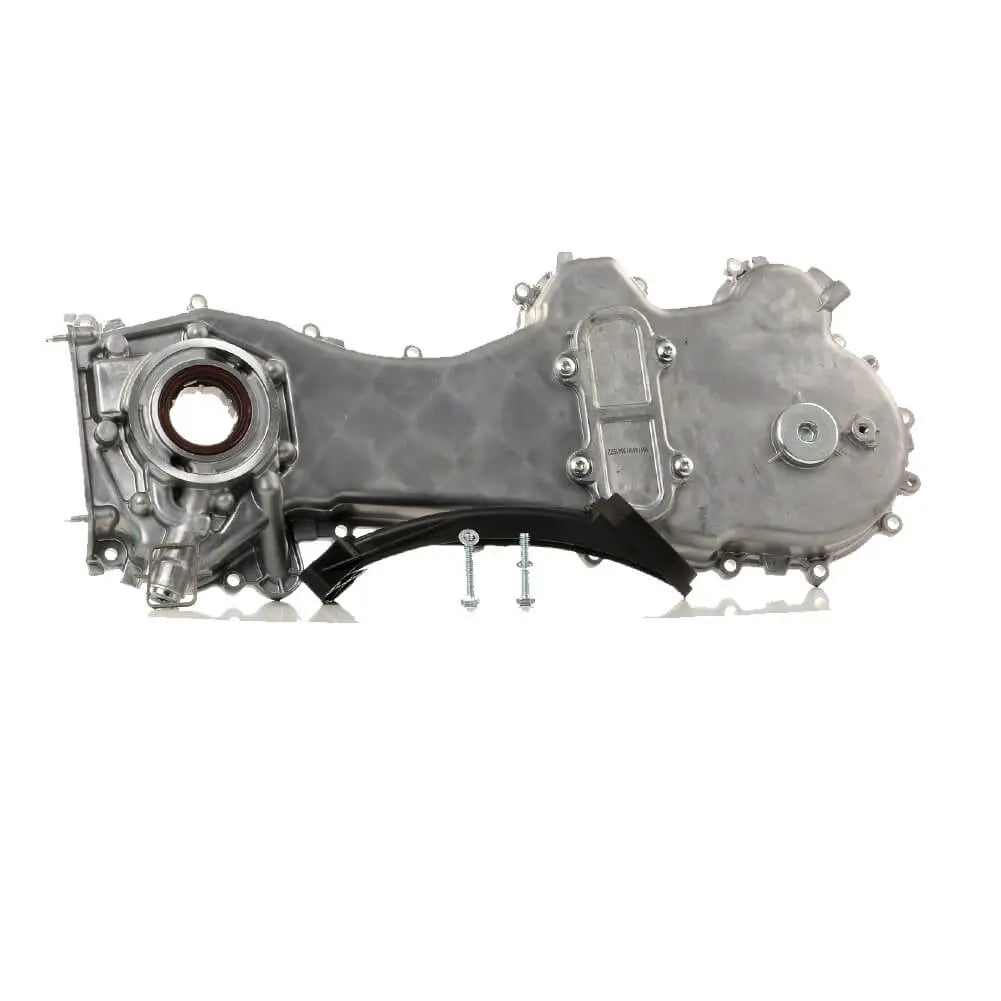
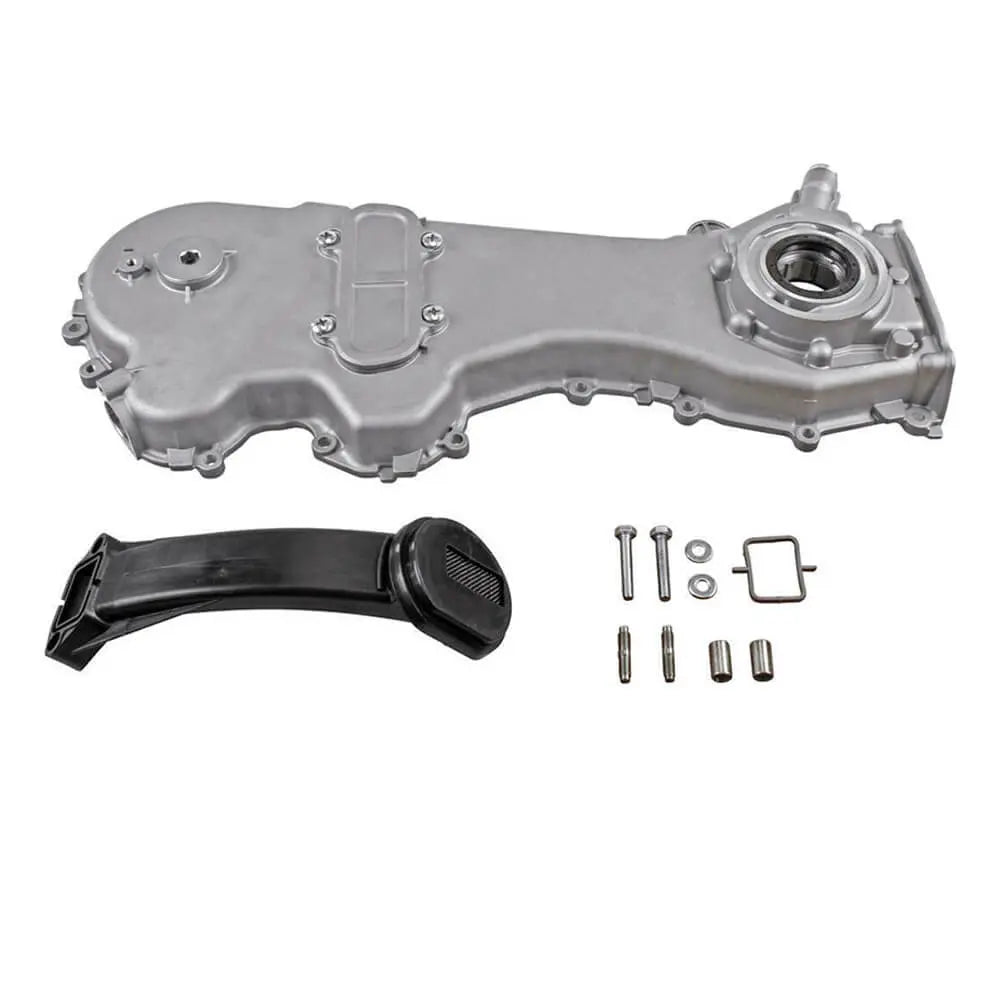
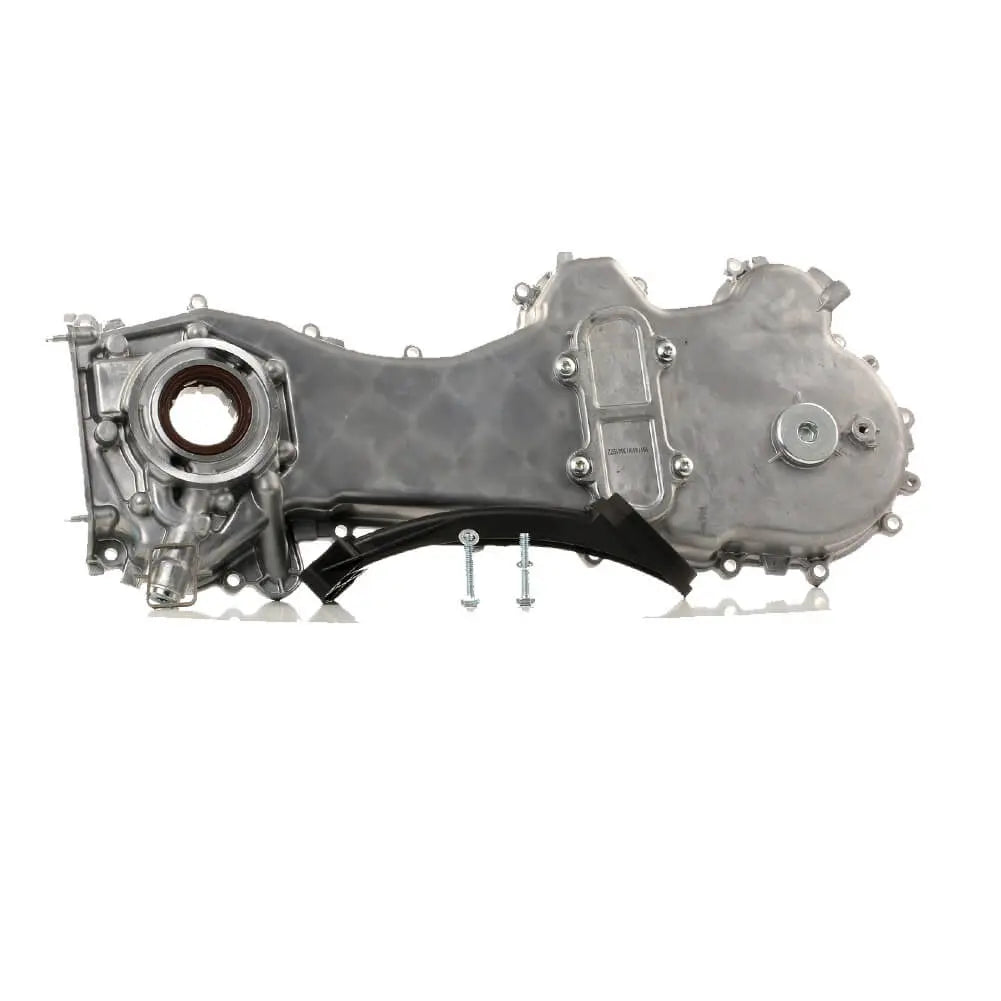
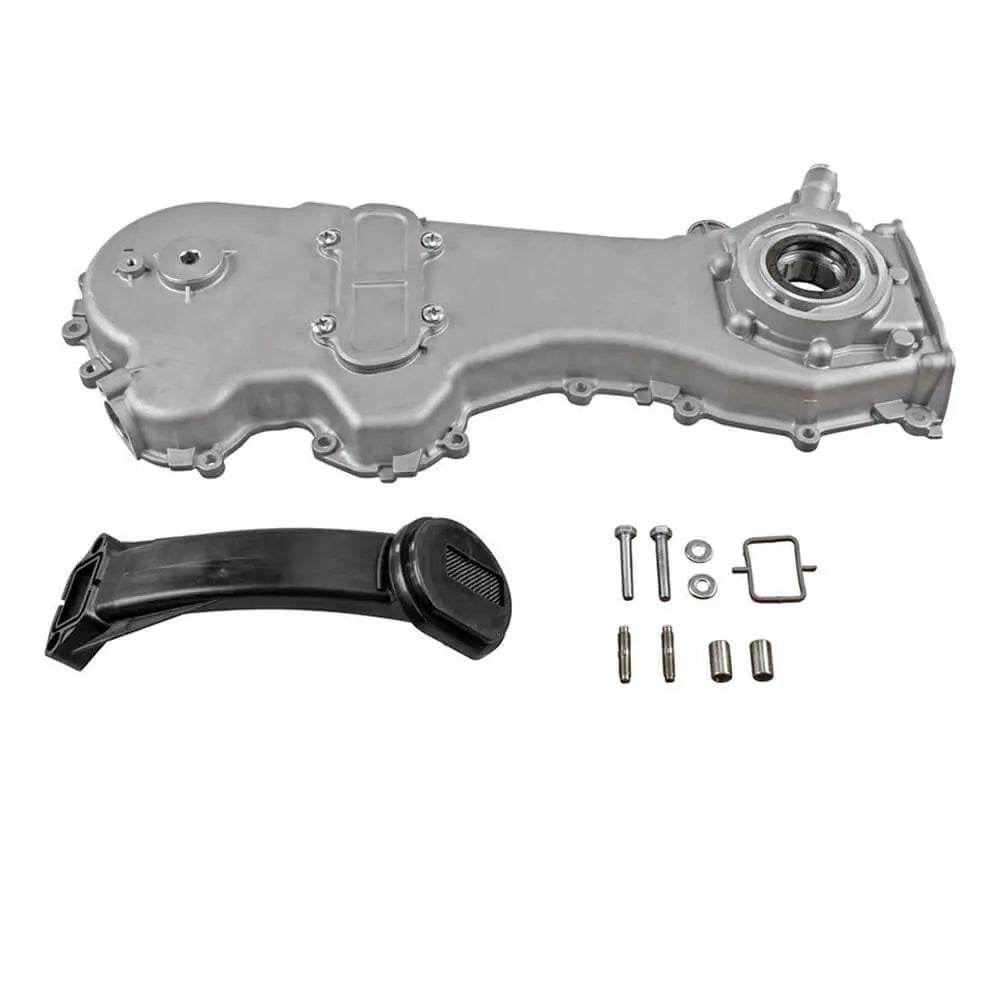
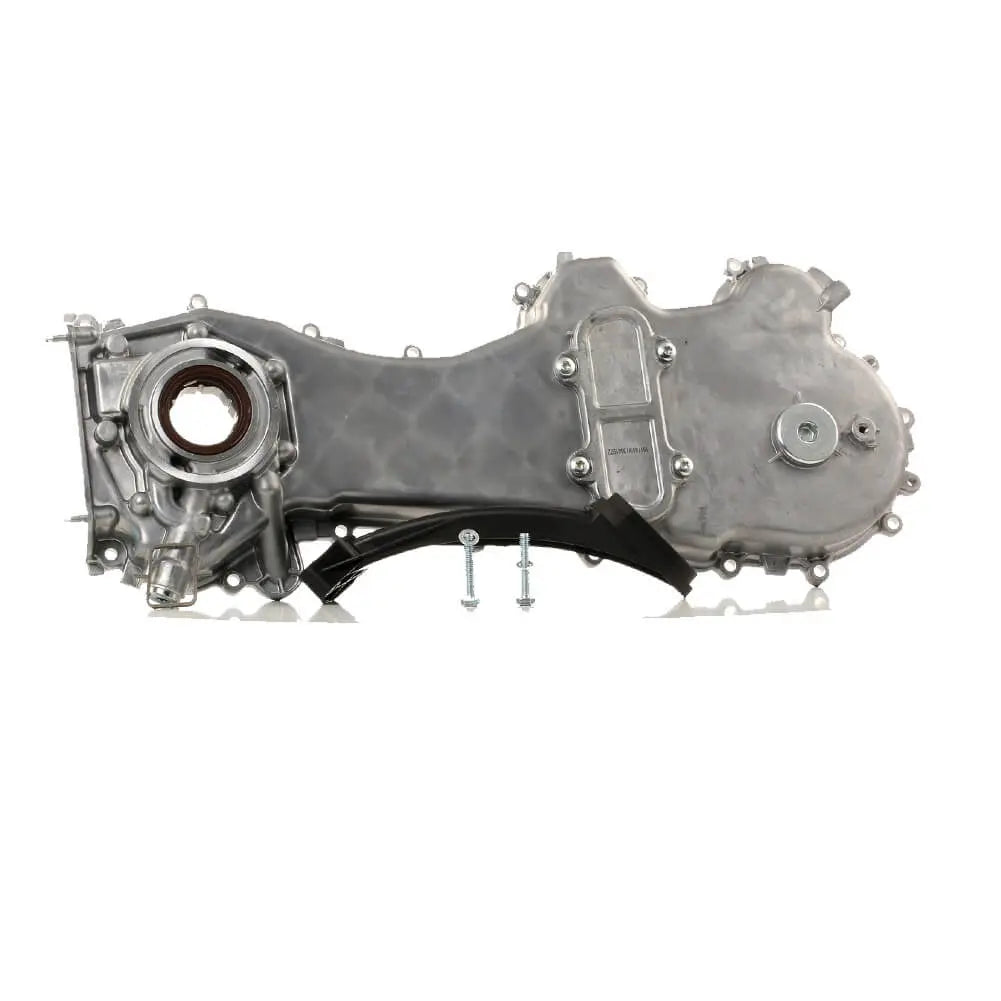
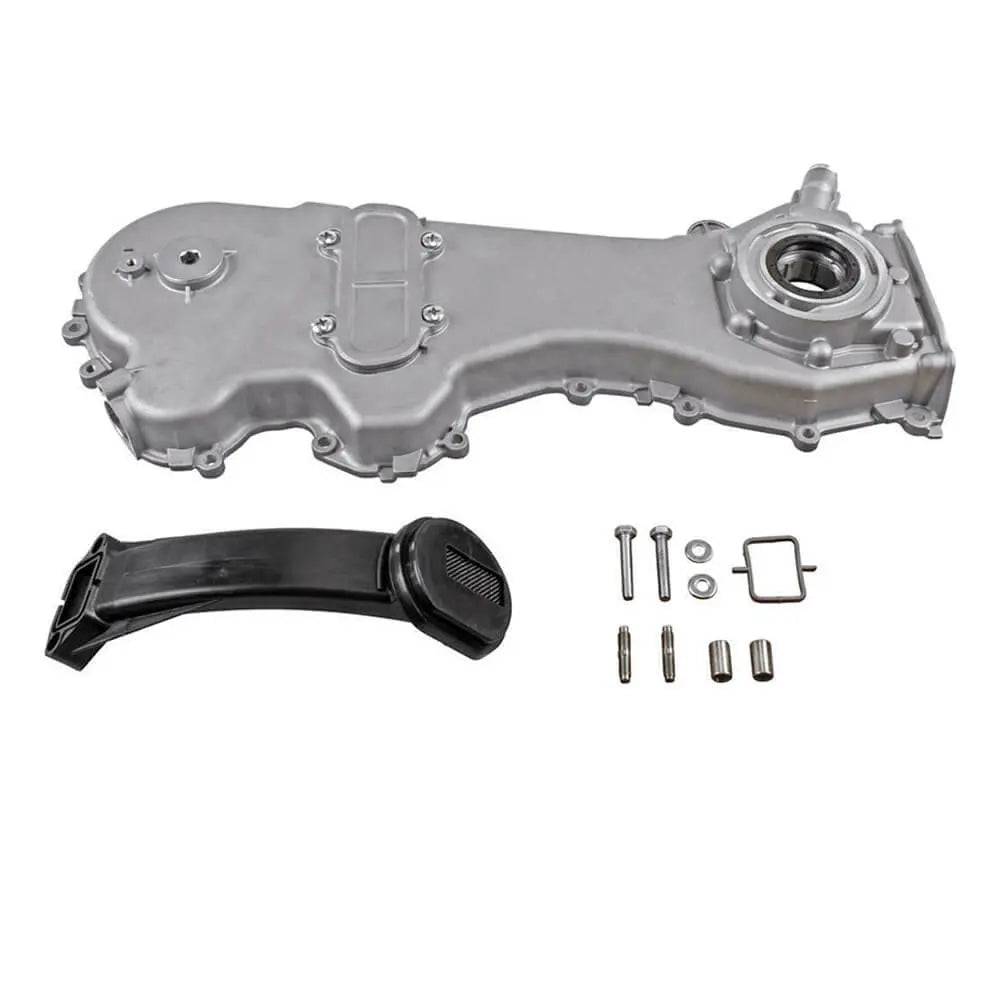
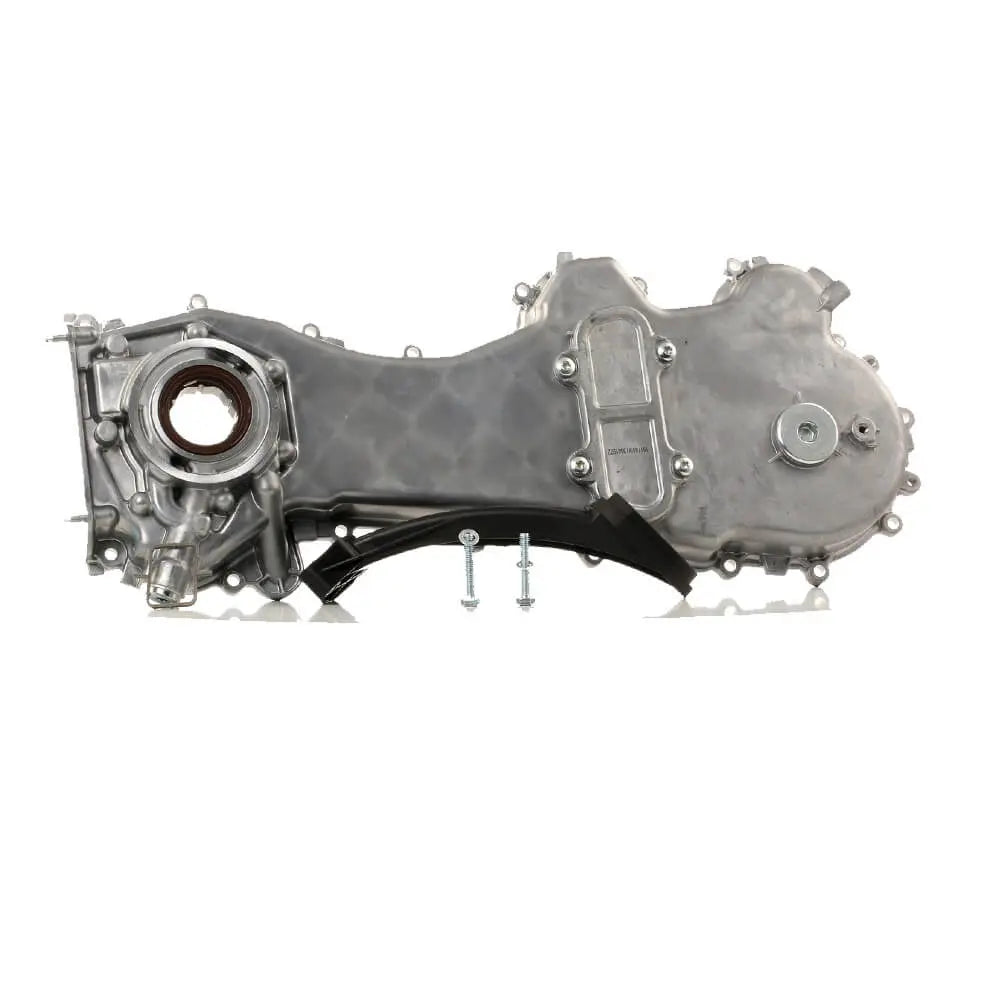
Oil Pump For Ford KA 1.3 TDCi For Suzuki Swift Ignis Wagon R+ 1.3 DDiS - 1723154, 1538742, 1652085E01
Sale price£149.00
No reviews
In stock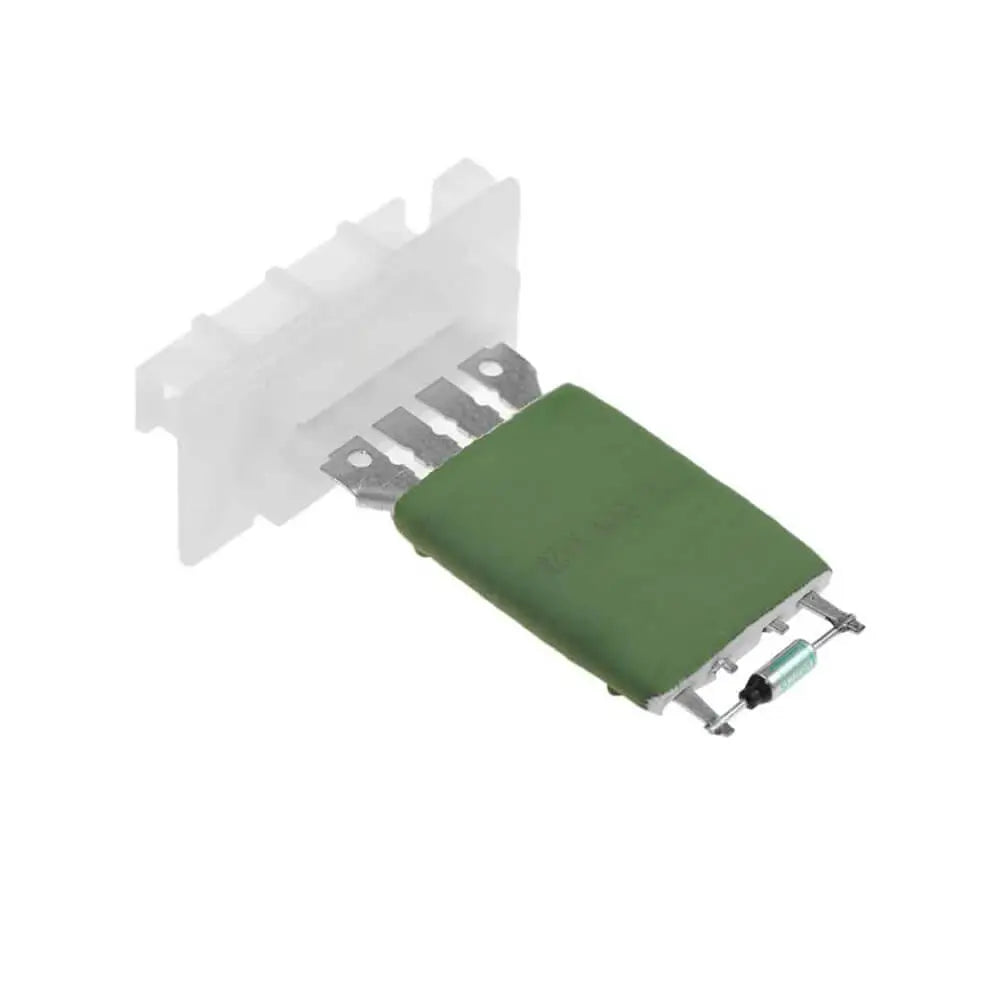

Heater Blower Motor Fan Resistor For Peugeot Partner Van MPV - 6450NV, 46770818, 6450.NV
Sale price£16.90
No reviews
In stockSave £10.00
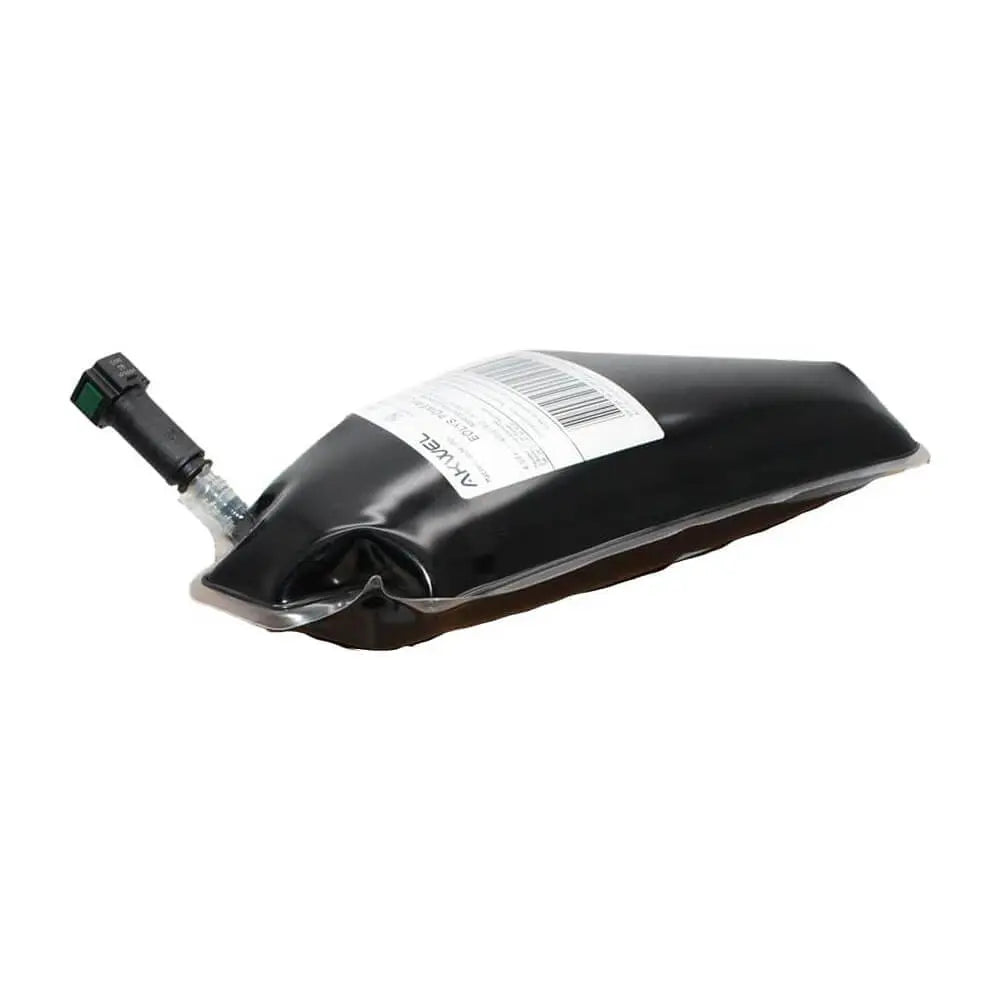
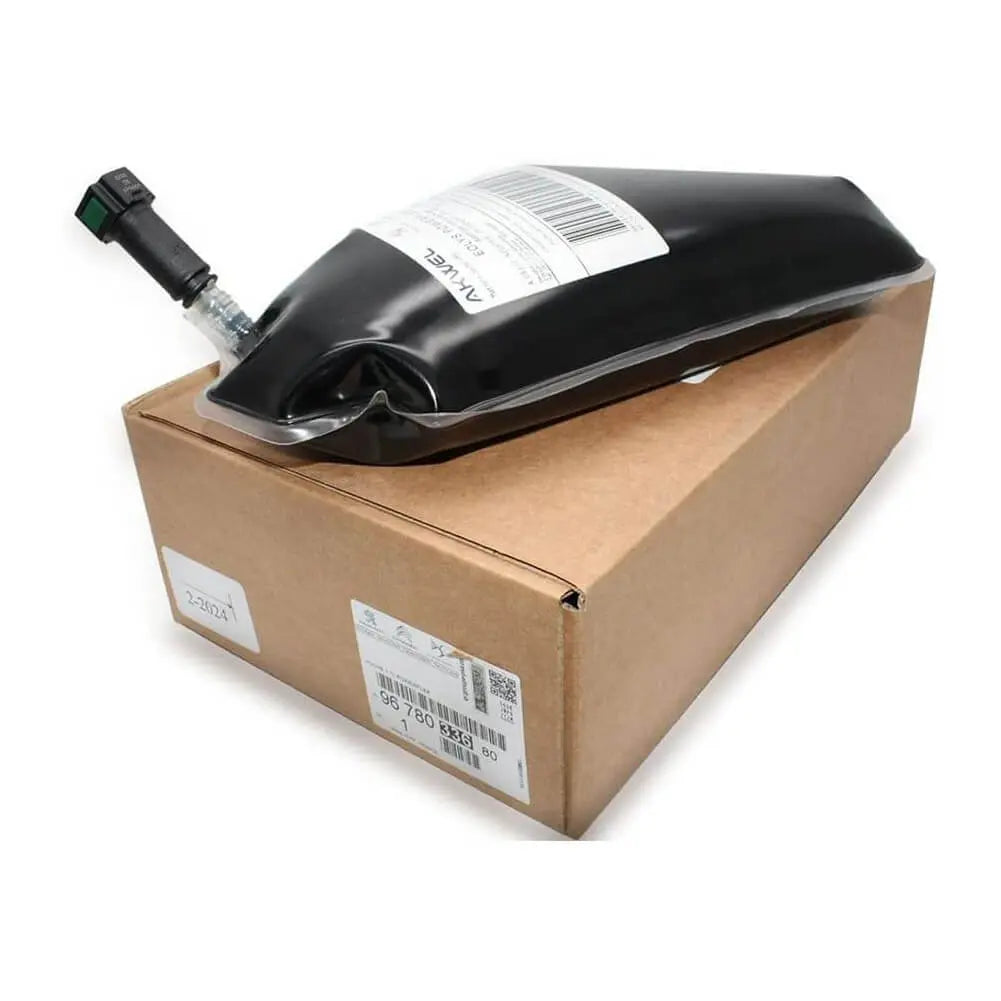


Particulate Additive Pouch For Peugeot 207 208 3008 301 307 308 407 5008 508 (2009 - ON) 9678101680, 1337646
Sale price£39.90
Regular price£49.90
1 review
In stockSave £10.00
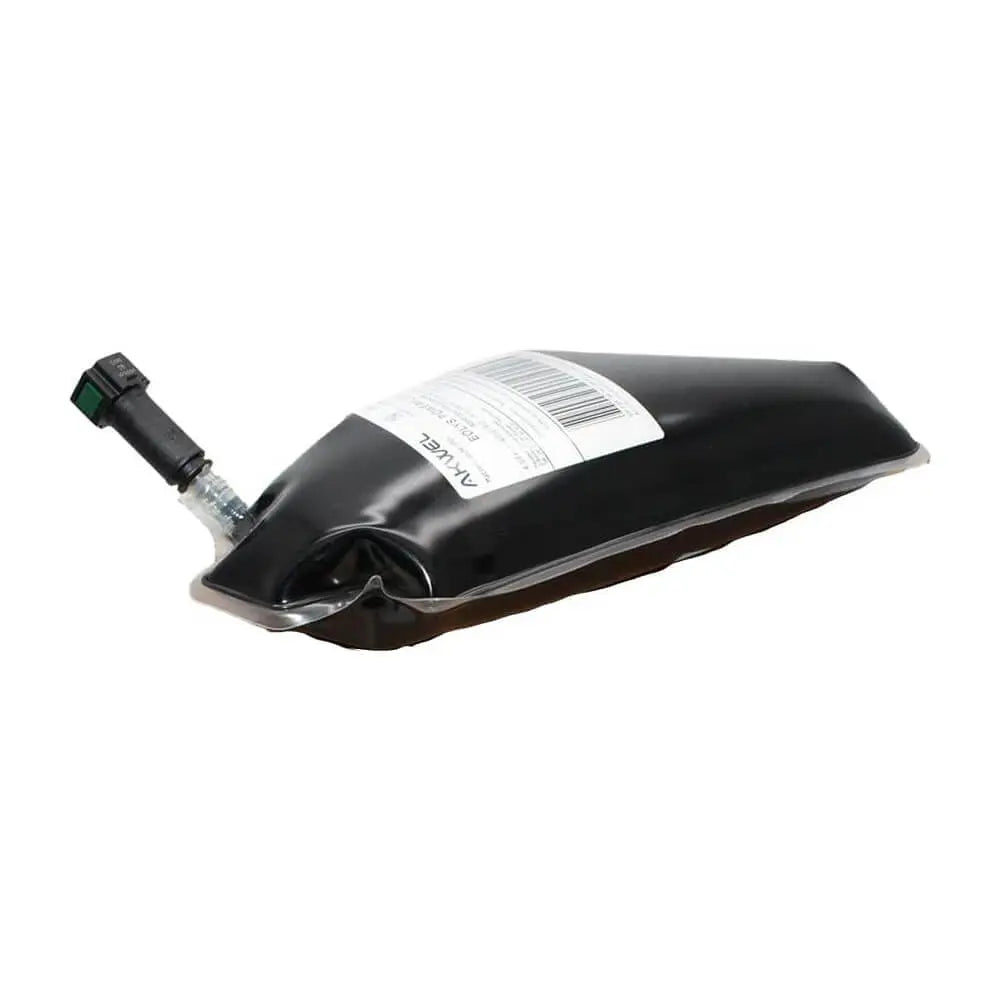


Particulate Additive Pouch For Citroen Berlingo C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C-ELYSEE C3 PICASSO - 9678101680
Sale price£39.90
Regular price£49.90
1 review
In stock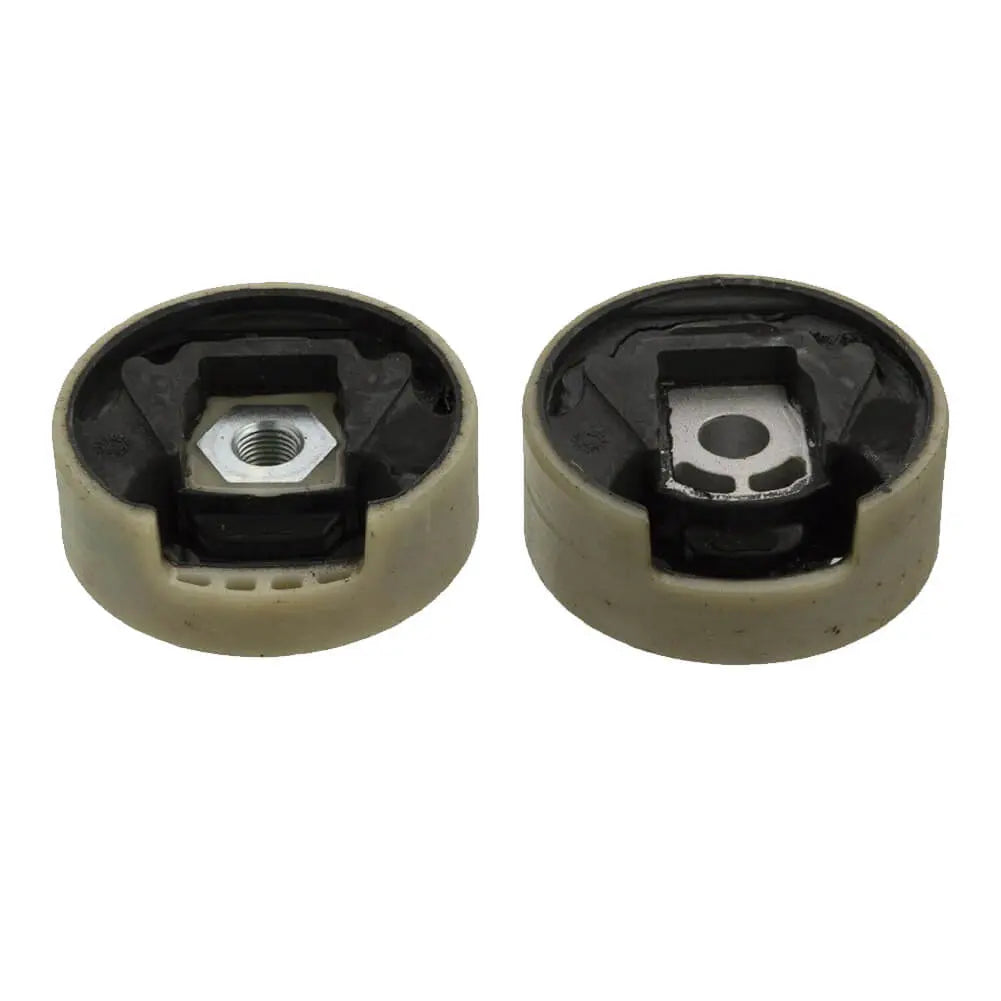
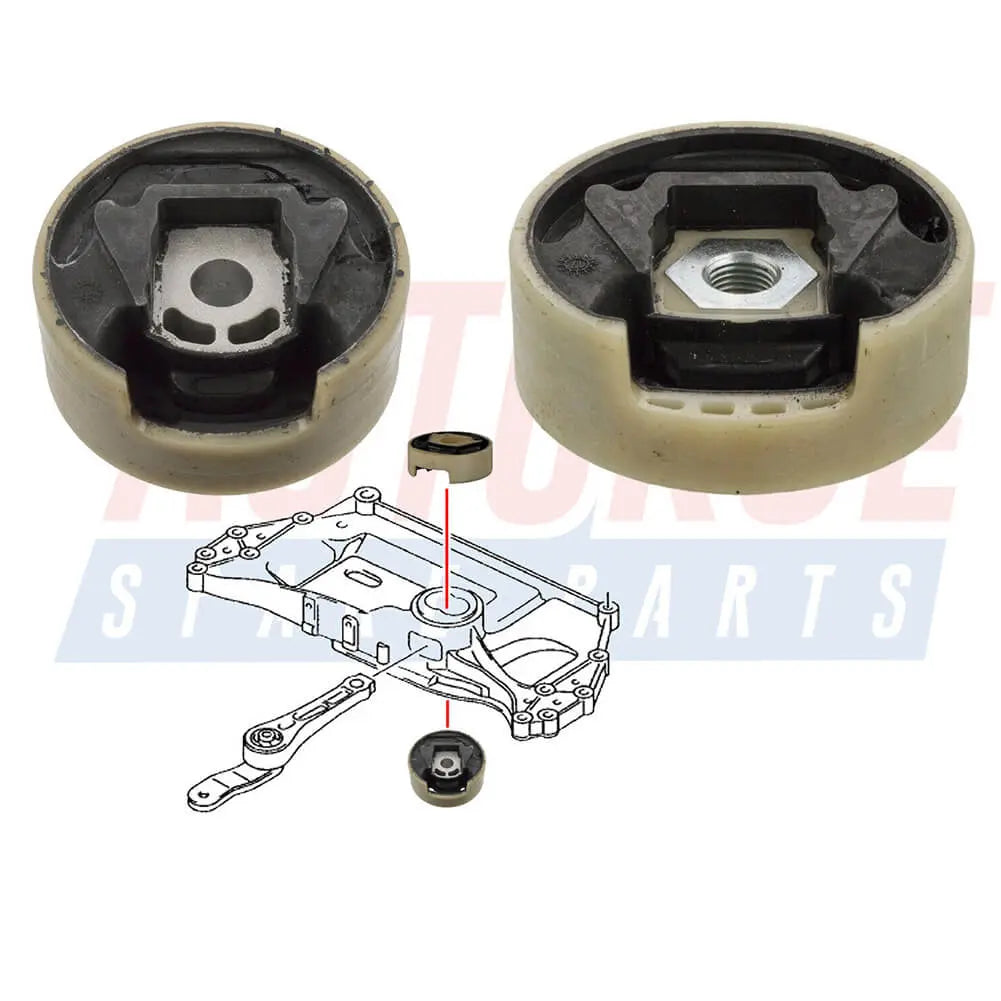

Lower Upper Set Engine Mounting For Skoda Octavia Superb Yeti (2004 - 2015) 1K0199867A, 1K0199868A
Sale price£16.99
No reviews
Sold out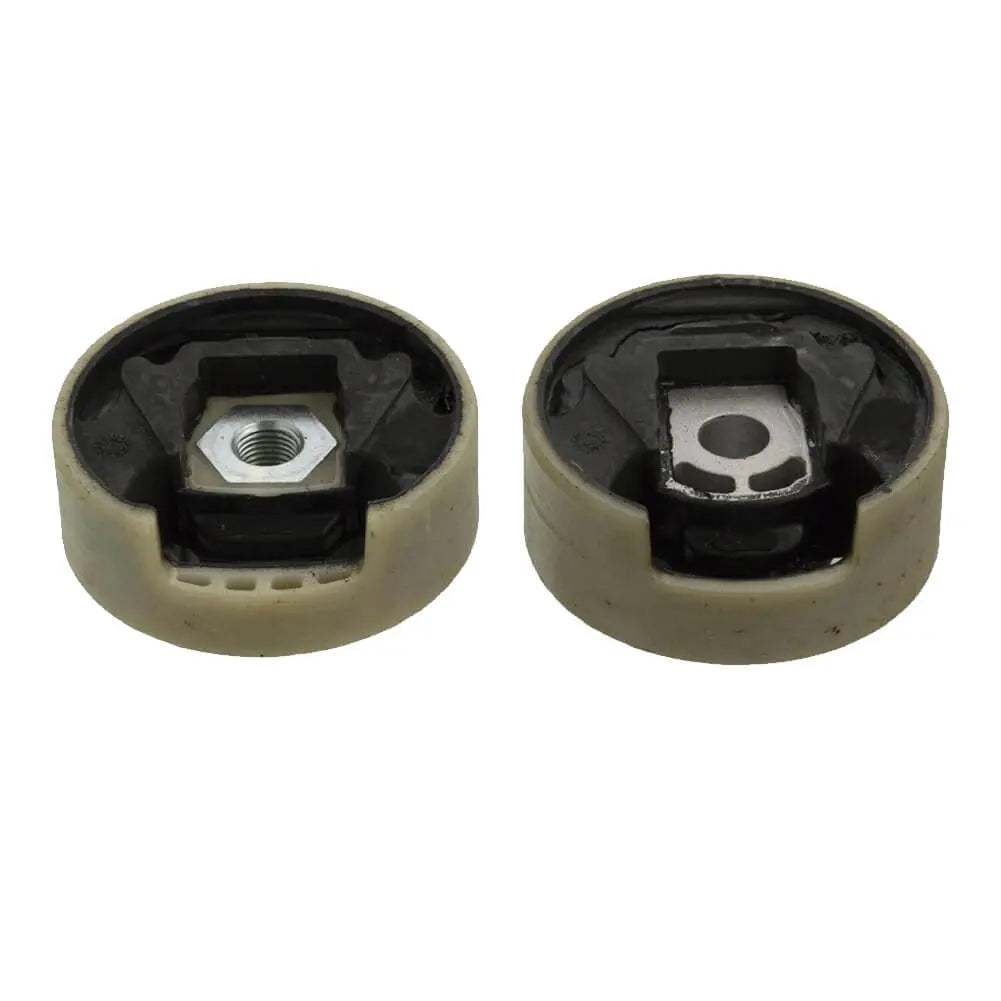
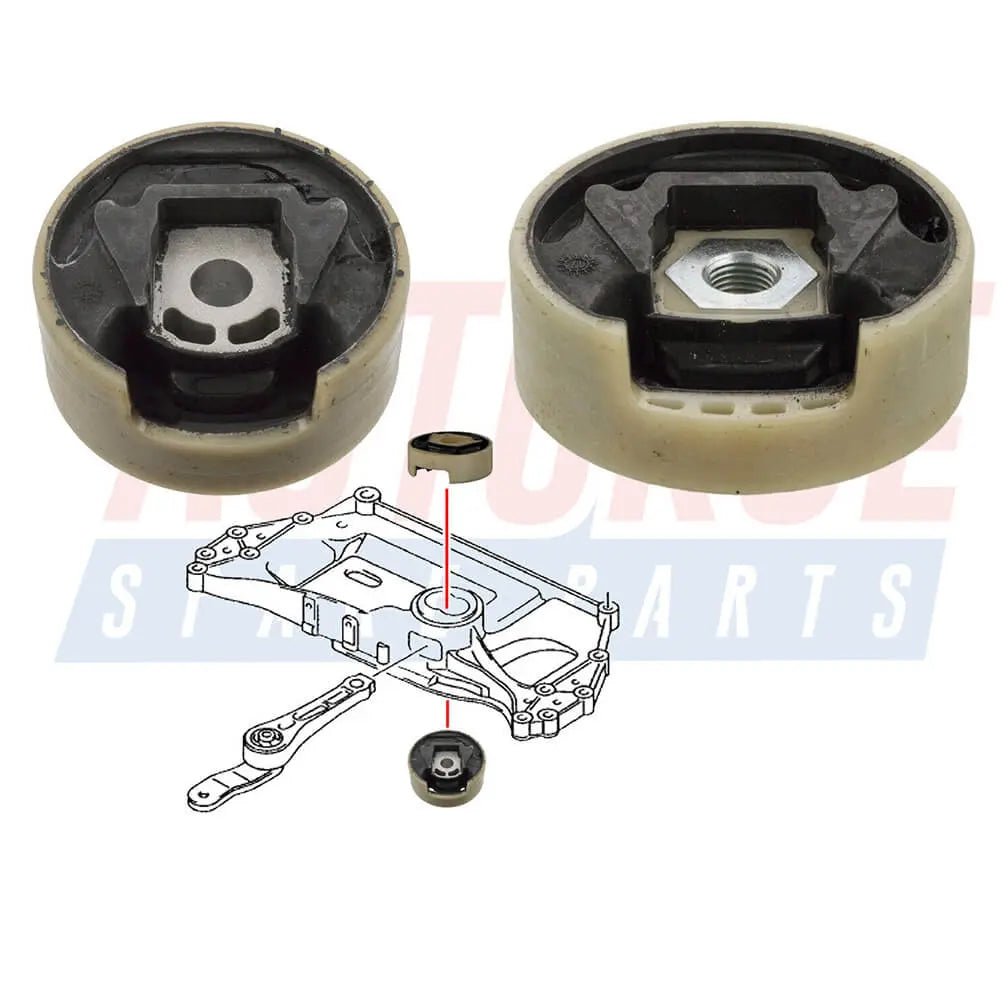

Lower Upper Set Engine Mounting For Audi A3 Q3 TT (2003 - 2018) 1K0199867A, 1K0199868A, 3C0199867C
Sale price£16.99
No reviews
Sold out
Filters (0)