Shop by Category
Fuel System Components
101 products
Showing 1 - 24 of 101 products
A Comprehensive Guide to Fuel System Components in Cars
The fuel system is an essential component of every modern car, ensuring the efficient and reliable delivery of fuel to the engine. Understanding the various fuel system components is crucial for both car enthusiasts and everyday drivers alike. In this article, we'll explore the key elements of a typical fuel system, how they work together, and their role in maintaining optimal engine performance.Fuel Tank:
The fuel tank is where the journey of fuel begins. It serves as a reservoir for storing gasoline or diesel. Usually located at the rear of the vehicle, the fuel tank is designed to be well-sealed to prevent fuel vapors from escaping. It is equipped with a fuel cap, which provides a secure seal and prevents contaminants from entering the tank.Fuel Pump:
The fuel pump is responsible for transferring fuel from the tank to the engine. Most modern cars have electric fuel pumps mounted inside the fuel tank. When you start the engine, the fuel pump is activated, pressurizing the fuel and delivering it to the fuel injectors or carburetor, depending on the type of engine.Fuel Filter:
The fuel filter plays a vital role in keeping the fuel system clean and free from contaminants. As fuel is drawn from the tank, it passes through the fuel filter, which traps dirt, debris, and rust particles. Regularly replacing the fuel filter is crucial to ensure a steady flow of clean fuel and prevent damage to other fuel system components.Fuel Lines:
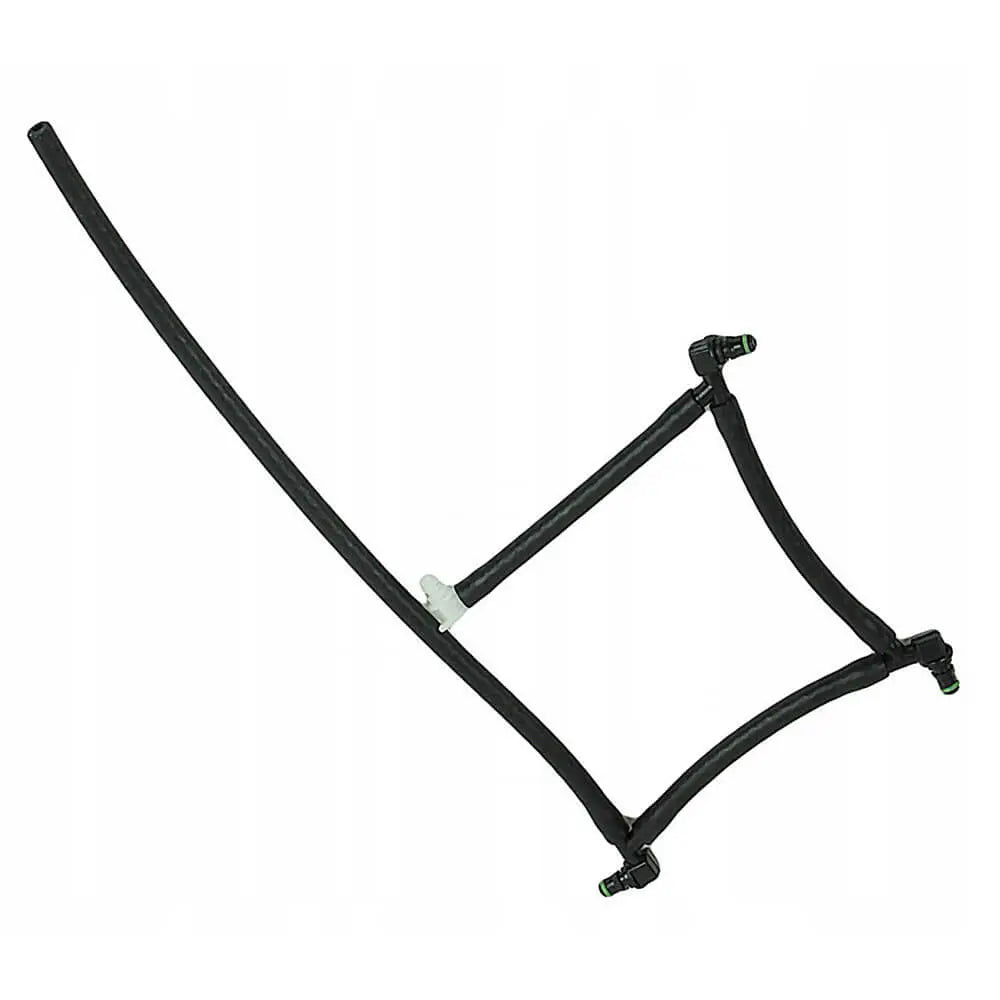
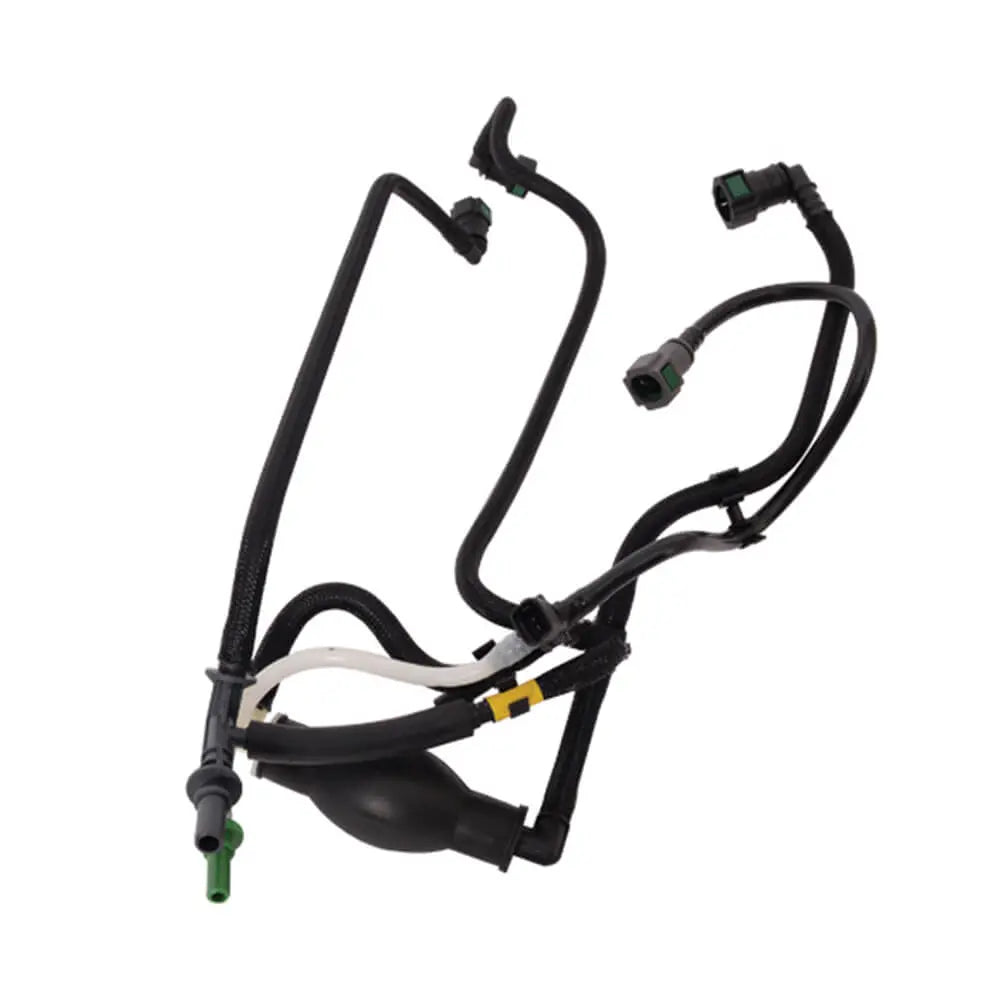
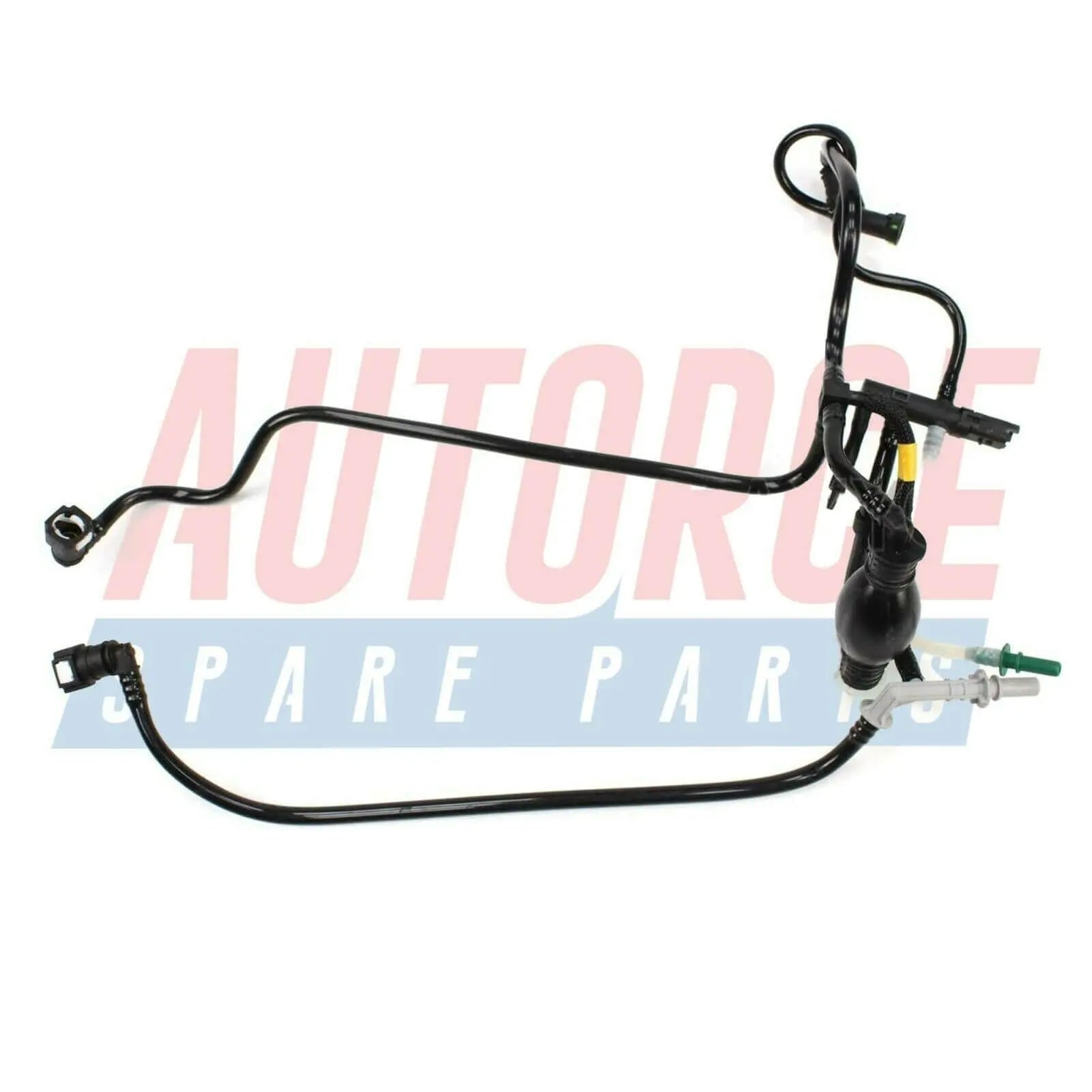
Fuel lines are the channels through which fuel travels from the fuel tank to the engine. These lines are usually made of steel or high-pressure rubber to withstand the rigors of fuel transportation. Over time, fuel lines may develop leaks or corrosion, requiring prompt repair or replacement to prevent fuel leaks and potential fire hazards.Fuel Injectors (or Carburetor):
In modern cars, fuel injectors have largely replaced carburetors. Fuel injectors are electronically controlled valves that spray precise amounts of fuel into the engine's intake manifold or directly into the combustion chamber. The amount of fuel injected is managed by the engine control unit (ECU), optimizing fuel consumption and tailoring the air-fuel mixture for different driving conditions.Throttle Body:
The throttle body regulates the airflow into the engine. In fuel-injected engines, it works in conjunction with the ECU to determine the right air-fuel mixture ratio. As you press the accelerator pedal, the throttle body opens wider, allowing more air into the engine, which triggers the ECU to inject the appropriate amount of fuel for combustion.Fuel Pressure Regulator:
The fuel pressure regulator ensures that the fuel delivered to the engine remains at a consistent pressure. It works by diverting excess fuel back to the fuel tank when the pressure exceeds the required level. This constant regulation of fuel pressure is crucial for maintaining engine performance and preventing damage to sensitive fuel system components.A car's fuel system is a complex and interconnected network of components that work together to supply the engine with the right amount of fuel for optimal performance. Regular maintenance and attention to the fuel system are essential to ensure fuel efficiency, engine longevity, and safe operation. By understanding the role of each fuel system component, drivers can better appreciate their vehicle's inner workings and make informed decisions when it comes to maintenance and repairs.
Showing 1 - 24 of 101 products
Display
View
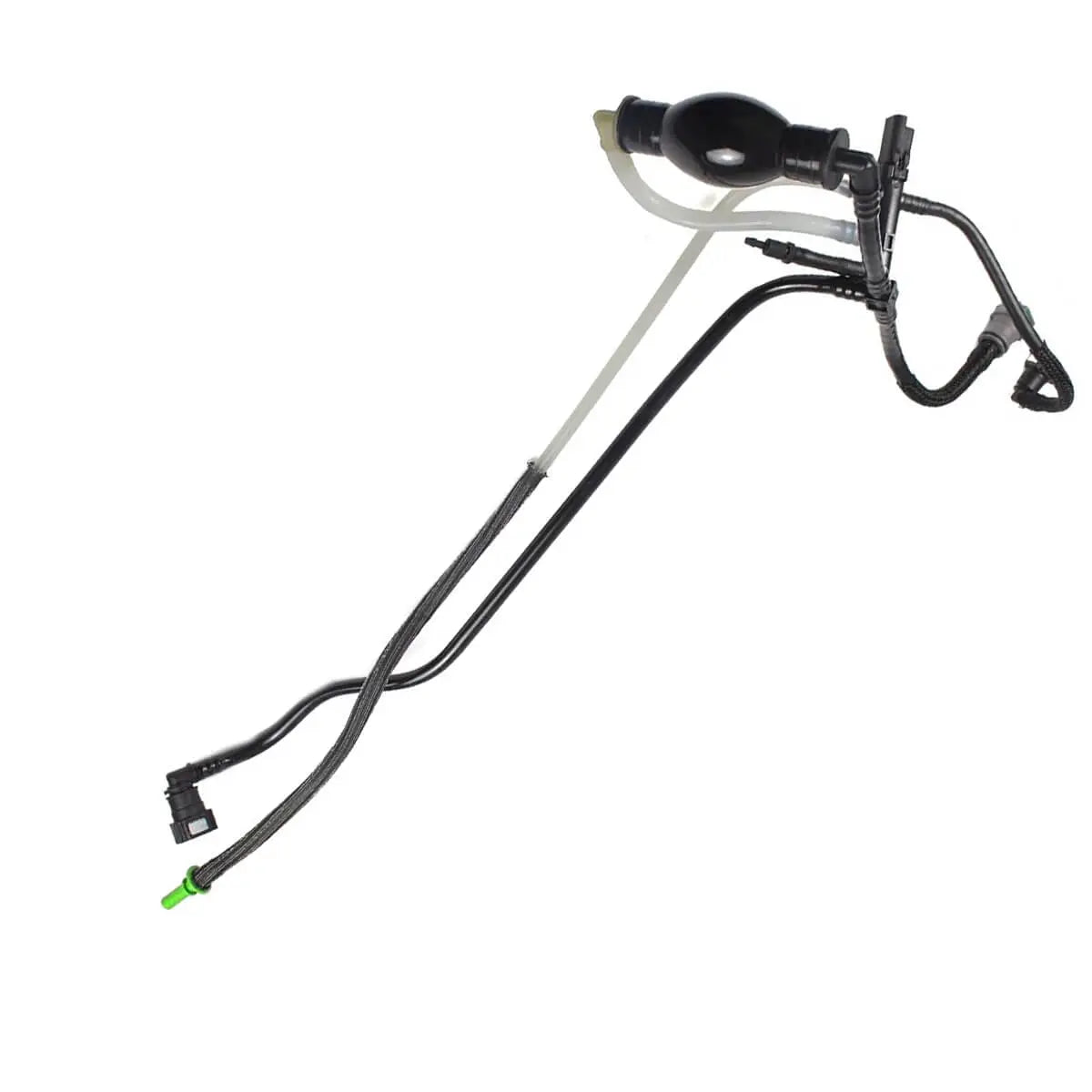
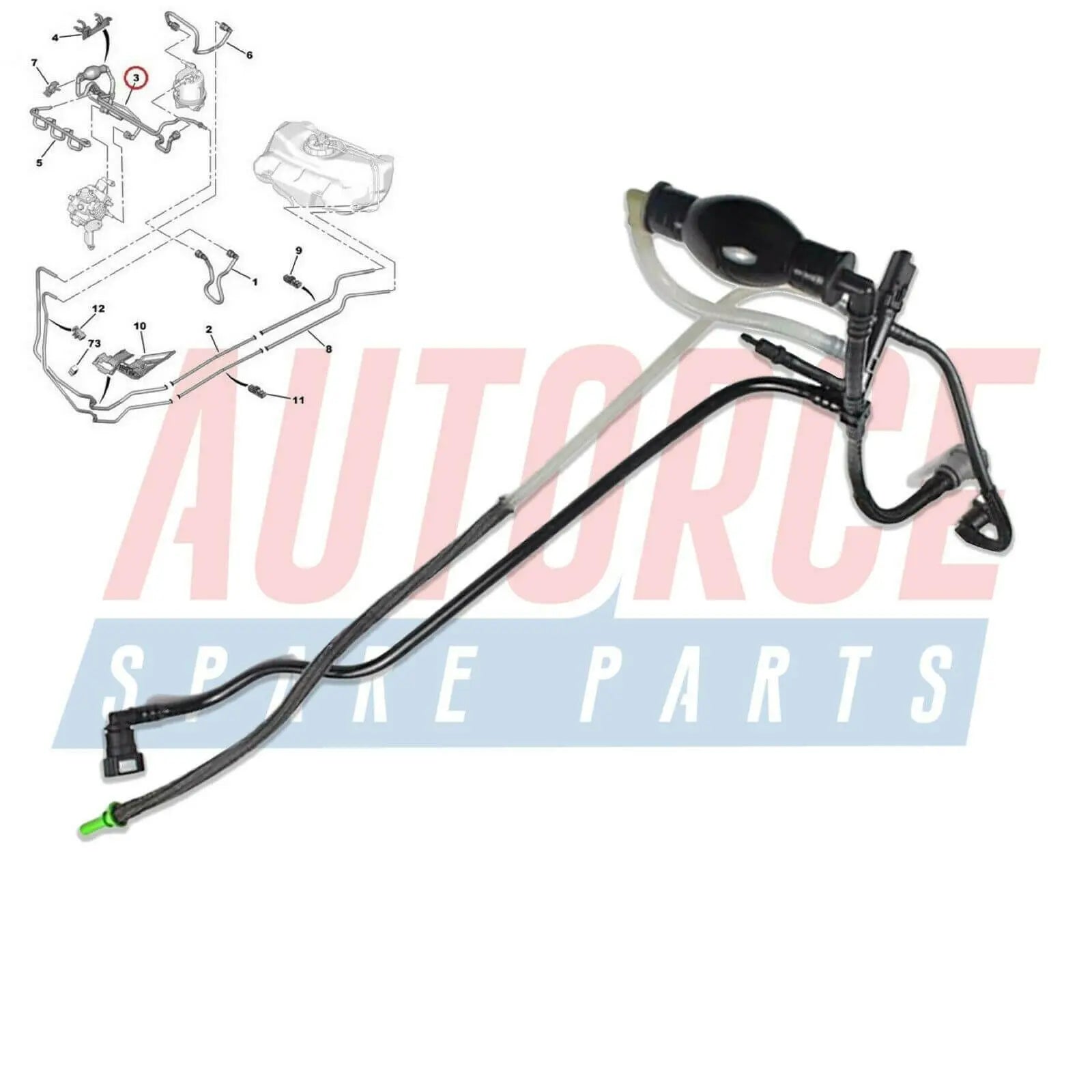


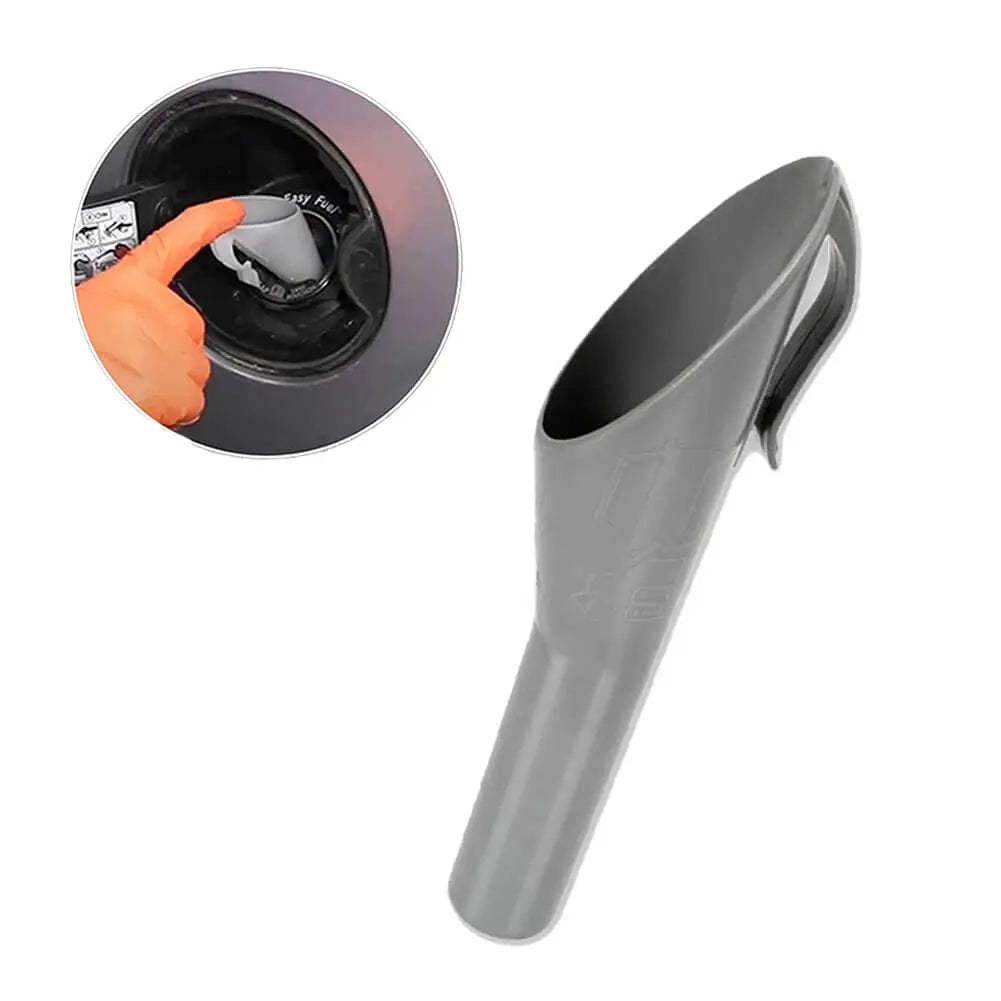
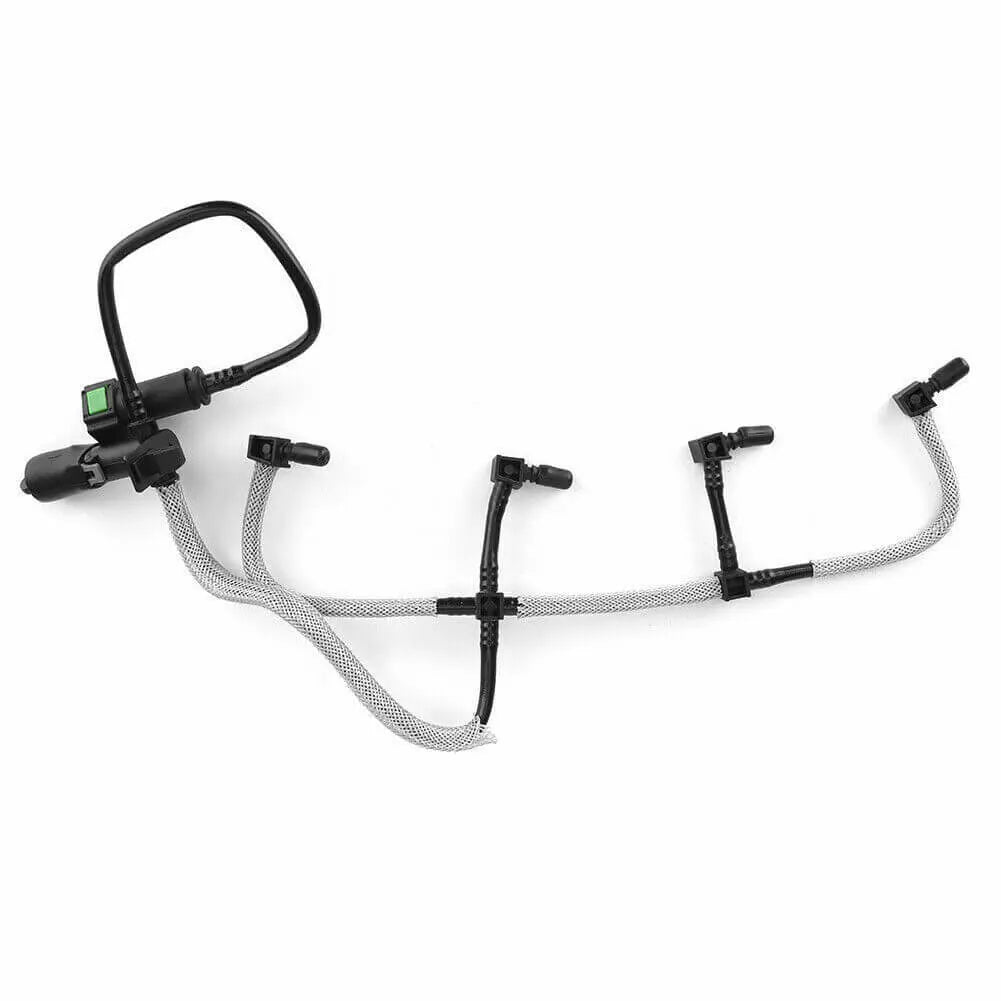
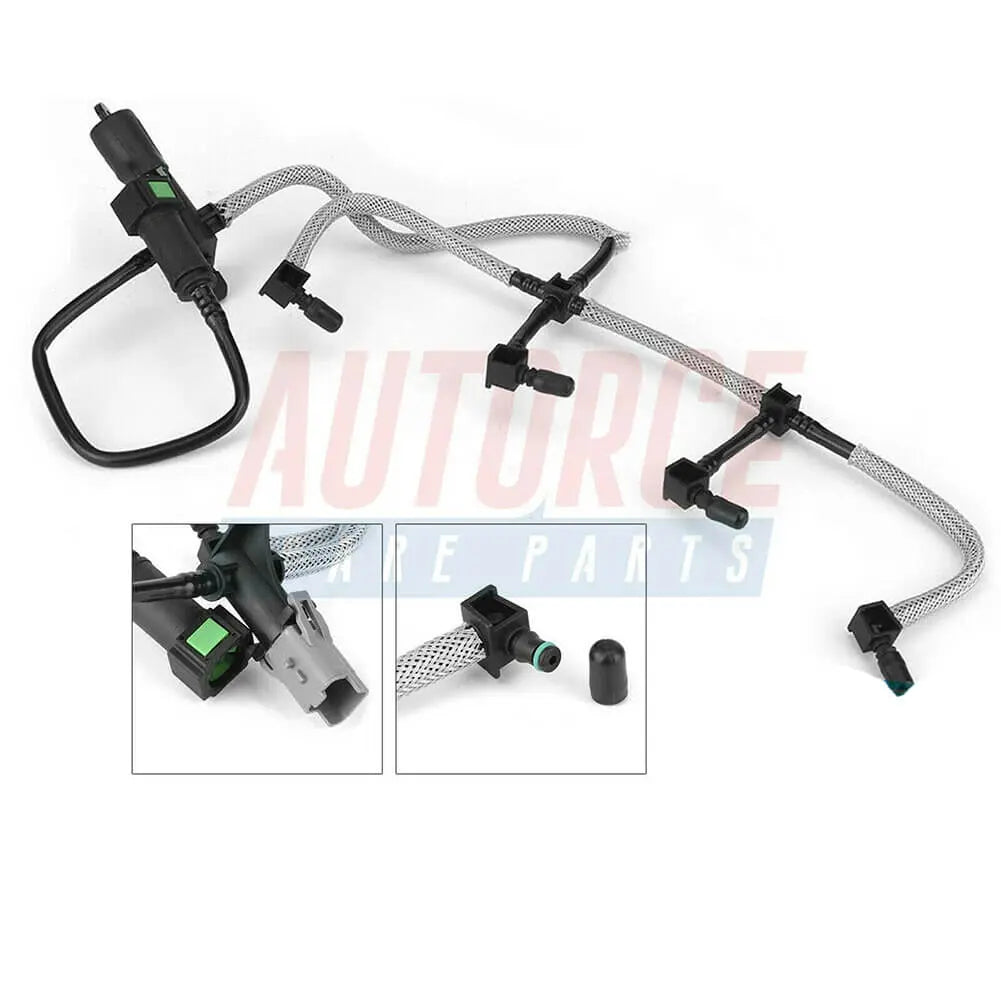
Fuel Line Pipe Primer Pump For Ford Fiesta Mk5 Fusion Estate 1.4 TDCi - 2S6Q9D350AF, 1501910
Sale price£23.99
No reviews
In stock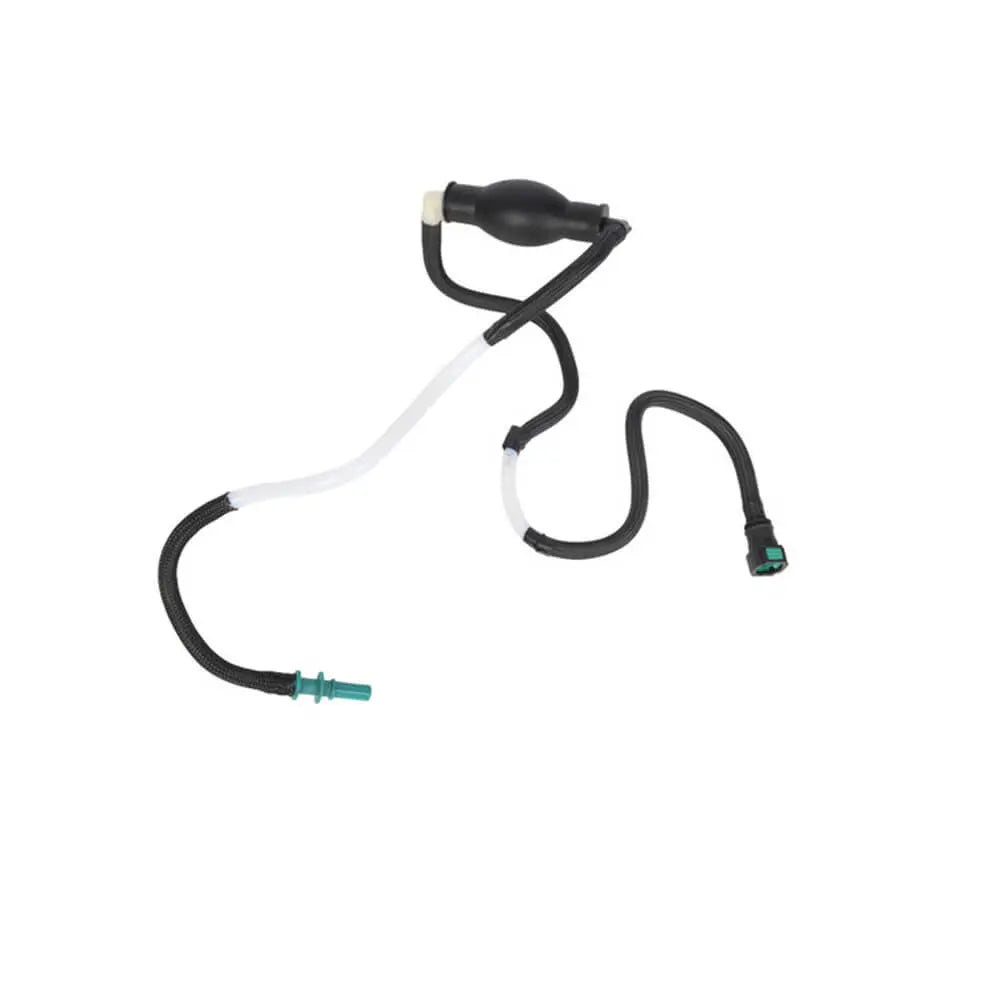

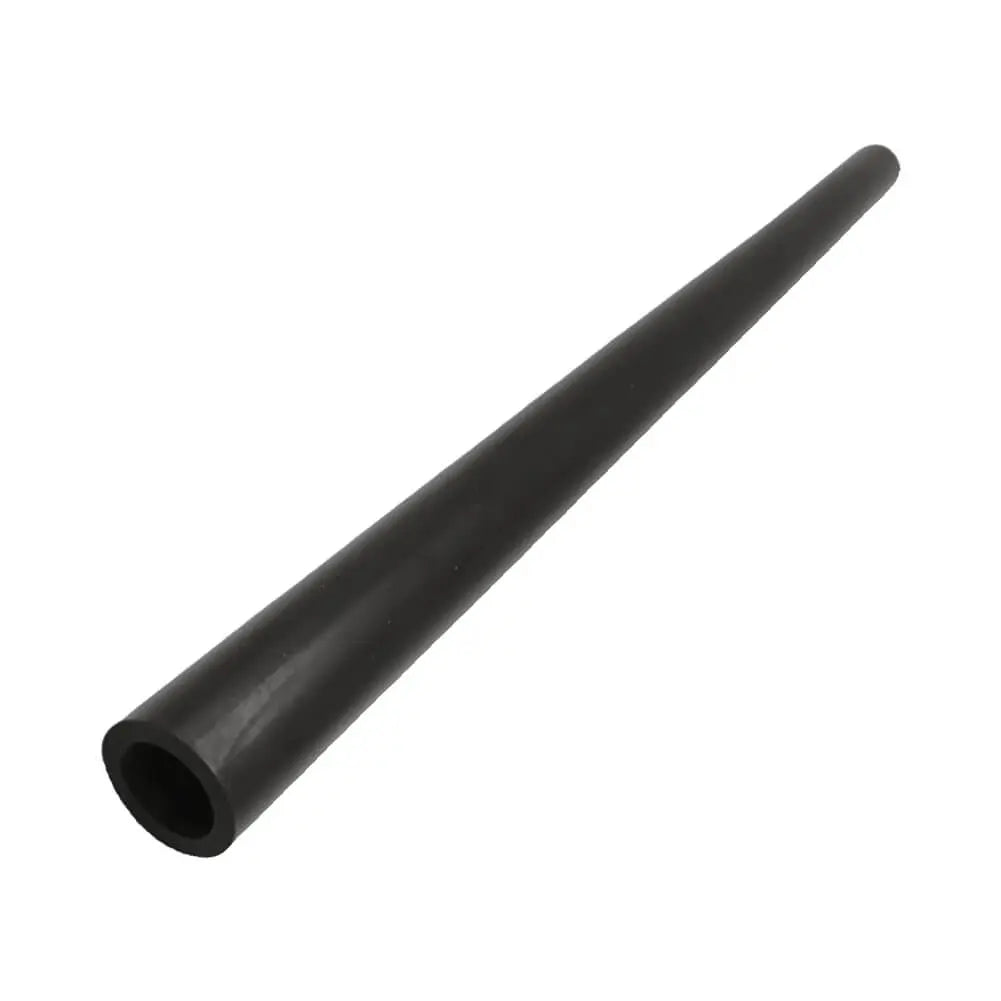
Fuel Hose Pipe For Dacia Duster 1.5 dCi (2013 - Onwards) - 175063943R
Sale price£27.90
No reviews
Sold out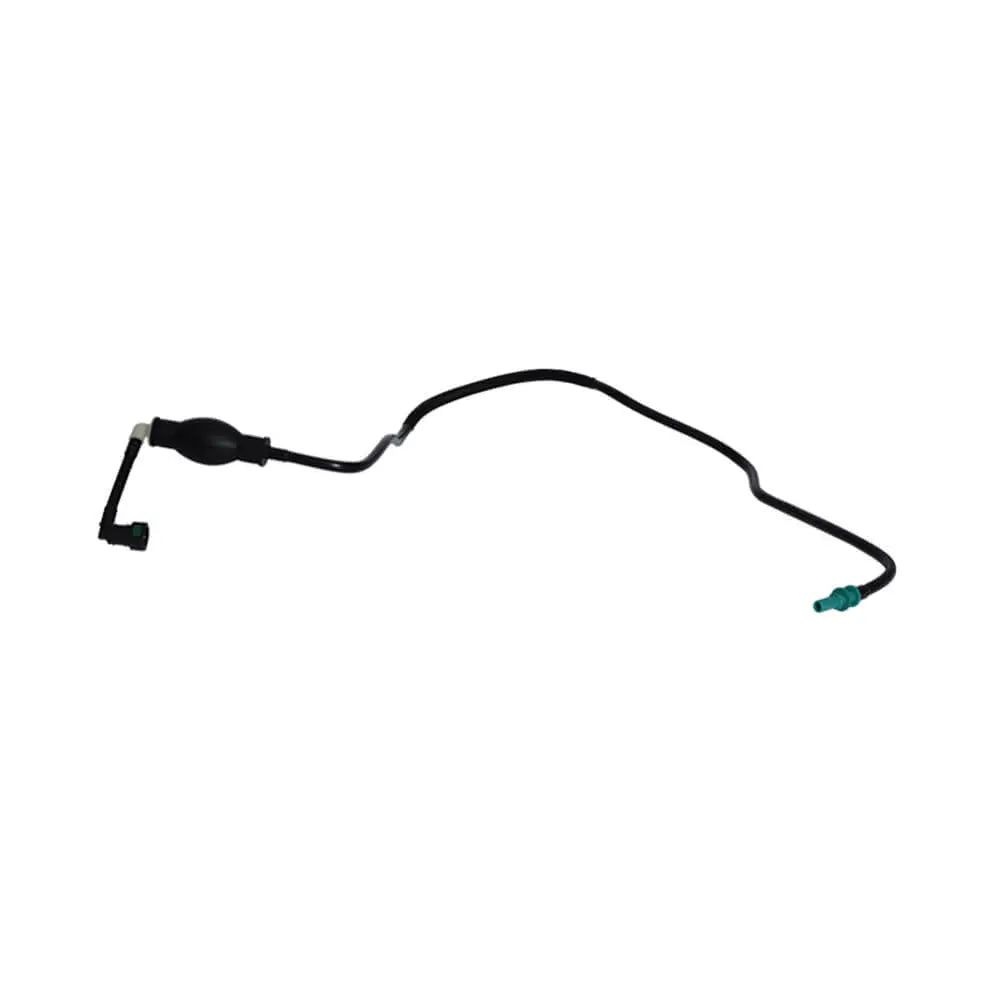

Fuel Injector Pipe For Vauxhall Vivaro (X83) - 8200505325, 4416876, GM 93857417
Sale price£14.90
No reviews
Hurry! Stock running out!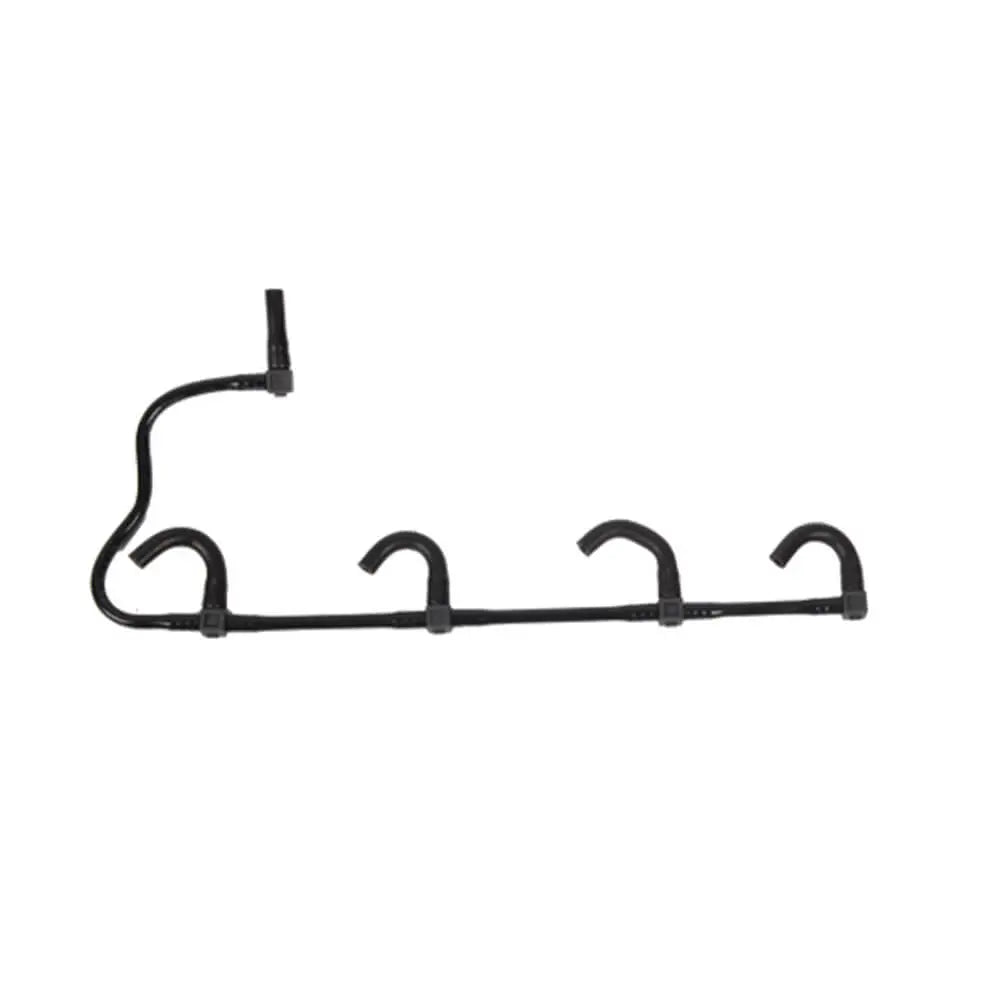

Fuel Return Leak-off Pipe For Dacia Dokker Duster Lodgy Logan Sandero - 8200171176
Sale price£11.90
No reviews
Hurry! Stock running out!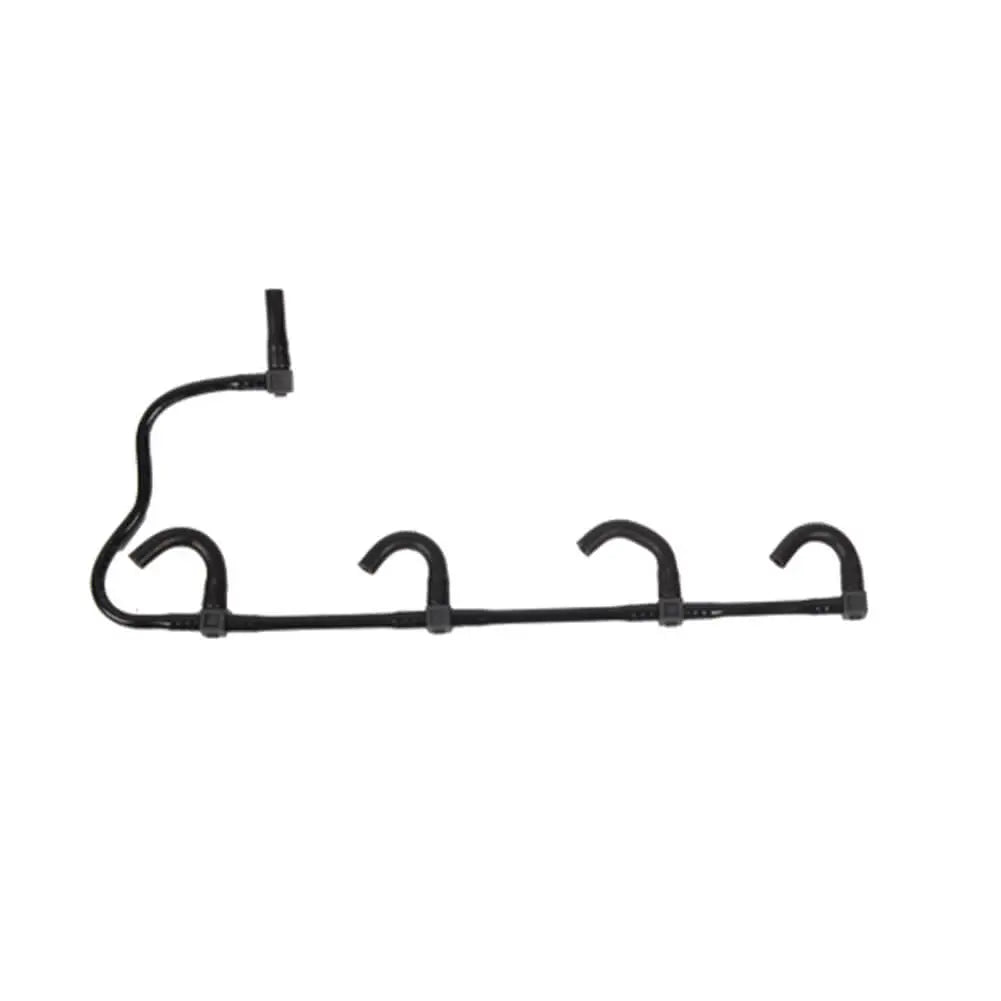

Fuel Return Leak-off Pipe For Renault Clio Kangoo Megane Scenic - 8200520596
Sale price£11.90
No reviews
Hurry! Stock running out!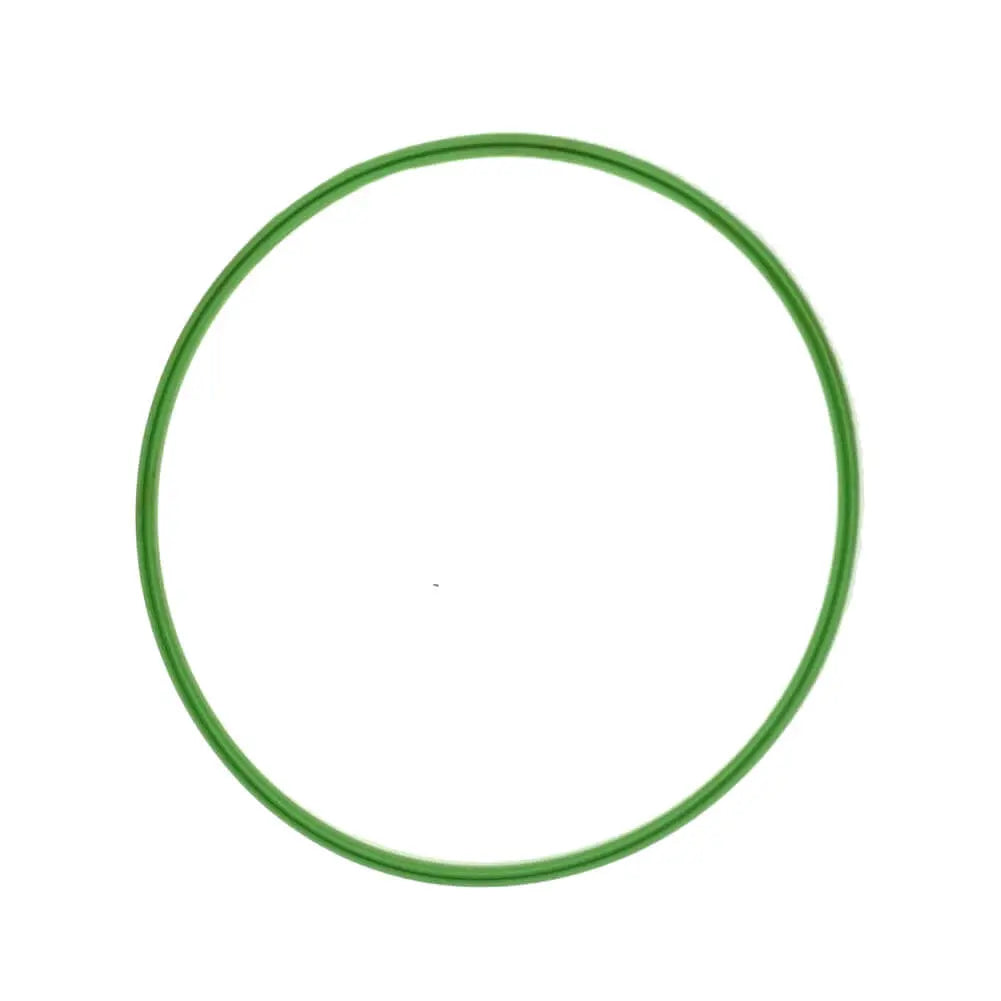

Fuel Pump Gasket Seal For Vauxhall Astra MK5 For Saab 9-3 - 24401341
Sale price£7.45
No reviews
In stockSave £3.21
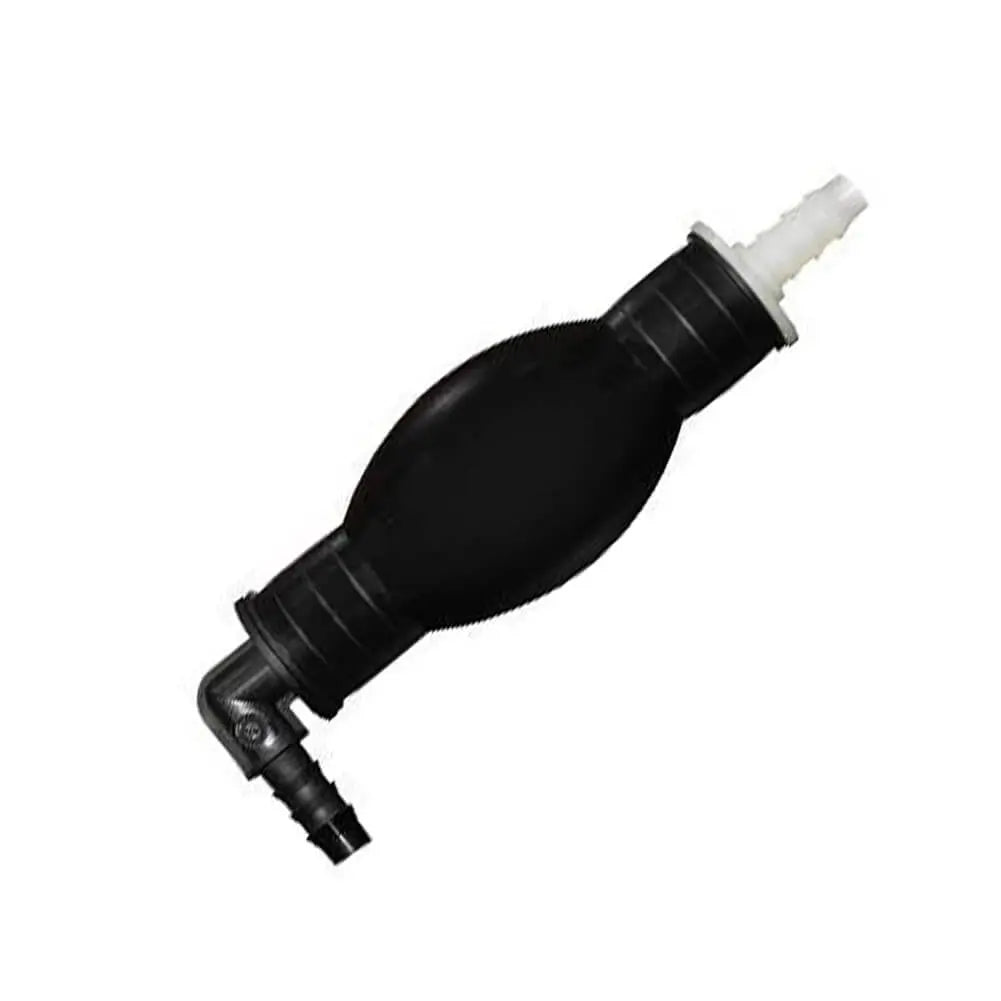
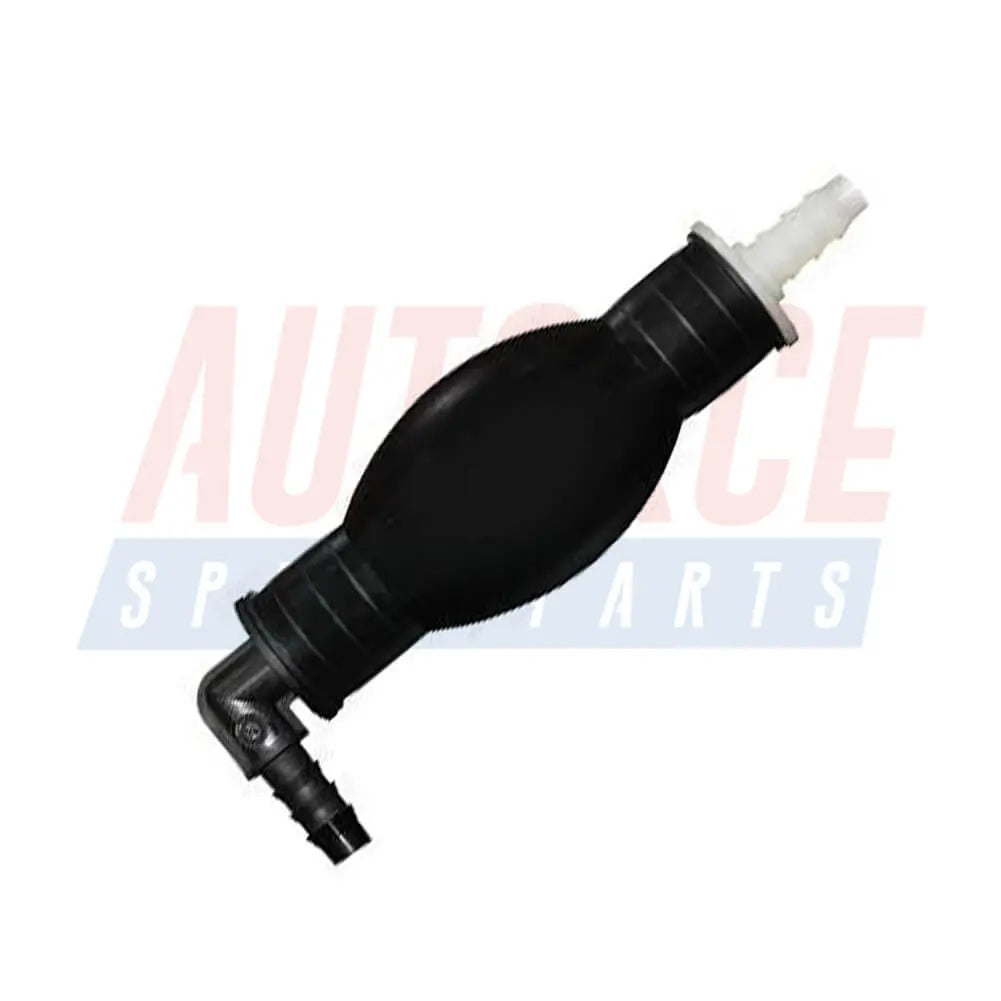


Diesel Primer Bulb Hand Pump For Renault Clio Kangoo Symbol Thalia 1.9 D - 7700111932
Sale price£7.90
Regular price£11.11
No reviews
In stock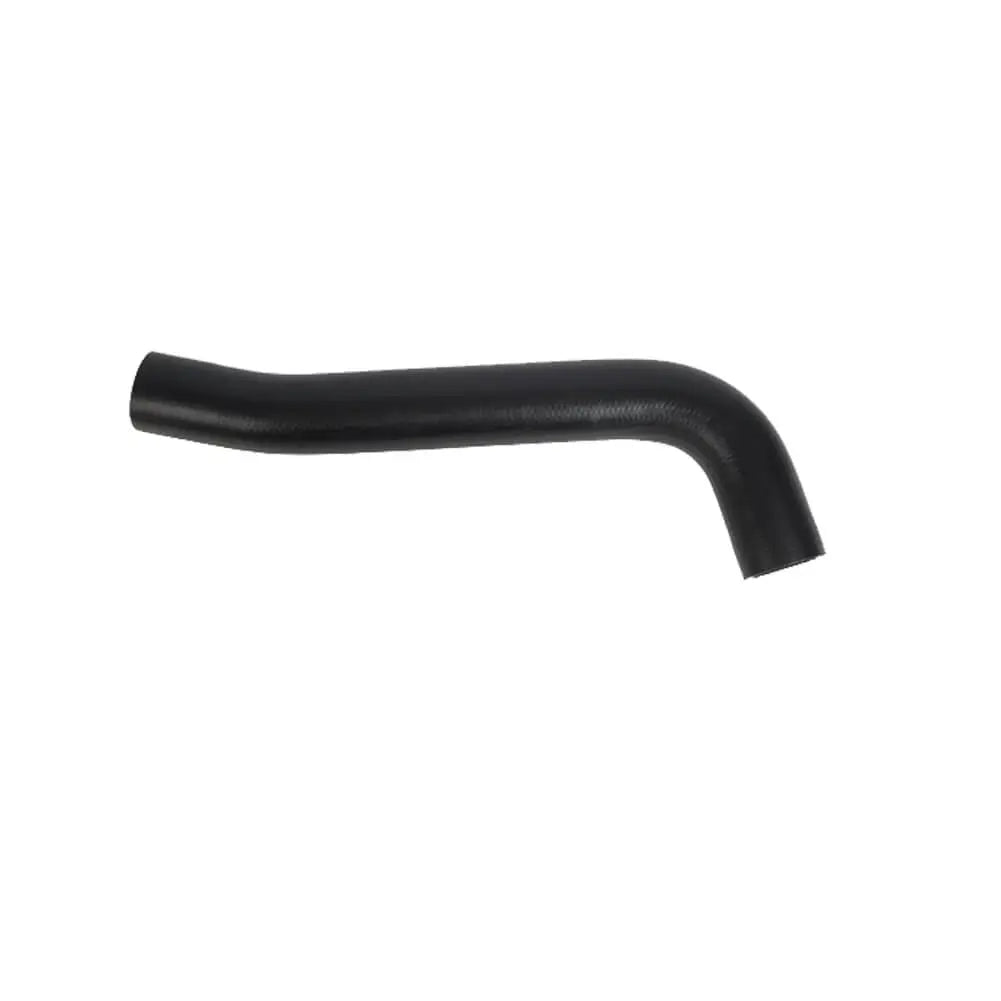
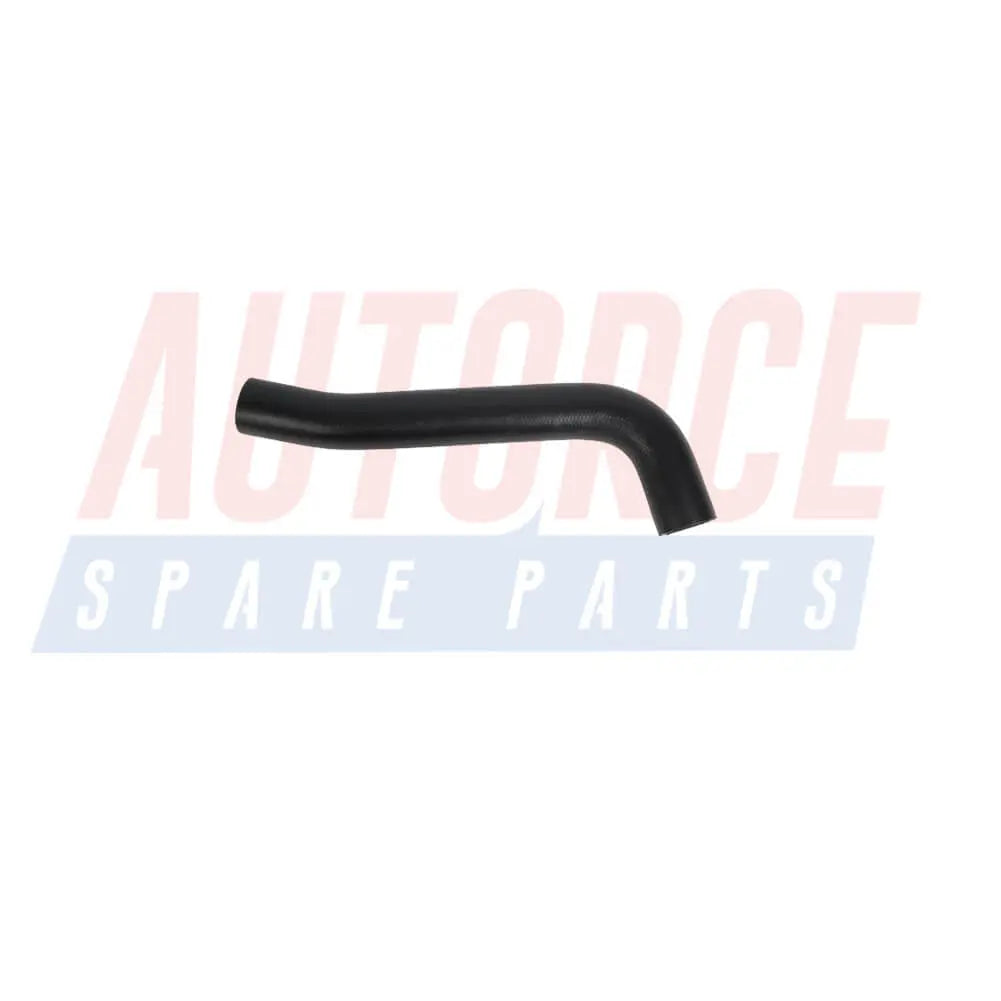

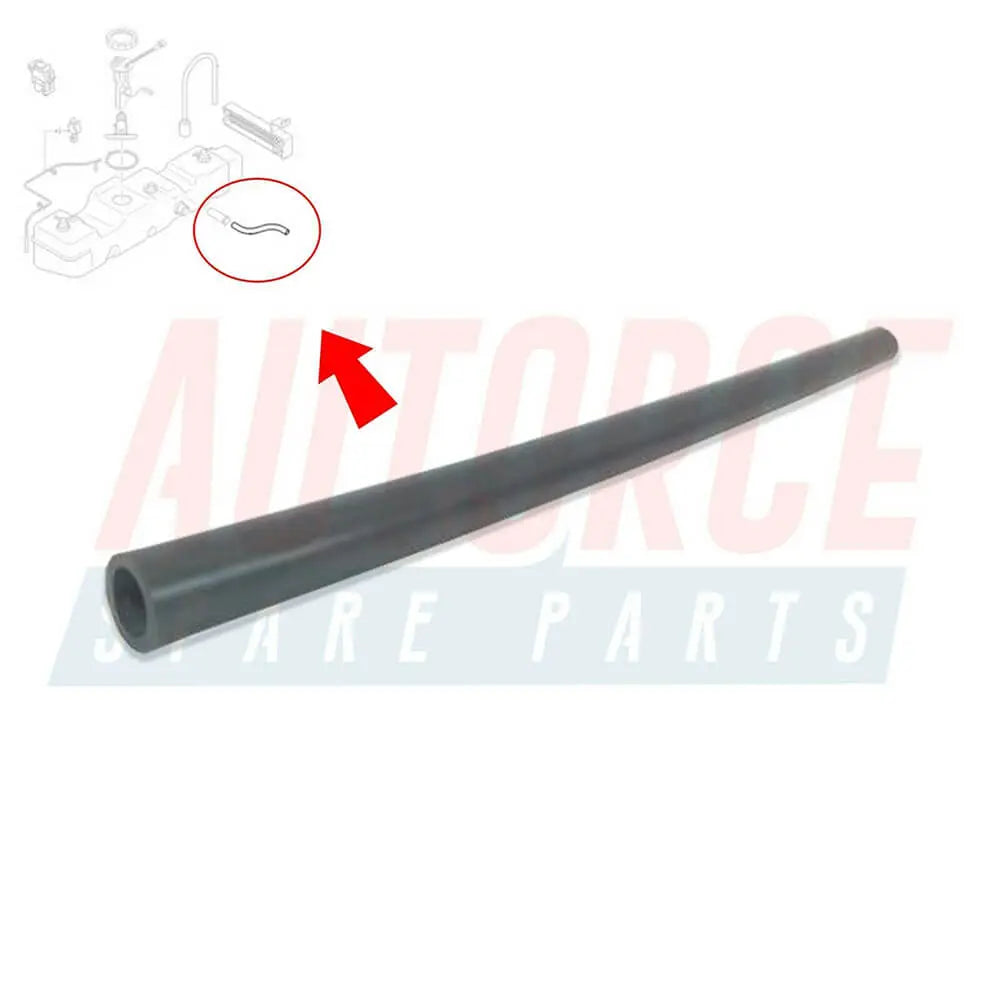
Fuel Tank Breather Hose Pipe For Vauxhall Corsa B Tigra I (1993 - 2000) GM 90467441, 806137
Sale price£14.90
No reviews
Sold out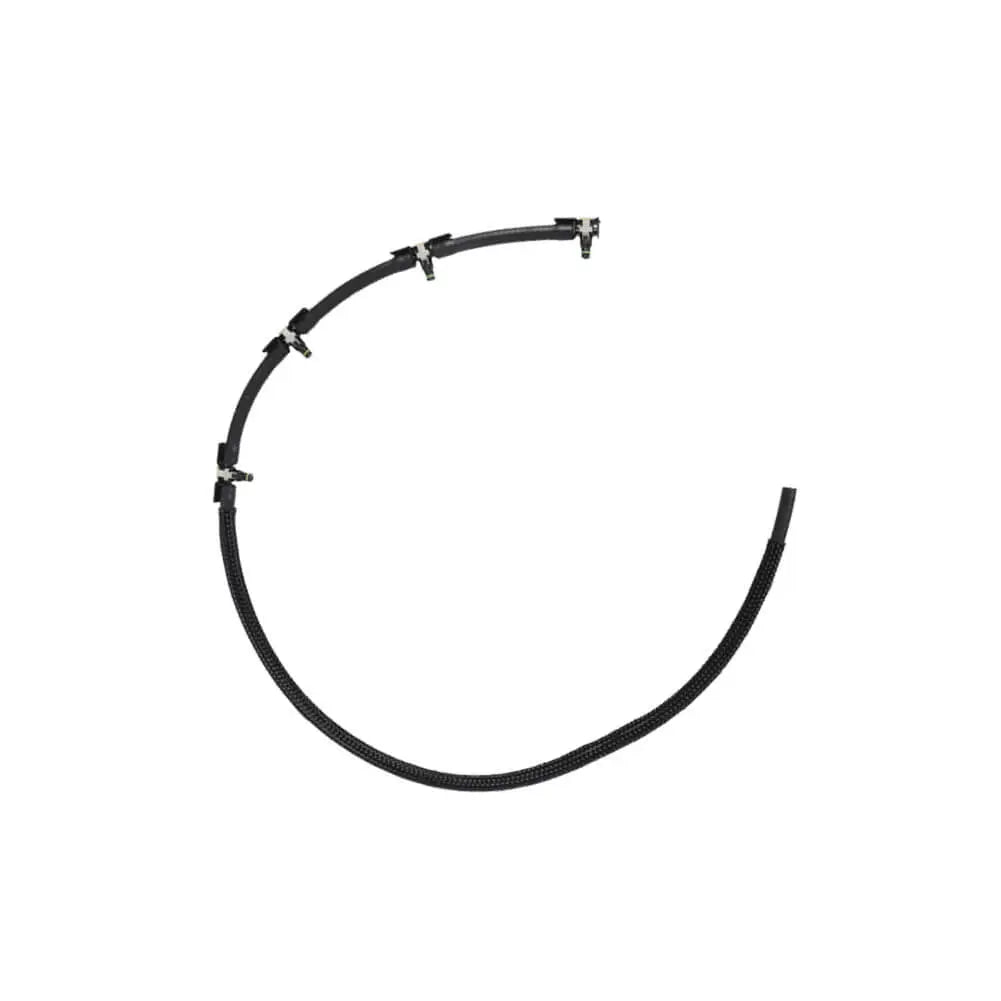
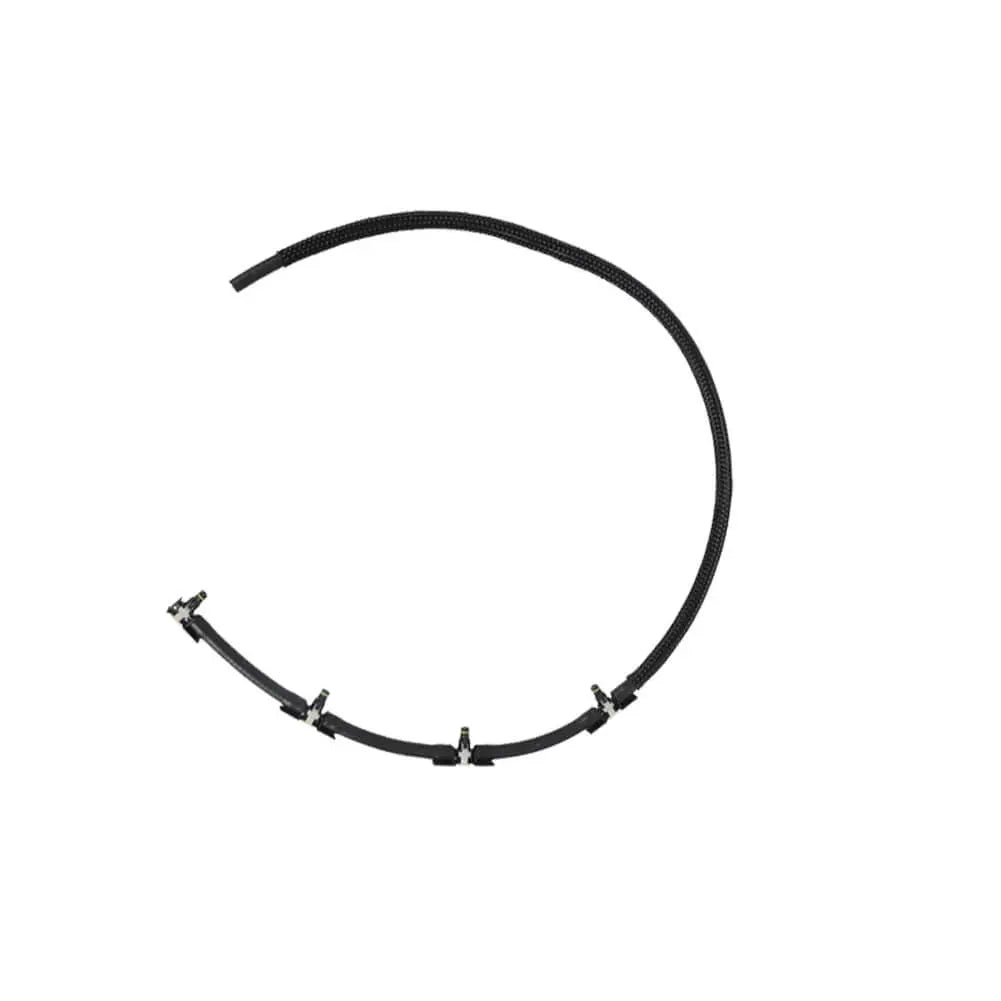

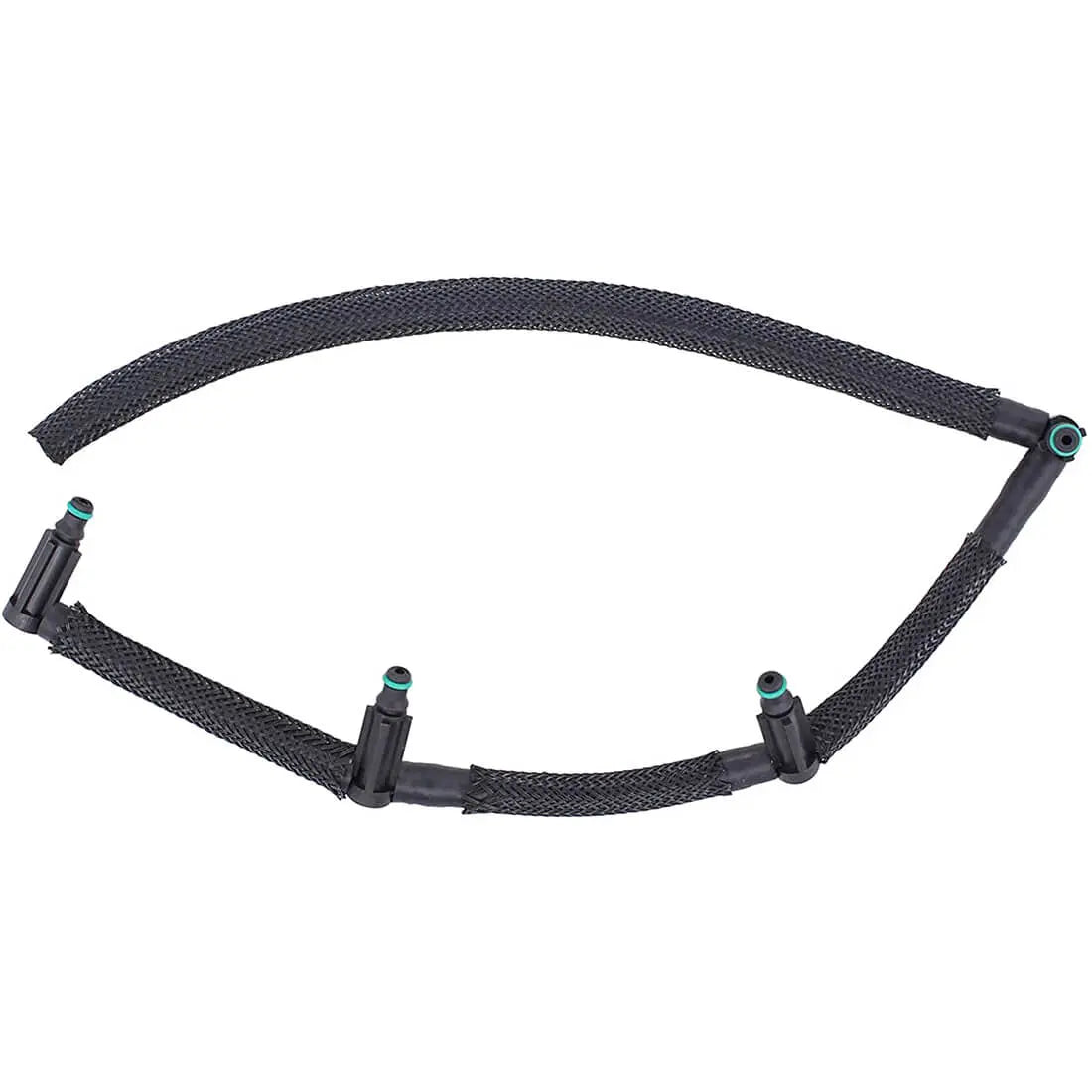
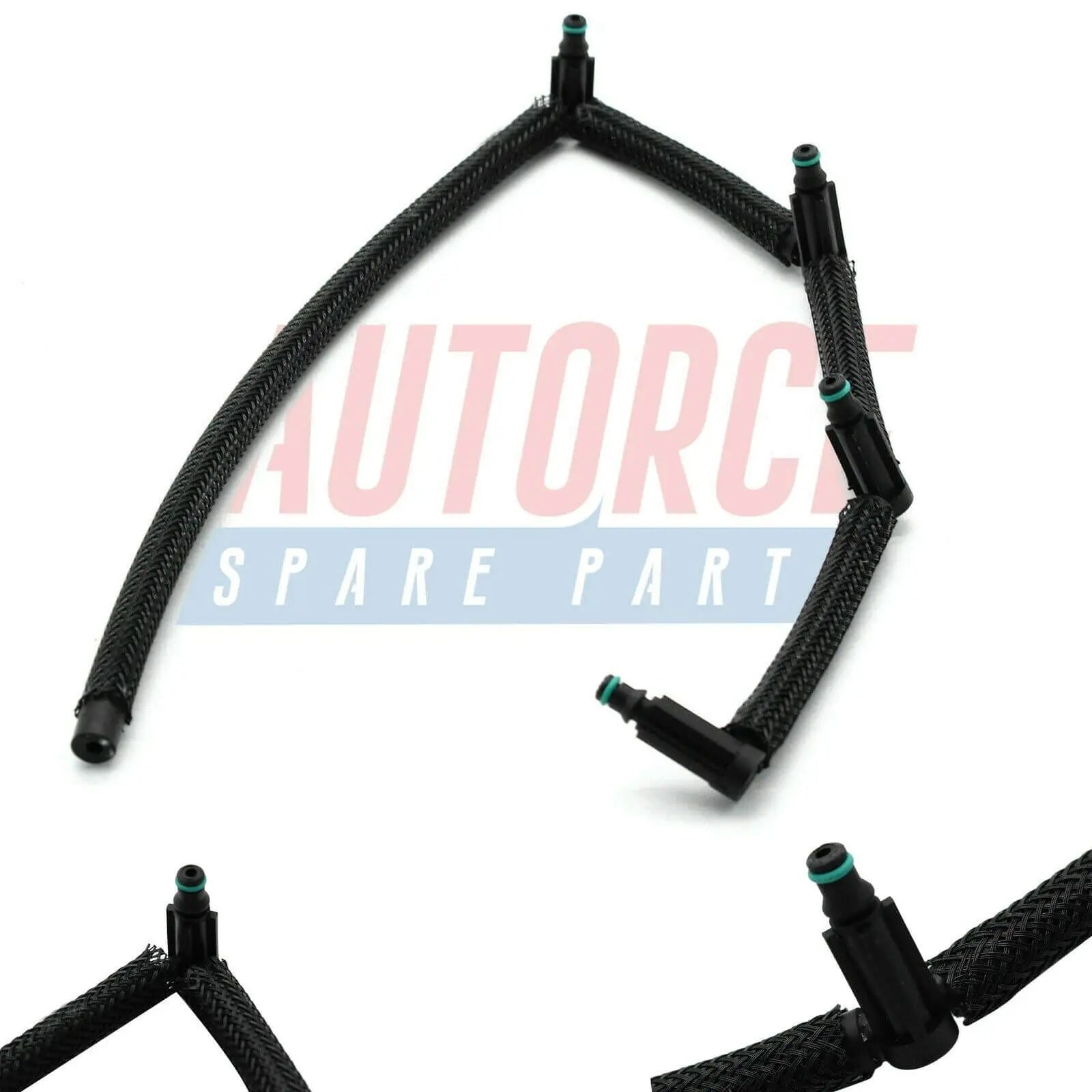
Injector Pipe Fuel Hose For BMW 1 2 3 4 5 X1 X2 X3 X4 (2009 - Onwards) 13538583458, 13538516196
Sale price£24.90
No reviews
In stock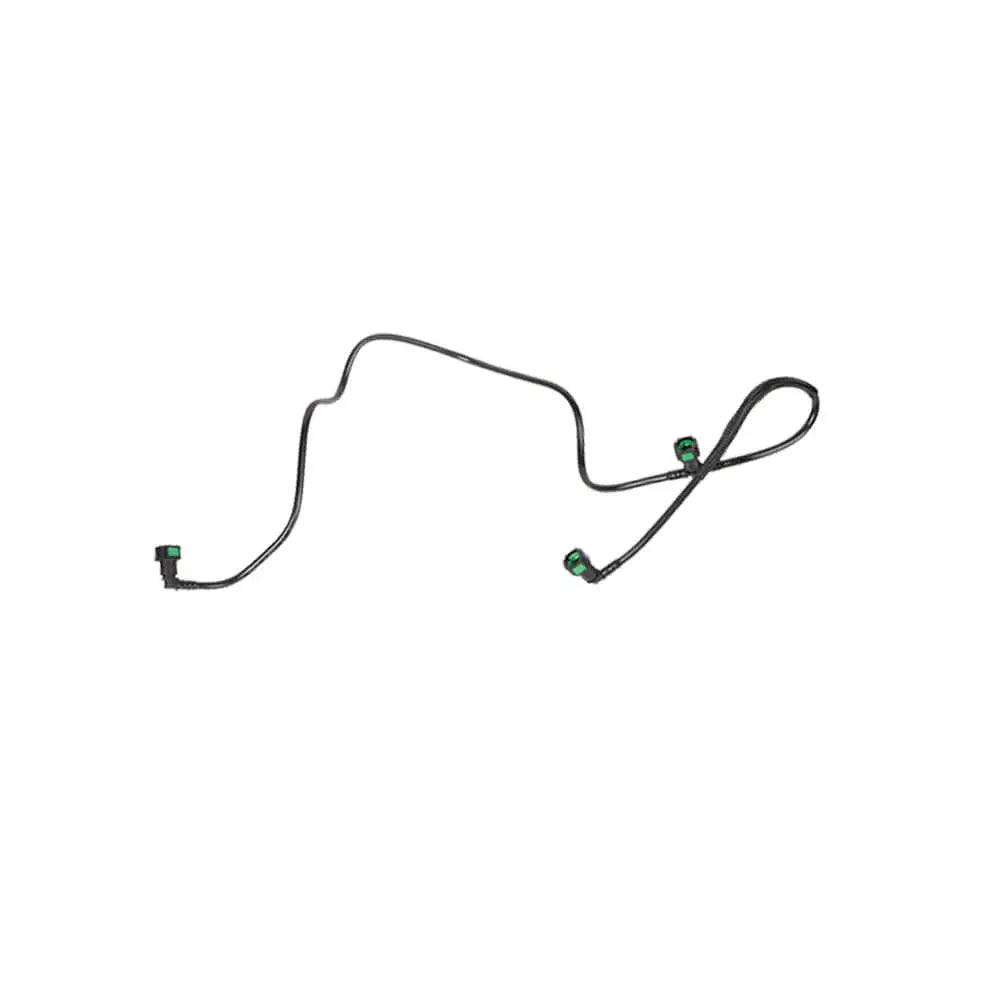

Fuel Hose Pipe For Ford Tourneo Connect 1.8 TDCi (2002 - 2013) 2T149B337CJ, 1477390, 1435468
Sale price£26.90
No reviews
Sold out
Filters (0)




























