Shop by Category
Engine Components
586 products
Showing 1 - 24 of 586 products
A Closer Look at the Essential Engine Components for Cars
The heart of every automobile lies beneath its hood - the engine. The engine is a marvel of engineering that converts fuel into the power required to move the vehicle. It comprises a complex system of components working in harmony to generate and control combustion, producing the energy needed to propel the car forward. Understanding the key engine components is vital for any car enthusiast or aspiring mechanic. In this article, we will explore the essential engine components that make modern automobiles possible.Cylinder Block:
The cylinder block, also known as the engine block, is the foundation upon which the entire engine is built. Typically made of cast iron or aluminum, it houses the engine's cylinders, providing a rigid framework for the reciprocating motion of the pistons. The number of cylinders varies depending on the engine type - ranging from four cylinders in most standard vehicles to eight or more in high-performance cars.Pistons and Connecting Rods:
Pistons are cylindrical components that move up and down inside each cylinder. As the fuel-air mixture combusts, the resulting high-pressure gases force the pistons downward in a controlled explosion. Connected to the pistons are the connecting rods, which transmit the piston's motion to the crankshaft. Pistons and connecting rods are critical for converting the energy from combustion into rotational motion, which drives the wheels.Crankshaft:
The crankshaft is a vital engine component responsible for transforming the reciprocal motion of the pistons into rotary motion. As the pistons move up and down, they turn the crankshaft, which subsequently transfers power to the transmission and, ultimately, the wheels. The crankshaft is typically made of high-strength steel and precisely balanced to minimize vibrations and ensure smooth engine operation.Camshaft and Valvetrain:
The camshaft, driven by the crankshaft via a timing belt or chain, controls the opening and closing of the engine's valves. The camshaft has lobes that press against the valve stems, causing them to open and close at precise intervals. The valvetrain includes components such as valves, valve springs, and lifters, ensuring proper timing and coordination of the engine's intake and exhaust processes. The camshaft's design and timing significantly influence the engine's performance characteristics.Cylinder Head:
Situated atop the cylinder block, the cylinder head seals the combustion chambers and houses the valves and their associated components. It is often made of aluminum to reduce weight and improve heat dissipation. The cylinder head plays a crucial role in the engine's efficiency and performance, as it controls the intake and exhaust processes while also providing proper sealing for the combustion chambers.Intake and Exhaust Manifolds:
The intake manifold delivers the air-fuel mixture to the cylinders from the throttle body, while the exhaust manifold collects the exhaust gases from the cylinders and directs them towards the exhaust system. Both manifolds are carefully designed to optimize the flow of gases, improving engine efficiency and power output.The engine is the beating heart of an automobile, and its components work together in a precise ballet to produce power and drive the vehicle forward. Understanding these essential engine components allows car enthusiasts, drivers, and mechanics to appreciate the complexity and elegance of the modern internal combustion engine. As automotive technology continues to evolve, advancements in engine design promise even greater efficiency, performance, and environmental friendliness for the cars of the future.
Showing 1 - 24 of 586 products
Display
View
Save £0.91
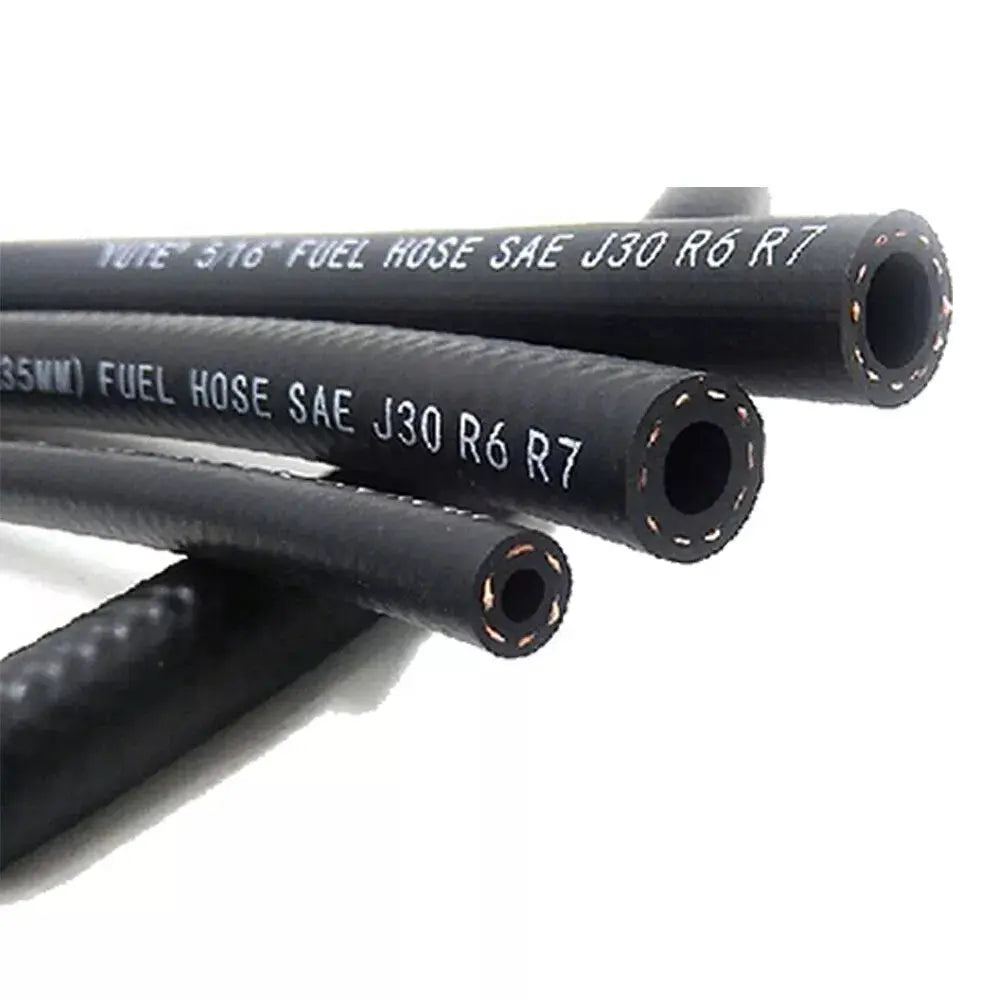
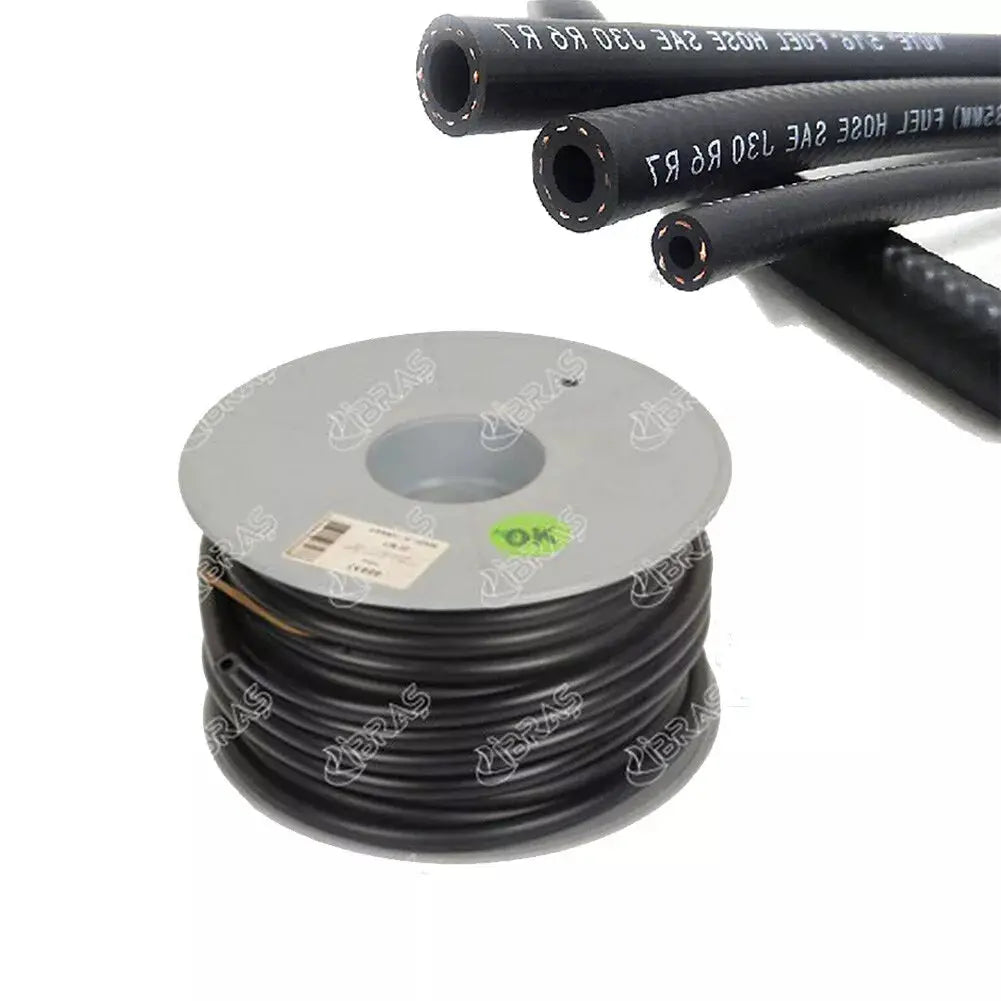


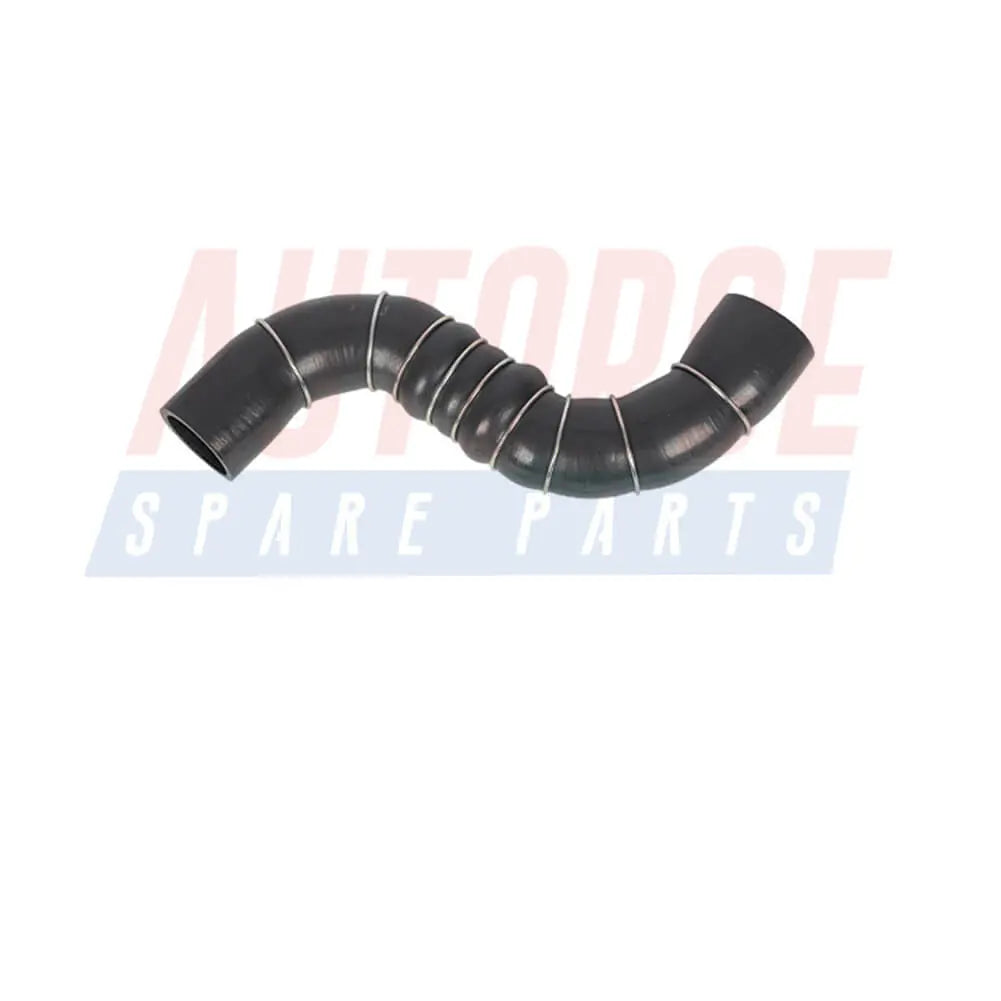
1 Mt Rubber Reinforced Fuel Hose Pipe Line Fuel Engine For Petrol Diesel Oil Or Water
Sale priceFrom £3.99
Regular price£4.90
2 reviews
In stock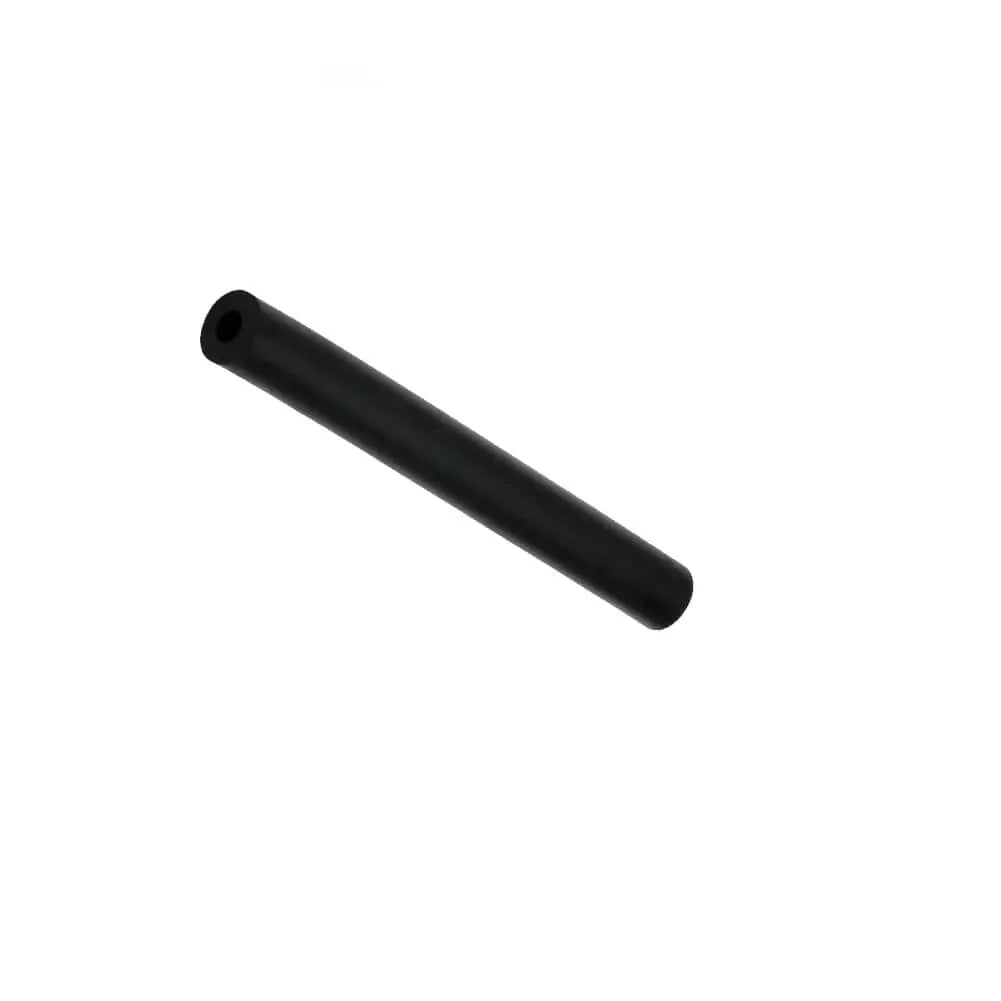

Turbo Pressure Sensor Hose For Dacia Dokker Duster Logan Sandero 1.5 dCi - 208744694R
Sale price£7.90
No reviews
In stock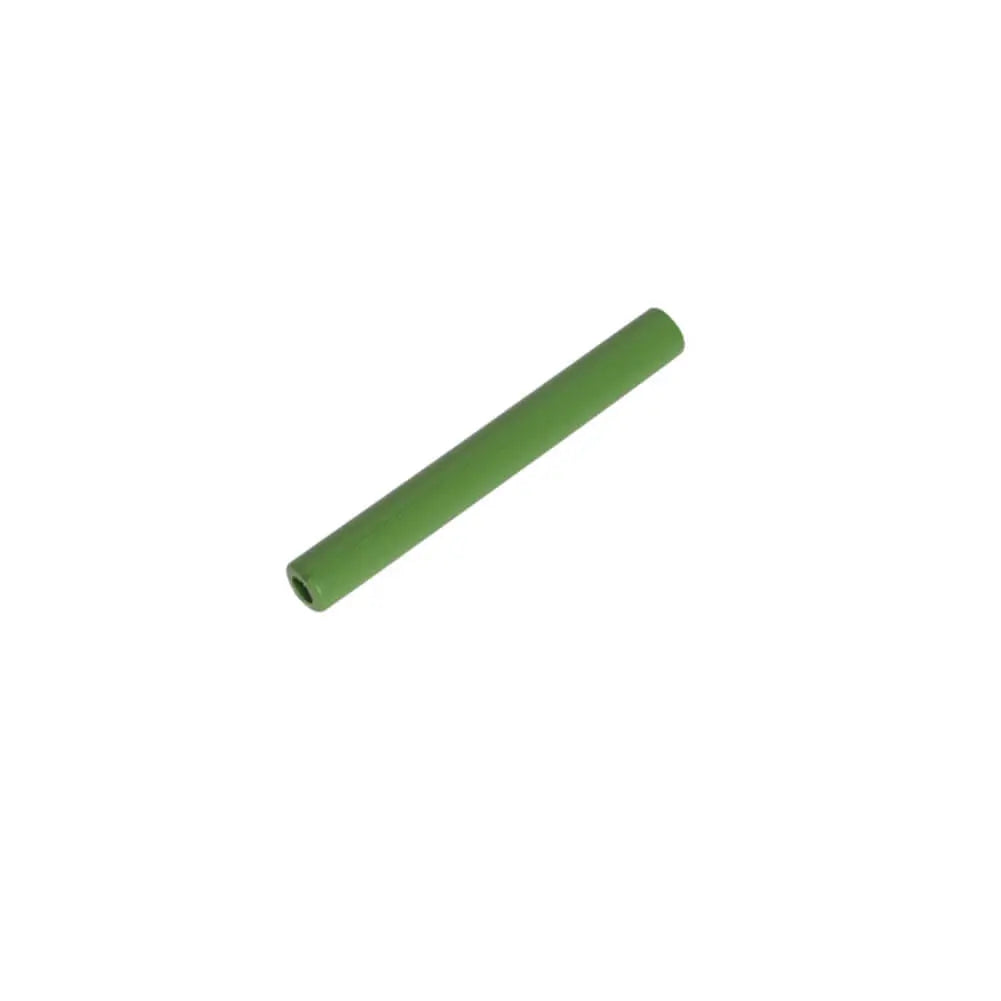

Turbo Pressure Sensor Hose For Dacia Dokker Duster Lodgy Logan Sandero - 208742477R
Sale price£7.90
No reviews
In stock
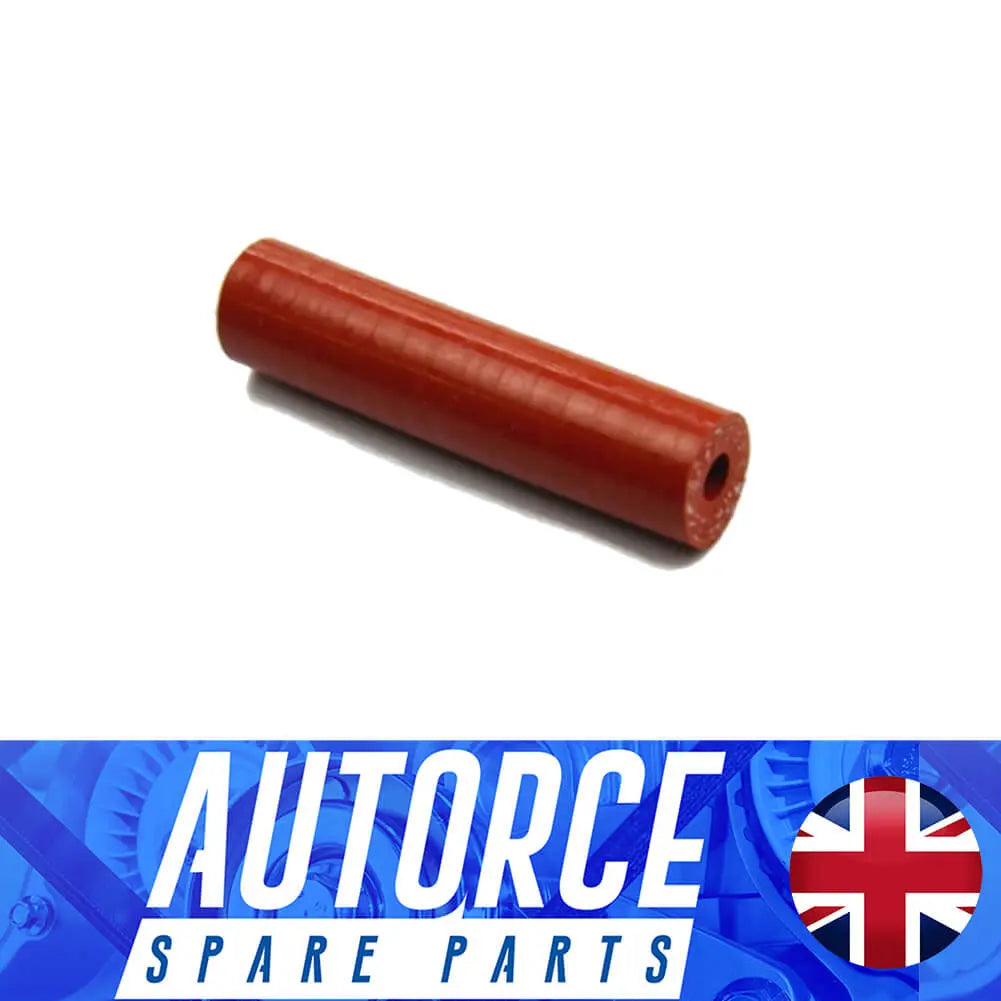

Turbo Pressure Hose For Nissan Cube Qashqai - 1412000Q0J, 1412000Q1E
Sale price£6.90
1 review
In stock

Turbo Intercooler Hose Repair Kit For Vauxhall Insignia 1.6 2.0 CDTI (2014 - 2017) - 13419441
Sale price£12.90
No reviews
Sold out

Intercooler Turbo Hose Pipe For Volvo S40 II V50 C30 1.6 D2 (2010 - 2012) 31319716, AV616K863VB
Sale price£17.90
No reviews
In stock

Turbo Pressure Sensor Hose For Renault Captur Clio Kangoo Megane Scenic Talisman - 208742477R
Sale price£7.90
No reviews
In stockSave £5.09
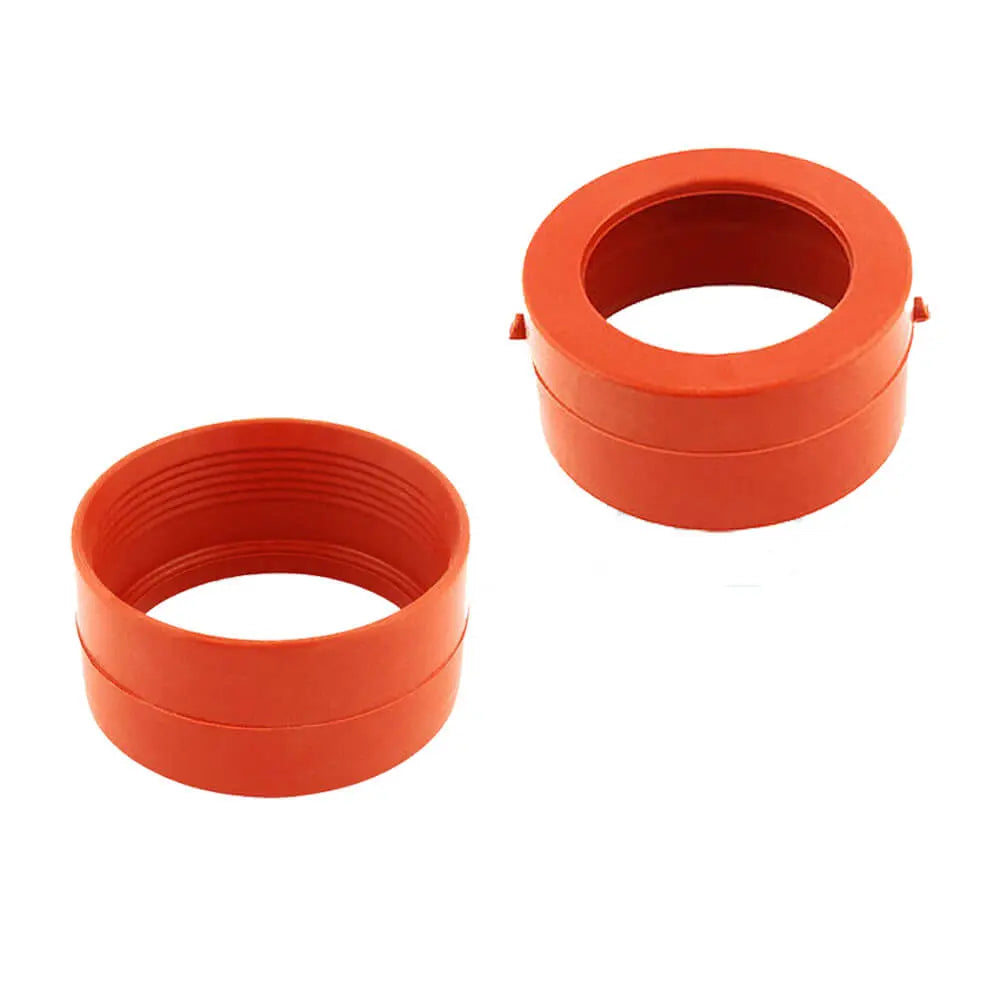


2 Pcs Engine Turbo Boost Pipe Seal Gasket Upper / Lower For Volvo V70 S60 XC70 V70 XC90 - 30778628, 30778629
Sale price£14.90
Regular price£19.99
No reviews
In stock

Turbo Intercooler Pipe Hose Seal For Mercedes A B Class CLA GLA - 0219976545
Sale price£5.90
No reviews
In stock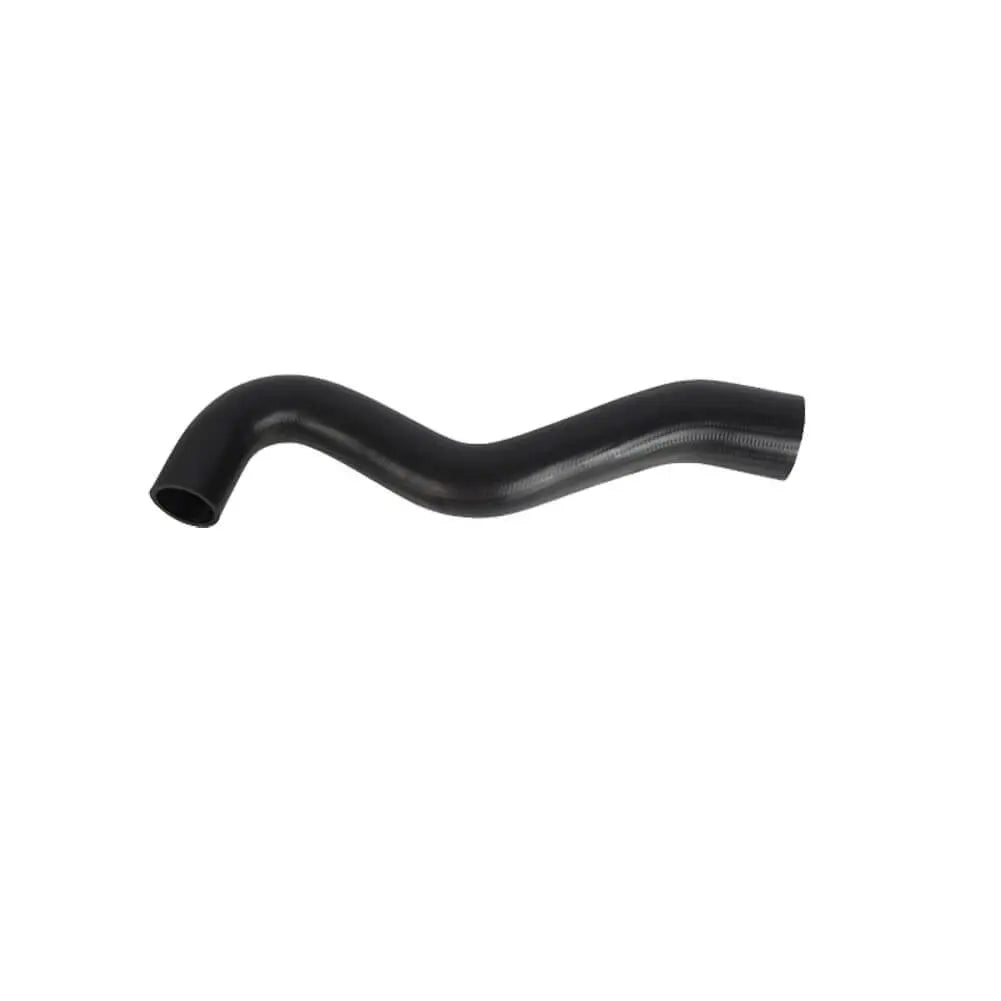
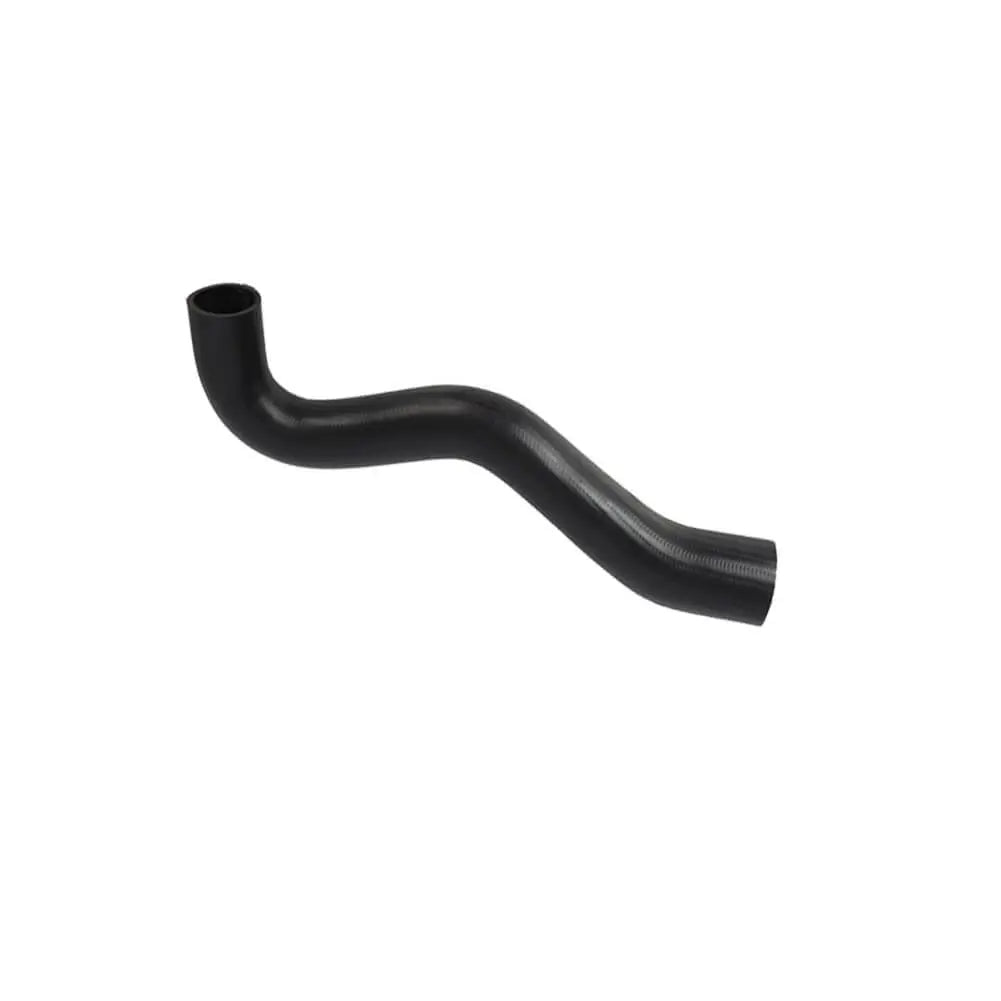

Intercooler Turbo Hose For Mitsubishi L200 Triton (2007 - Onwards) MN171051
Sale price£22.90
No reviews
In stock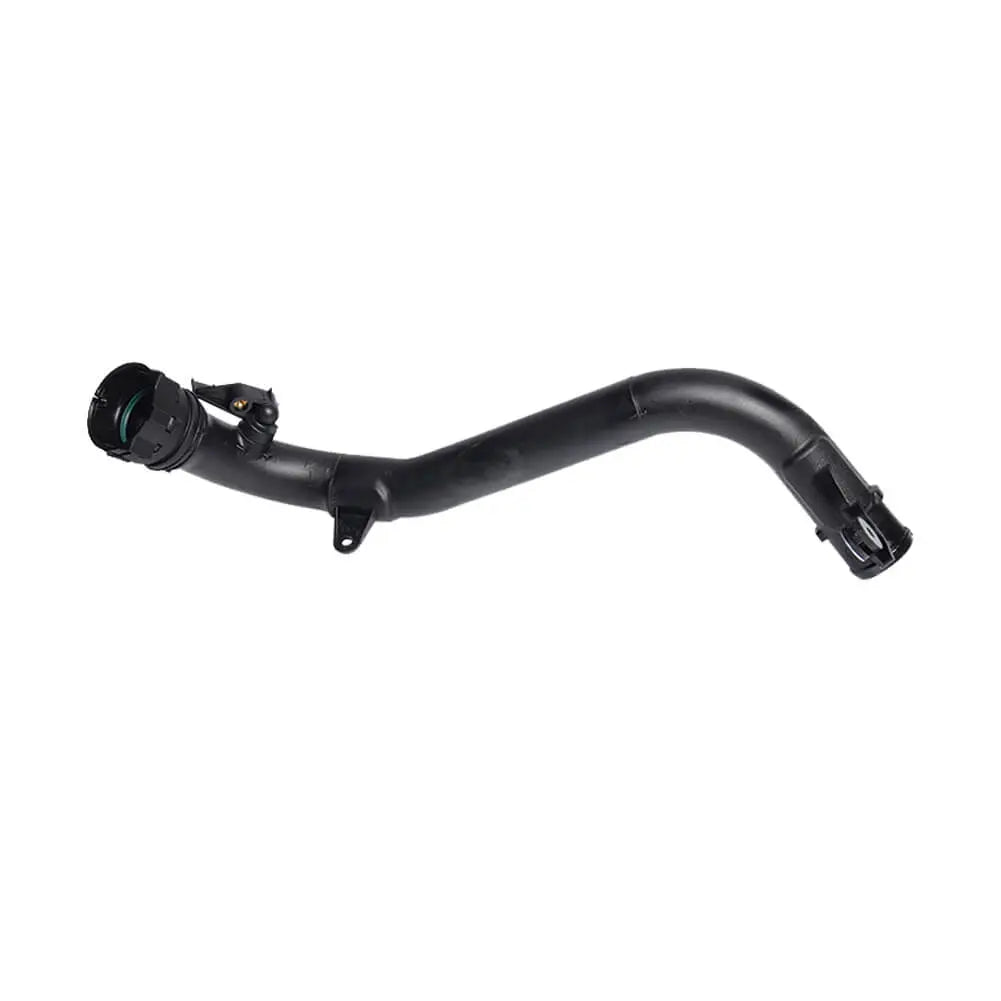
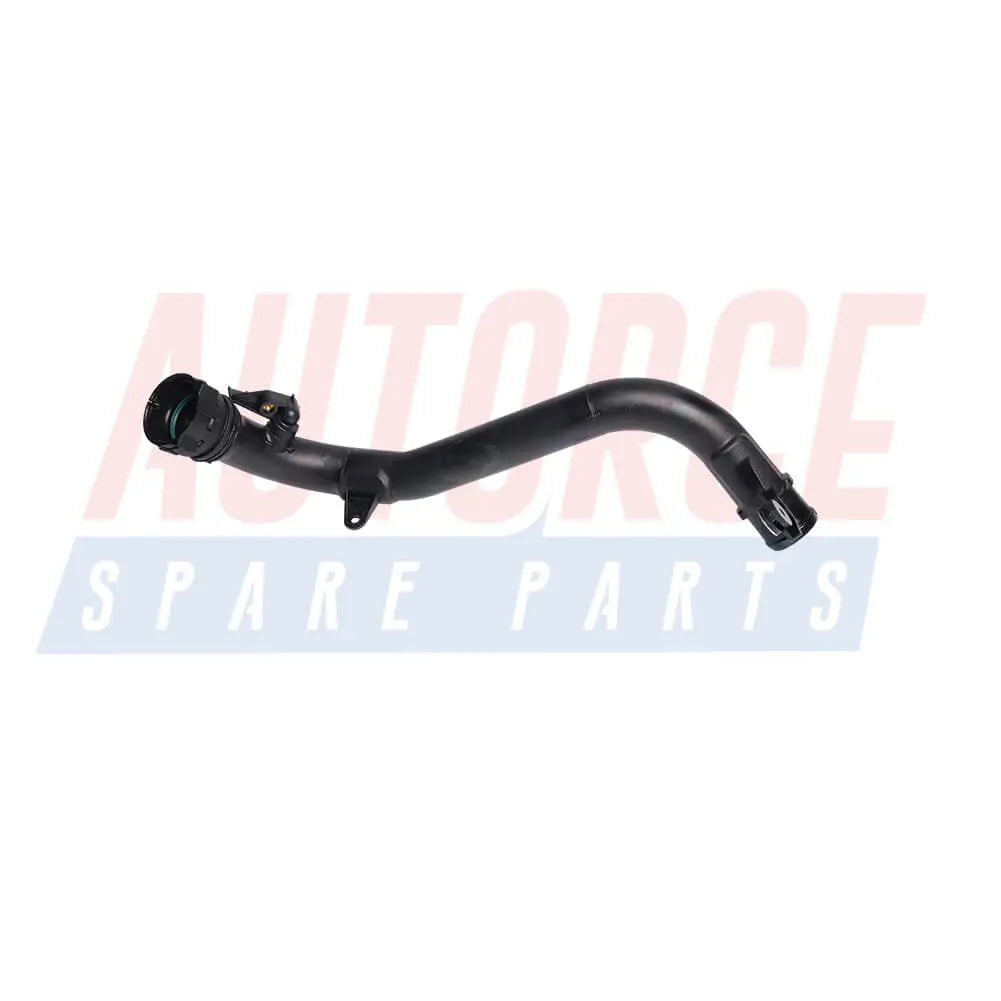

Intercooler Turbo Hose Pipe For Nissan Juke Cube Nv200 1.5 dCi (2010 - Onwards) 144601FE0C, 144601FE1C
Sale price£44.99
No reviews
Hurry! Stock running out!Save £17.00
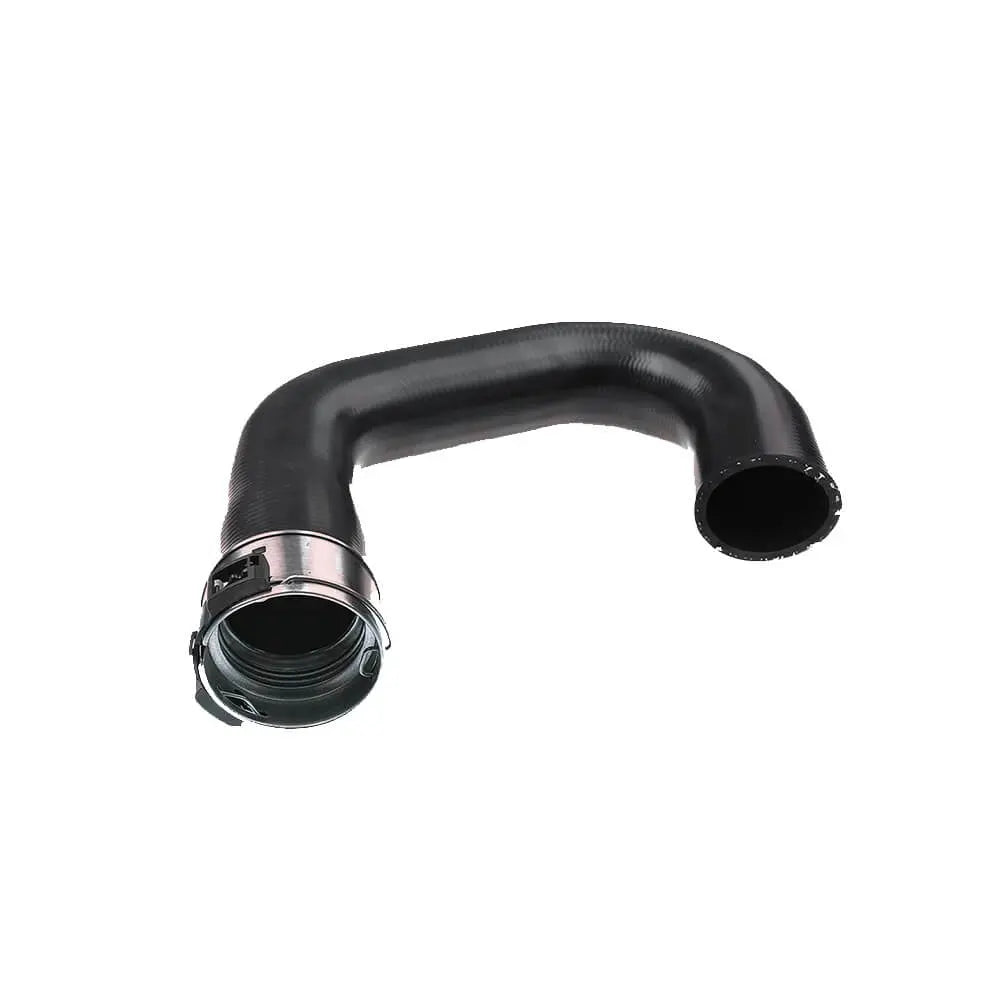
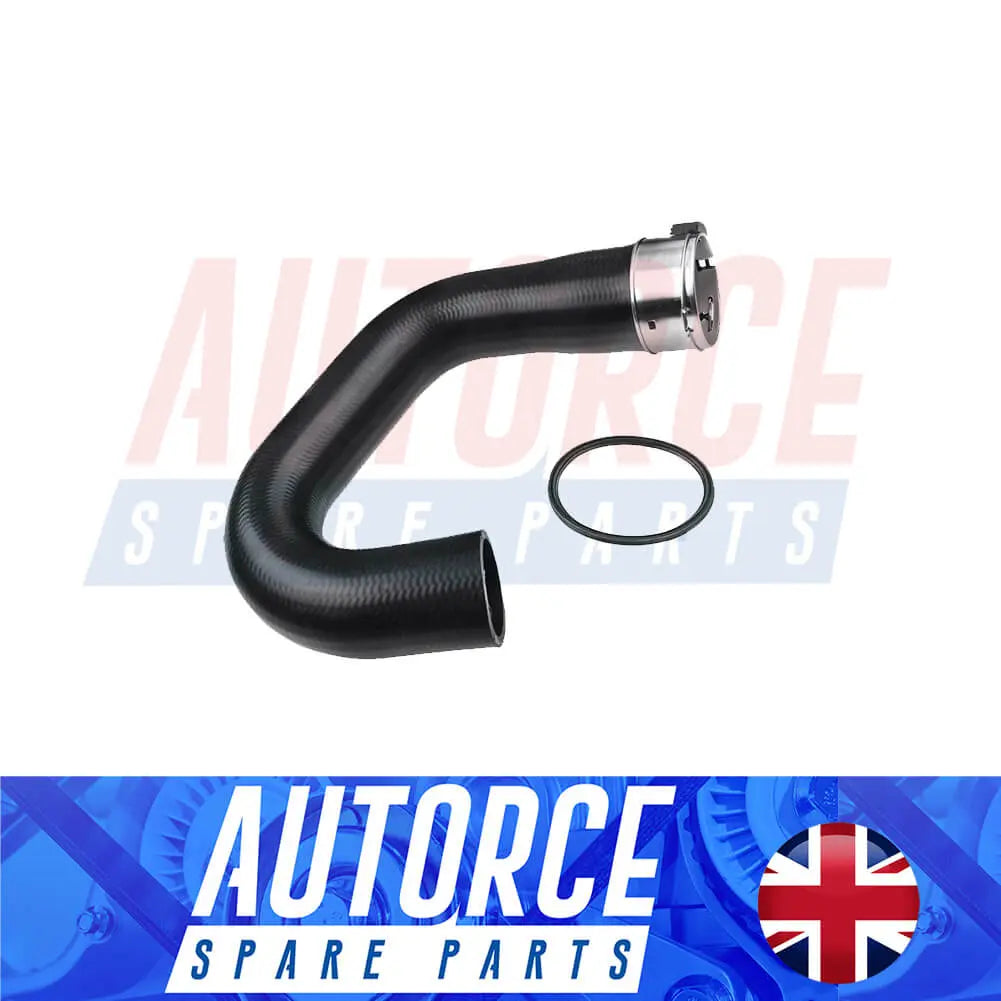


Intercooler Turbo Hose For Vauxhall Opel Mokka X (J13) 1.6 CDTI, 1.7 CDTI (2012 - Onwards) 1302287, 835134
Sale price£47.90
Regular price£64.90
1 review
Hurry! Stock running out!

Turbo Pressure Sensor Hose For Renault Captur Clio Kangoo Megane Scenic Talisman - 208744694R
Sale price£7.90
No reviews
In stock

Turbo Pressure Sensor Hose For Renault Captur Clio Kangoo Megane Scenic Talisman - 208741307R, 6071420083, 6071420300
Sale price£7.90
No reviews
Hurry! Stock running out!
Filters (0)