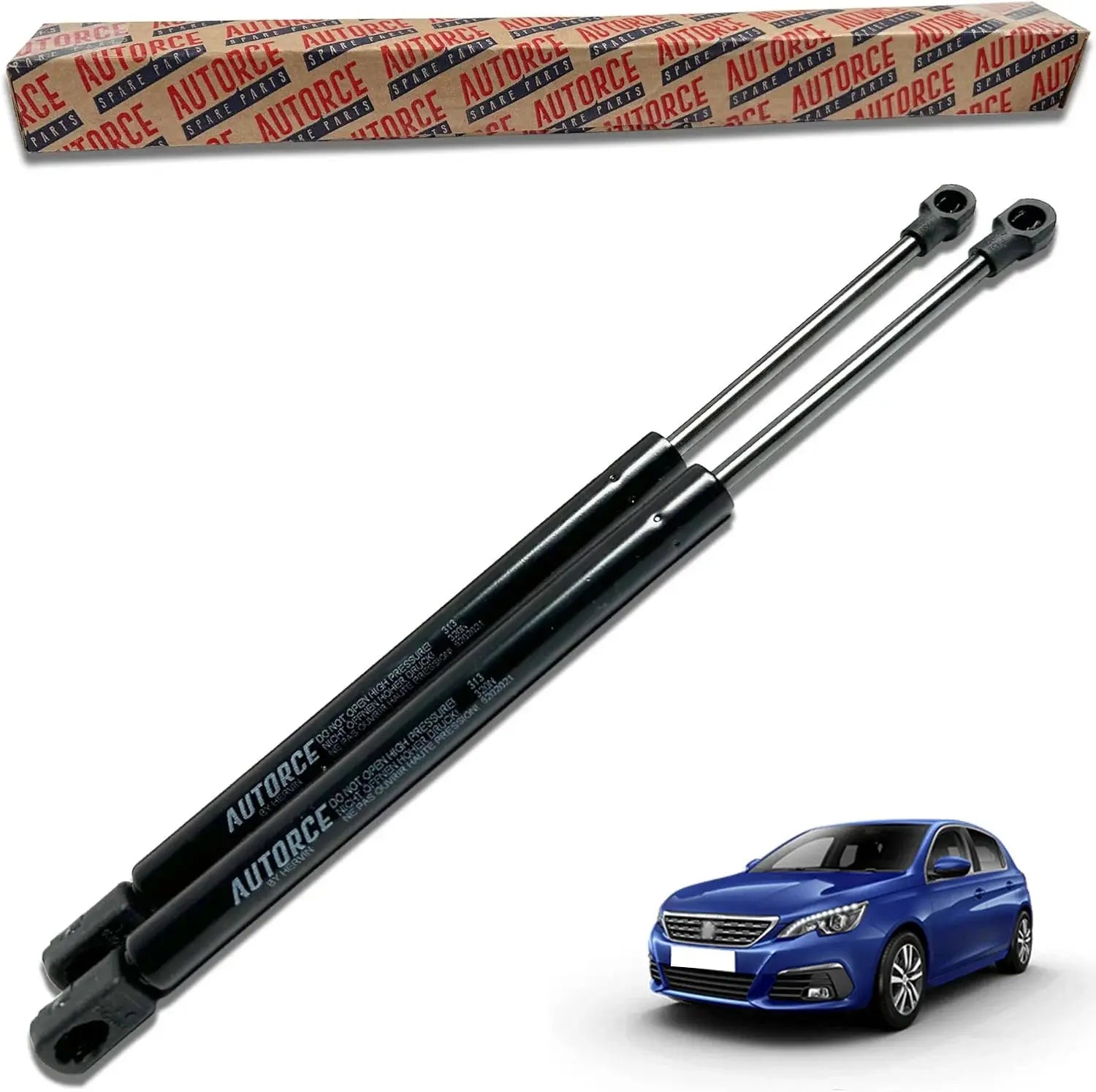
Shop by Category
Gas springs
266 products
Showing 1 - 24 of 266 products
Vehicle gas springs are a critical component of modern vehicle design, providing the force necessary to lift, support, and control various parts of a car, truck, or other vehicle. Gas springs are commonly used in hoods, trunks, and tailgates, as well as in seats, doors, and other areas where controlled movement is necessary. In this article, we'll take a closer look at what gas springs are, how they work, and some of the key factors to consider when selecting and using them in your vehicle.
Gas springs are a type of hydraulic actuator that use compressed gas to generate force. They consist of a cylinder filled with a gas (typically nitrogen) and a piston that moves within the cylinder. The piston is attached to a rod that extends outside the cylinder and is used to push or pull on another object. When the gas inside the cylinder is compressed, it creates a force that pushes the piston and rod outward. When the gas is released, the piston and rod are pulled back into the cylinder.
Gas springs are typically designed with specific force and travel specifications. The force generated by a gas spring is determined by the size of the cylinder, the pressure of the gas inside it, and the area of the piston. The travel of a gas spring refers to the distance that the rod can move in and out of the cylinder. Gas springs are available in a wide range of sizes, forces, and travels, making them versatile and adaptable to many different applications.
How do Gas Springs Work in Vehicles?
Gas springs are used in vehicles to provide controlled movement of various parts, such as hoods, trunks, and tailgates. In these applications, gas springs are typically installed in pairs, with one spring on each side of the part being lifted or supported. The gas springs are attached to the vehicle frame on one end and the part being lifted or supported on the other end.
When the part is opened or lifted, the gas springs extend, generating force to support the weight of the part and keep it in place. When the part is closed or lowered, the gas springs compress, providing a cushioning effect and controlling the rate at which the part moves. Gas springs can also be used in seats and other areas of the vehicle where controlled movement is necessary.
Factors to Consider When Using Gas Springs in Vehicles
When selecting and using gas springs in vehicles, there are several factors to consider to ensure optimal performance and safety. These include:
Load capacity: Gas springs must be rated to support the weight of the part they are lifting or supporting. It's important to choose a gas spring with a load capacity that matches the weight of the part, to ensure that it can be lifted and supported safely.
Travel distance: Gas springs should be selected based on the distance that the part needs to travel. The travel distance of the gas spring should be equal to or slightly greater than the distance the part needs to move.
Mounting orientation: Gas springs are designed to be mounted in specific orientations (e.g., horizontal or vertical), and should be installed according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Temperature range: Gas springs can be affected by temperature changes, and their performance can be impacted if they are used outside of their recommended temperature range.
Maintenance: Gas springs should be inspected regularly for signs of wear or damage, and should be replaced if they are no longer functioning properly.
Conclusion
Gas springs are an essential component of modern vehicle design, providing the force necessary to lift, support, and control various parts of a car, truck, or other vehicle. When selecting and using gas springs in vehicles, it's important to consider factors such as load capacity, travel distance, mounting orientation, temperature range, and maintenance requirements to ensure optimal performance and safety.
What are Gas Springs?
Gas springs are a type of hydraulic actuator that use compressed gas to generate force. They consist of a cylinder filled with a gas (typically nitrogen) and a piston that moves within the cylinder. The piston is attached to a rod that extends outside the cylinder and is used to push or pull on another object. When the gas inside the cylinder is compressed, it creates a force that pushes the piston and rod outward. When the gas is released, the piston and rod are pulled back into the cylinder.
Gas springs are typically designed with specific force and travel specifications. The force generated by a gas spring is determined by the size of the cylinder, the pressure of the gas inside it, and the area of the piston. The travel of a gas spring refers to the distance that the rod can move in and out of the cylinder. Gas springs are available in a wide range of sizes, forces, and travels, making them versatile and adaptable to many different applications.
How do Gas Springs Work in Vehicles?
Gas springs are used in vehicles to provide controlled movement of various parts, such as hoods, trunks, and tailgates. In these applications, gas springs are typically installed in pairs, with one spring on each side of the part being lifted or supported. The gas springs are attached to the vehicle frame on one end and the part being lifted or supported on the other end.
When the part is opened or lifted, the gas springs extend, generating force to support the weight of the part and keep it in place. When the part is closed or lowered, the gas springs compress, providing a cushioning effect and controlling the rate at which the part moves. Gas springs can also be used in seats and other areas of the vehicle where controlled movement is necessary.
Factors to Consider When Using Gas Springs in Vehicles
When selecting and using gas springs in vehicles, there are several factors to consider to ensure optimal performance and safety. These include:
Load capacity: Gas springs must be rated to support the weight of the part they are lifting or supporting. It's important to choose a gas spring with a load capacity that matches the weight of the part, to ensure that it can be lifted and supported safely.
Travel distance: Gas springs should be selected based on the distance that the part needs to travel. The travel distance of the gas spring should be equal to or slightly greater than the distance the part needs to move.
Mounting orientation: Gas springs are designed to be mounted in specific orientations (e.g., horizontal or vertical), and should be installed according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Temperature range: Gas springs can be affected by temperature changes, and their performance can be impacted if they are used outside of their recommended temperature range.
Maintenance: Gas springs should be inspected regularly for signs of wear or damage, and should be replaced if they are no longer functioning properly.
Conclusion
Gas springs are an essential component of modern vehicle design, providing the force necessary to lift, support, and control various parts of a car, truck, or other vehicle. When selecting and using gas springs in vehicles, it's important to consider factors such as load capacity, travel distance, mounting orientation, temperature range, and maintenance requirements to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Showing 1 - 24 of 266 products
Display
View
Save £3.00

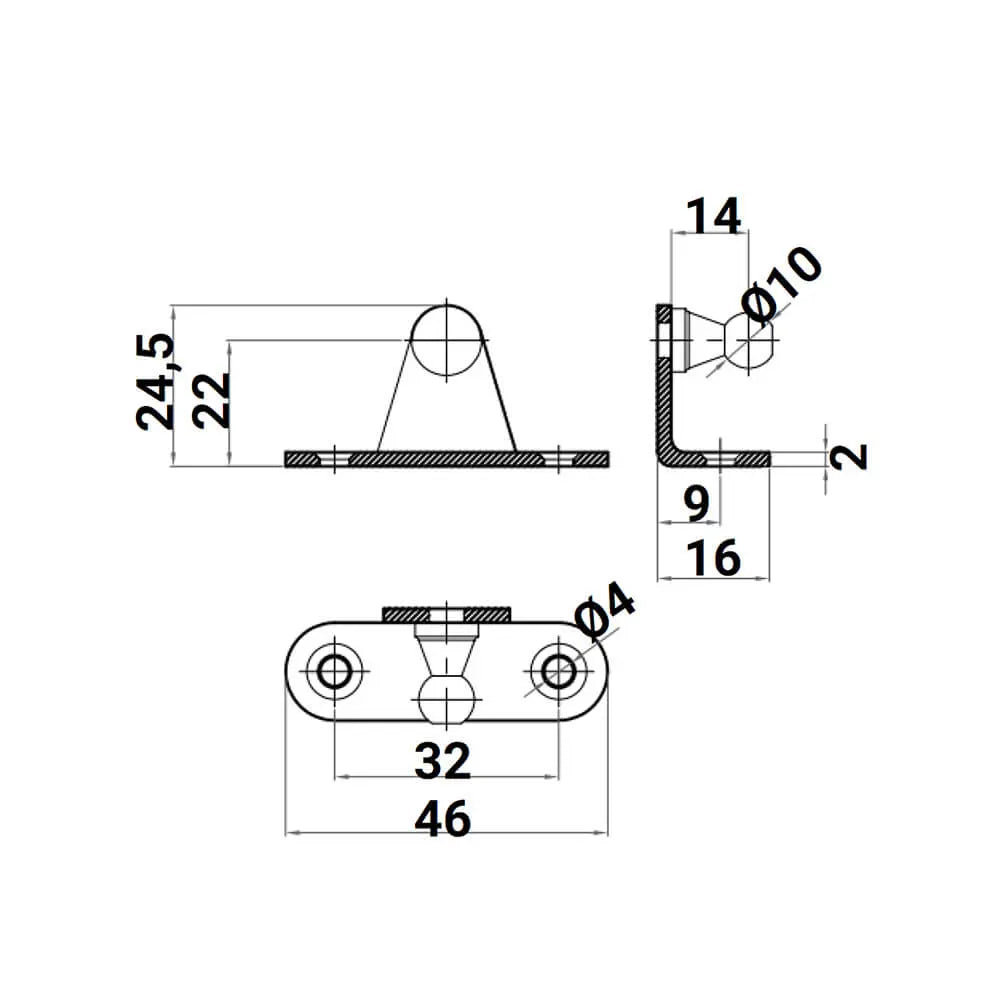
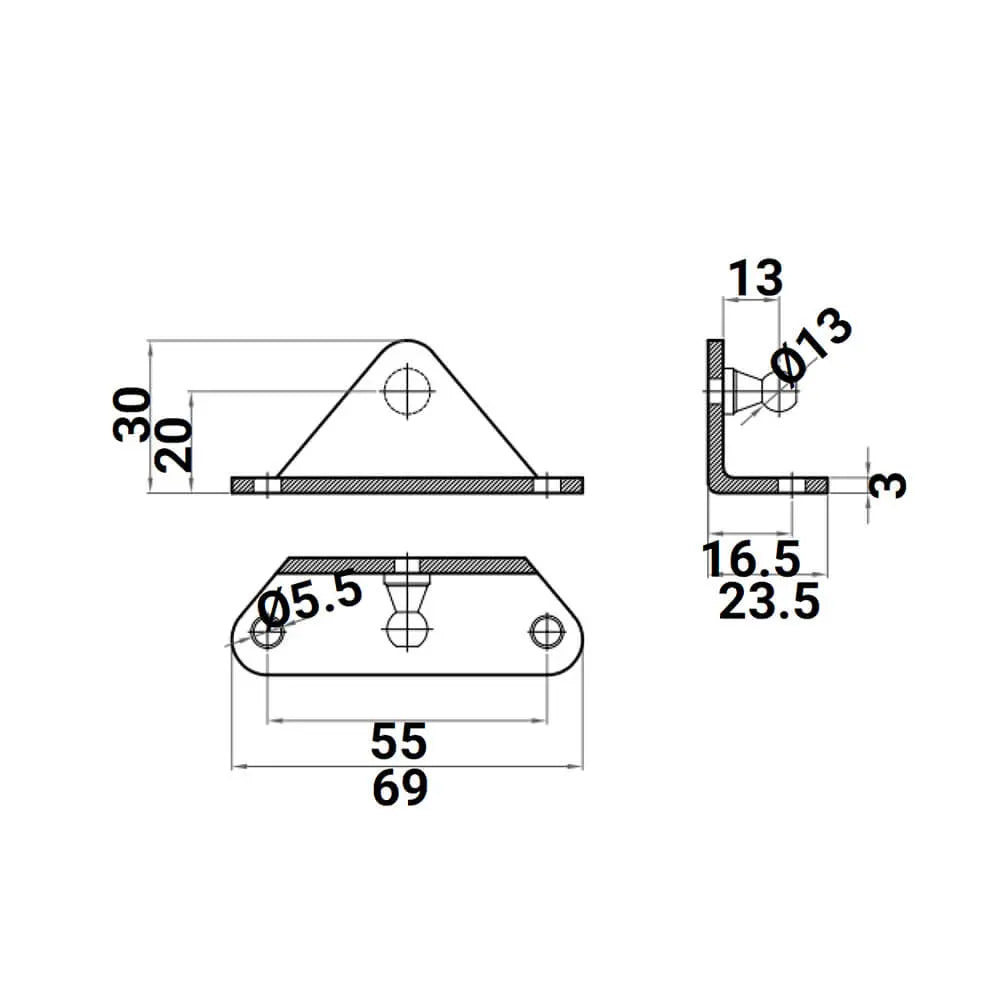
2X M6 Ball L Type Bracket - Gas Spring Lift Support Mounting Brackets 10mm Ball Stud
Sale price£6.90
Regular price£9.90
No reviews
In stockSave £4.00

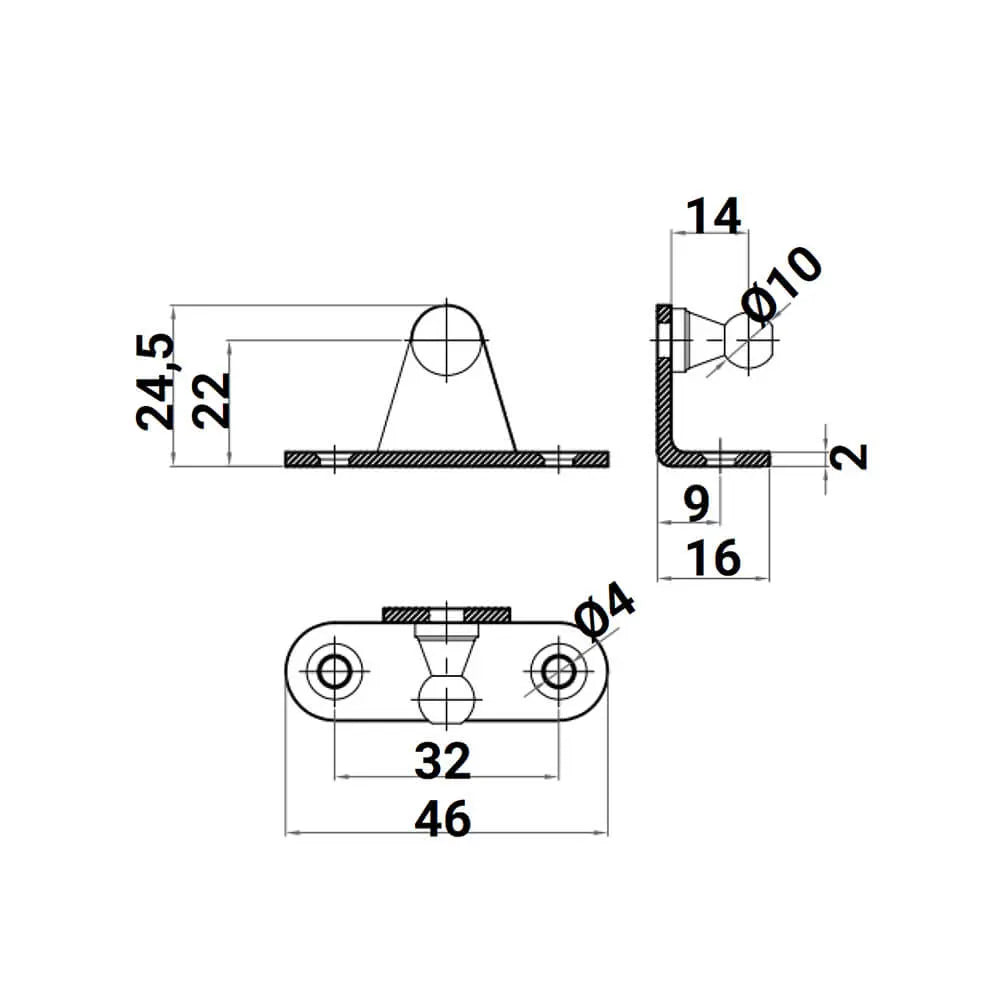
4X M6 Ball L Type Bracket - Gas Spring Lift Support Mounting Brackets 10mm Ball Stud
Sale price£10.90
Regular price£14.90
No reviews
In stockSave £1.00

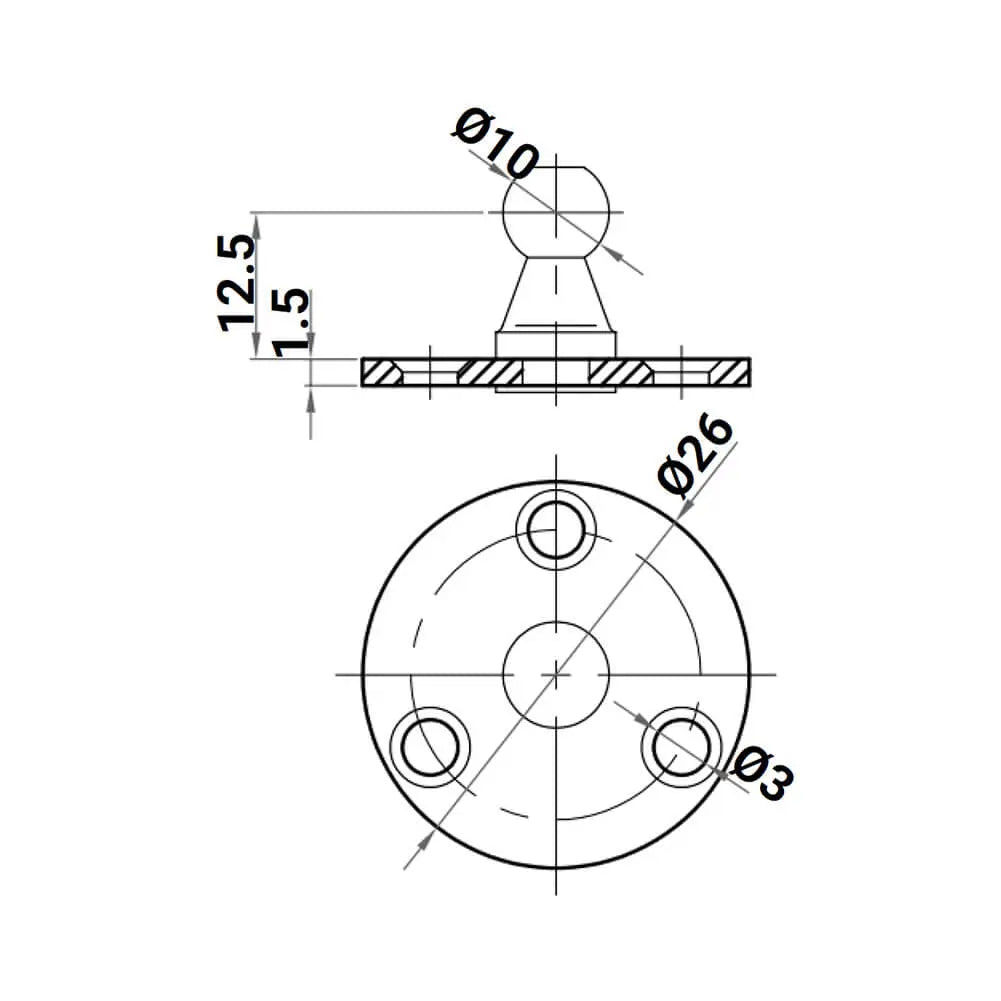
2X M6 Ball Bracket 10mm Ball Pin - Gas Spring Lift Support Mounting
Sale price£6.90
Regular price£7.90
No reviews
Hurry! Stock running out!
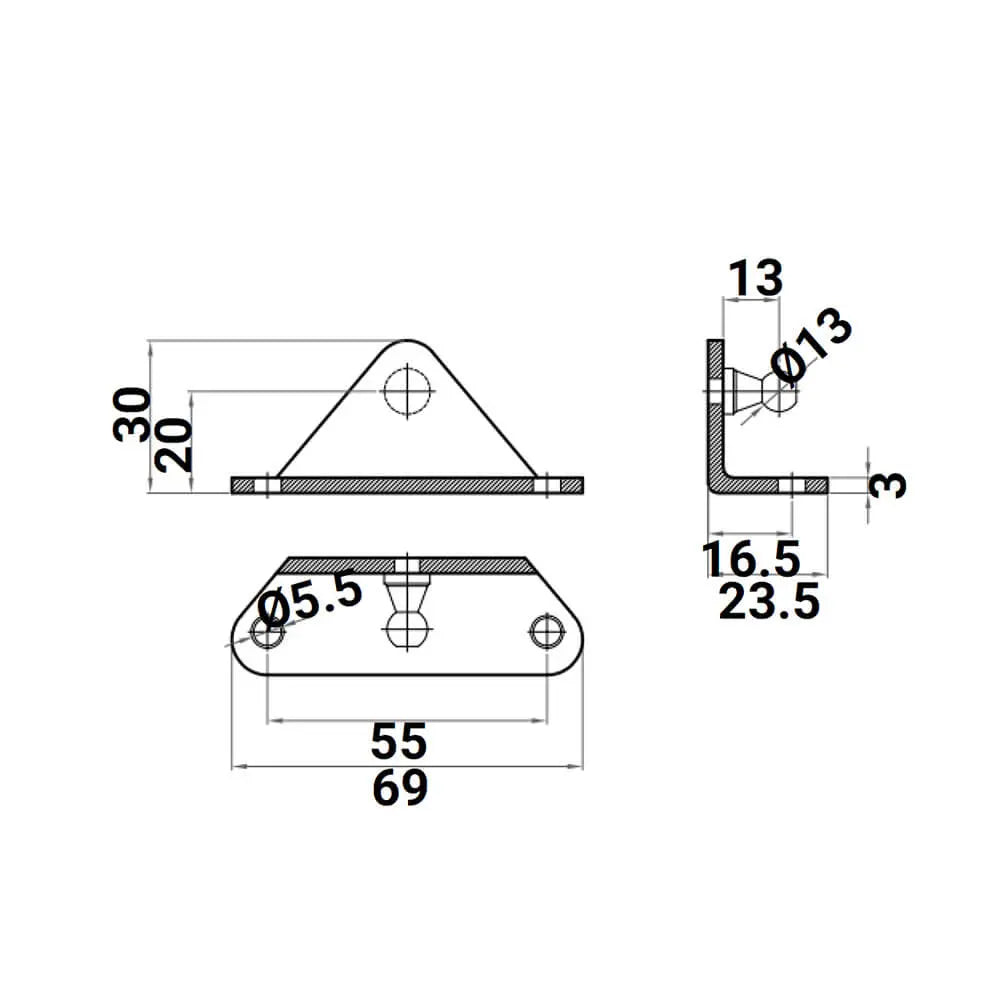
2X M8 Ball Bracket 13mm Ball Pin - Gas Spring Lift Support Mounting
Sale price£6.90
No reviews
In stockSave £2.91
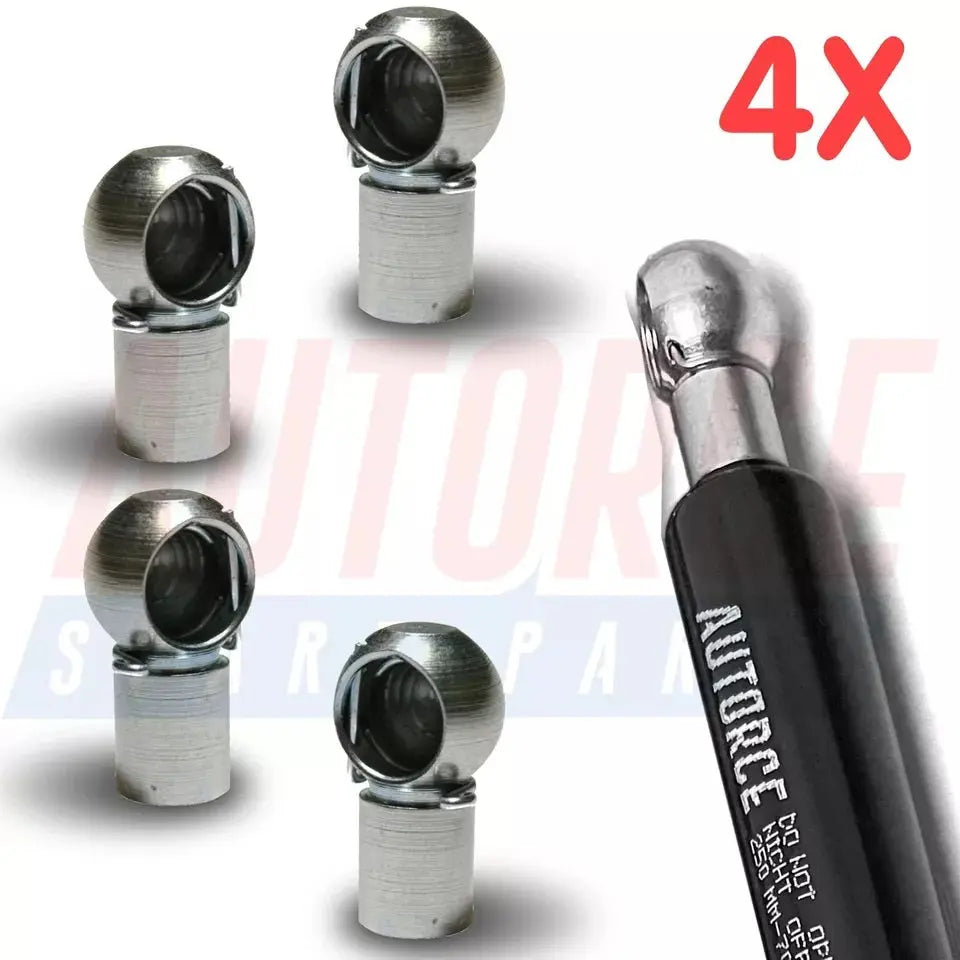


4 Piece Set of M6 M8 M10 Ball Heads for Gas Struts End Fittings, Boot Bonnet or Universal Gas Lift Ball Heads
Sale priceFrom £8.99
Regular price£11.90
No reviews
In stockSave £2.91
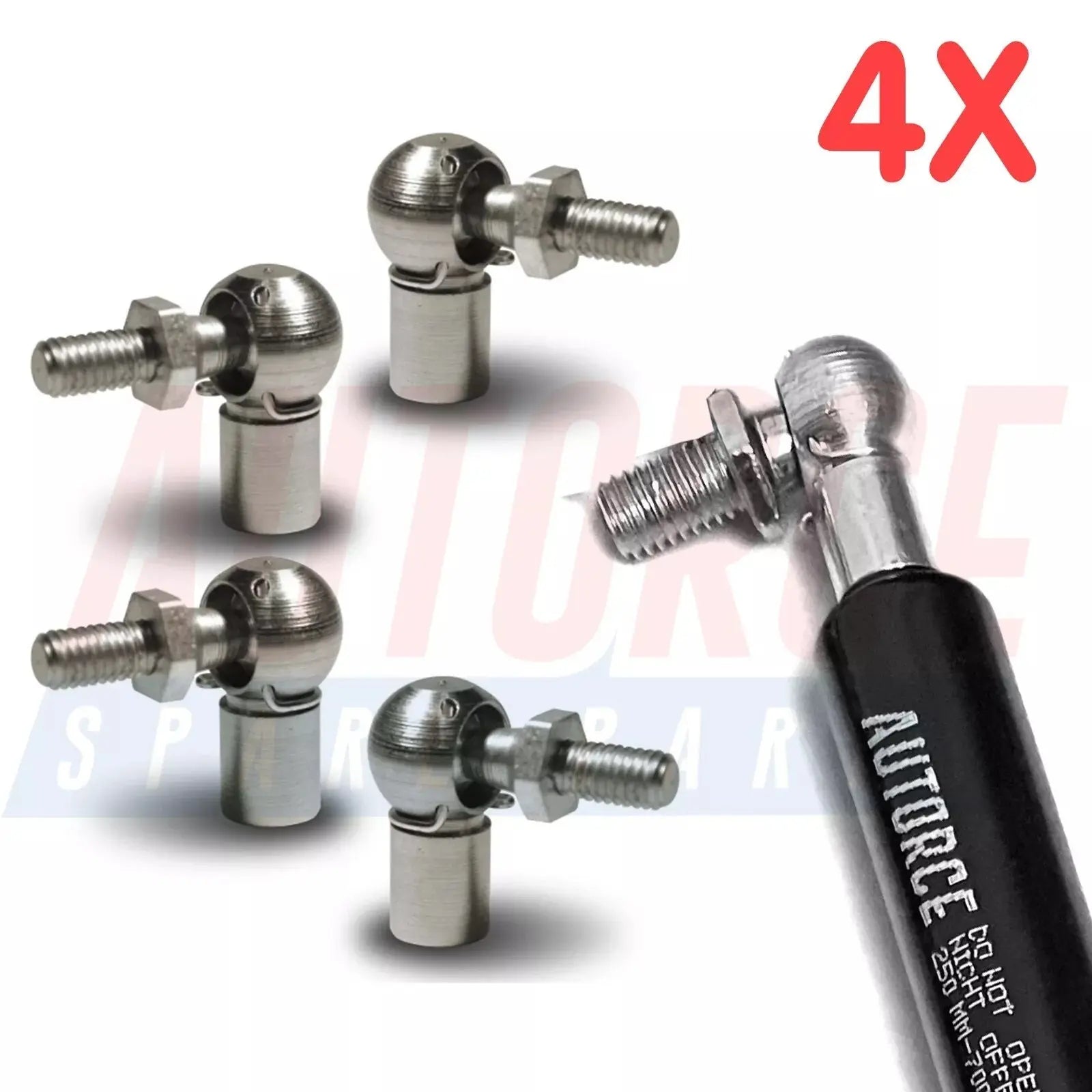
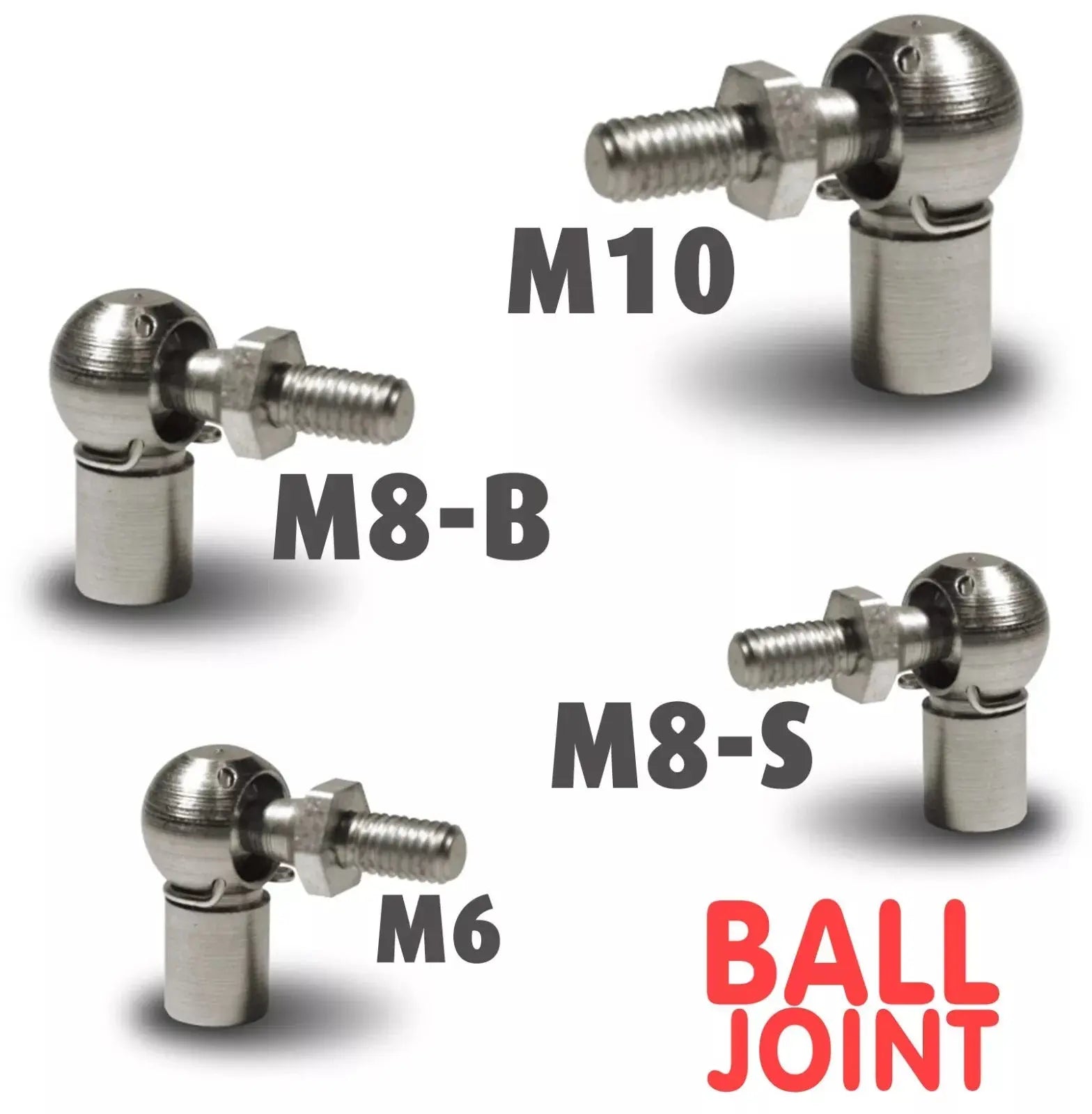


4 Piece Set of M6 M8 M10 Ball Joint Heads for Gas Struts End Fittings Ball Stud Boot Bonnet or Universal Gas Lift Heads
Sale priceFrom £8.99
Regular price£11.90
No reviews
In stockSave £4.09

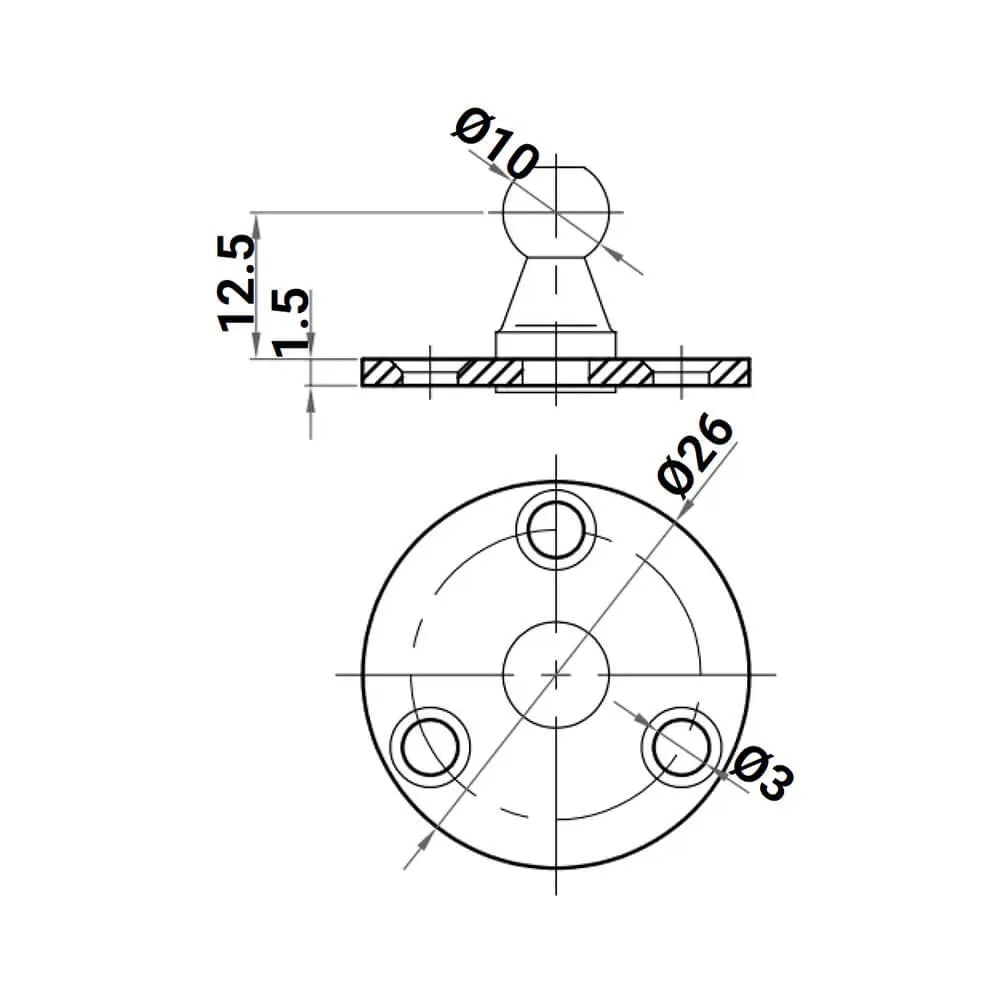
4X M6 Ball Bracket 10mm Ball Pin - Gas Spring Lift Support Mounting
Sale price£10.90
Regular price£14.99
No reviews
In stockSave £2.91
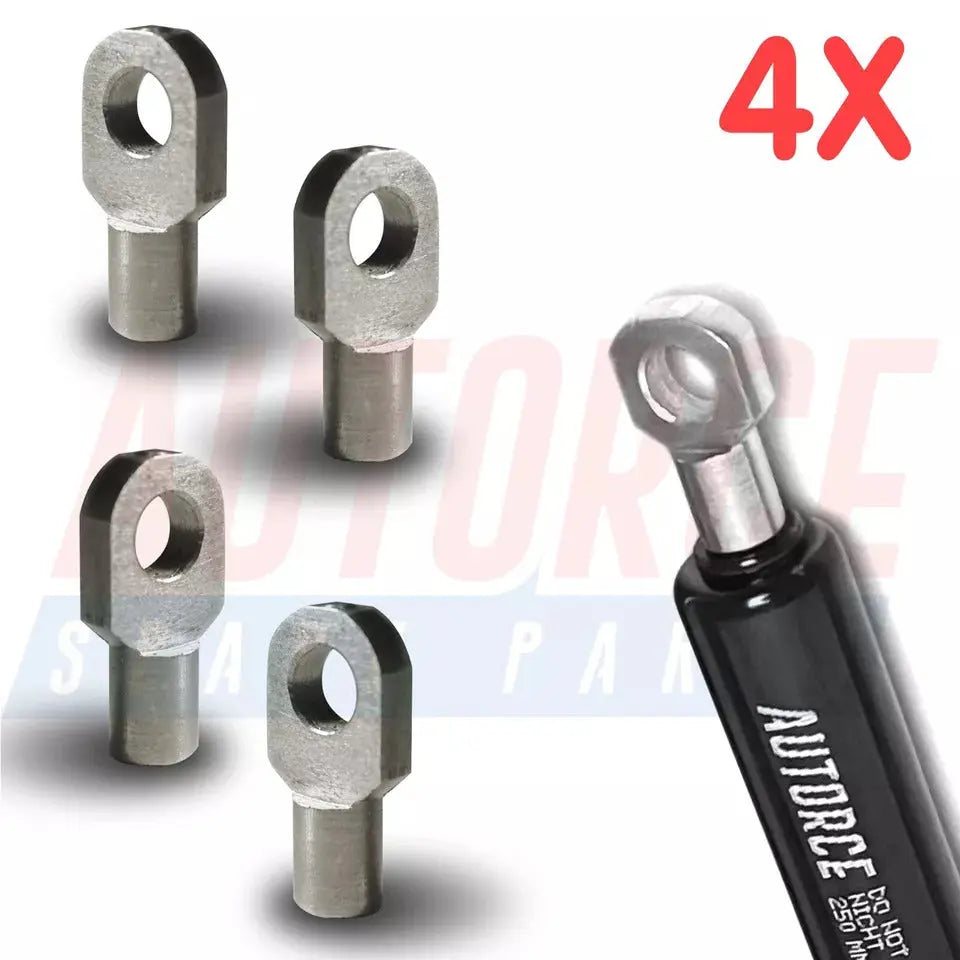


4 Piece Set of M6 M8 M10 Eyelet Heads for Gas Struts End Fittings Eyelet Boot Bonnet or Universal Gas Lift Heads
Sale priceFrom £8.99
Regular price£11.90
No reviews
In stockSave £3.91
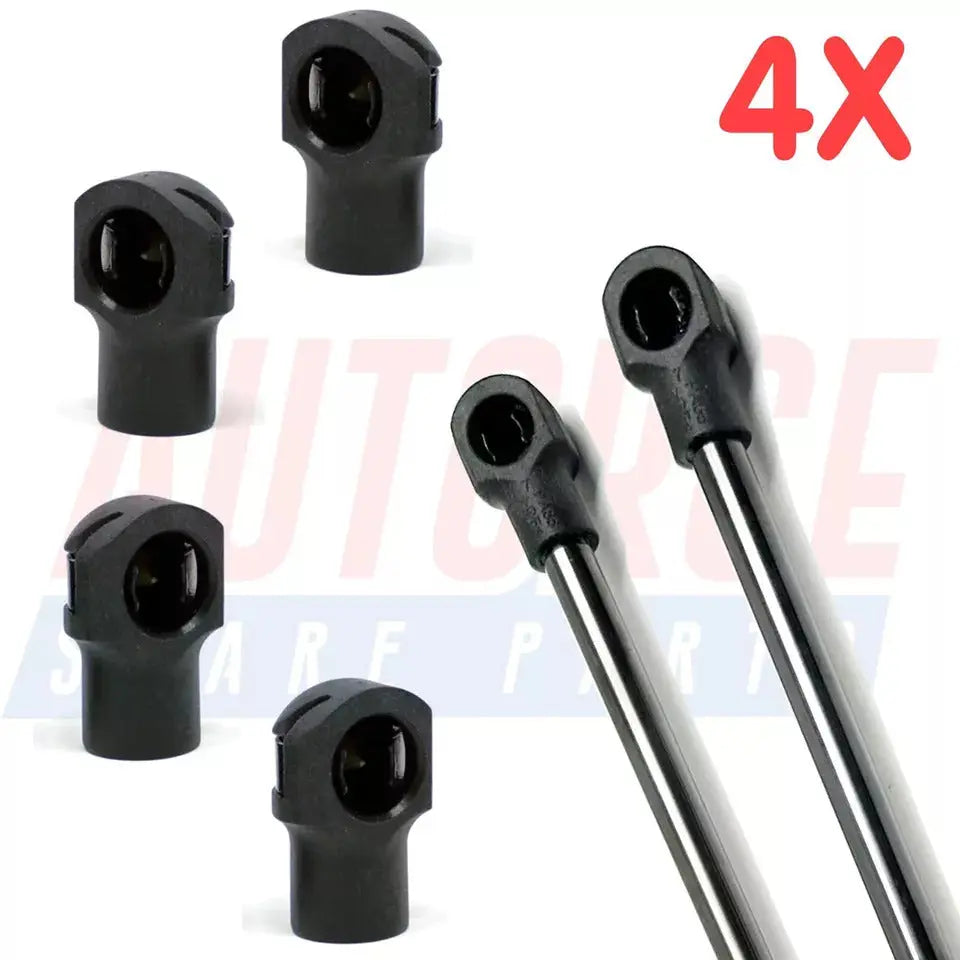
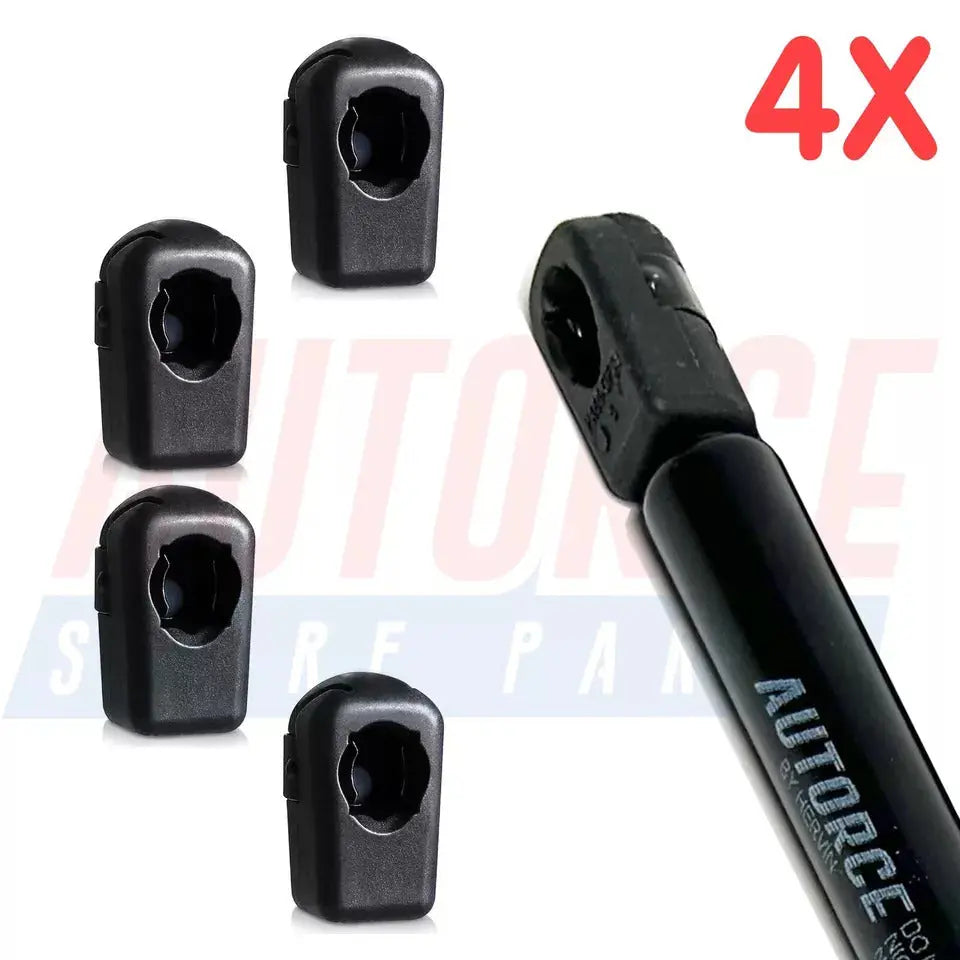


4 Piece Set of M6 M8 M10 Plastic Ball Heads for Gas Struts End Fittings, Boot Bonnet or Universal Gas Lift Plastic Ball Heads
Sale priceFrom £7.99
Regular price£11.90
No reviews
In stock
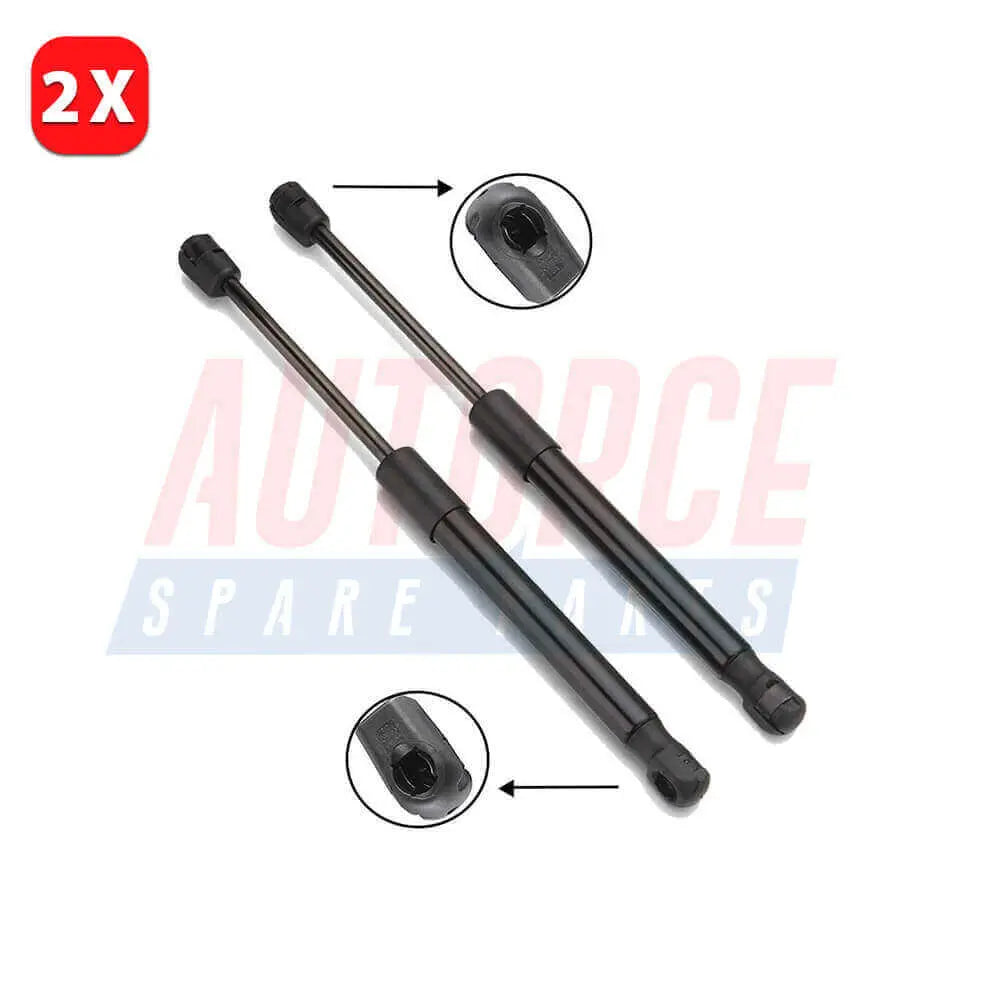

2 Pcs Rear Tailgate Boot Gas Struts For Renault Grand Scenic MK3 (2009 - Onwards) 904517337R
Sale price£14.90
No reviews
In stock

2 Pcs Rear Tailgate Boot Gas Struts For Renault Clio MK3 (2005 - 2013) 32062565
Sale price£12.90
No reviews
In stock
4X M8 Ball Bracket 13mm Ball Pin - Gas Spring Lift Support Mounting
Sale price£10.90
No reviews
In stock

2 Pcs Rear Tailgate Boot Gas Strut For Renault Scenic MK3 (2008-On) 904500004R
Sale price£15.90
No reviews
In stockSave £5.00
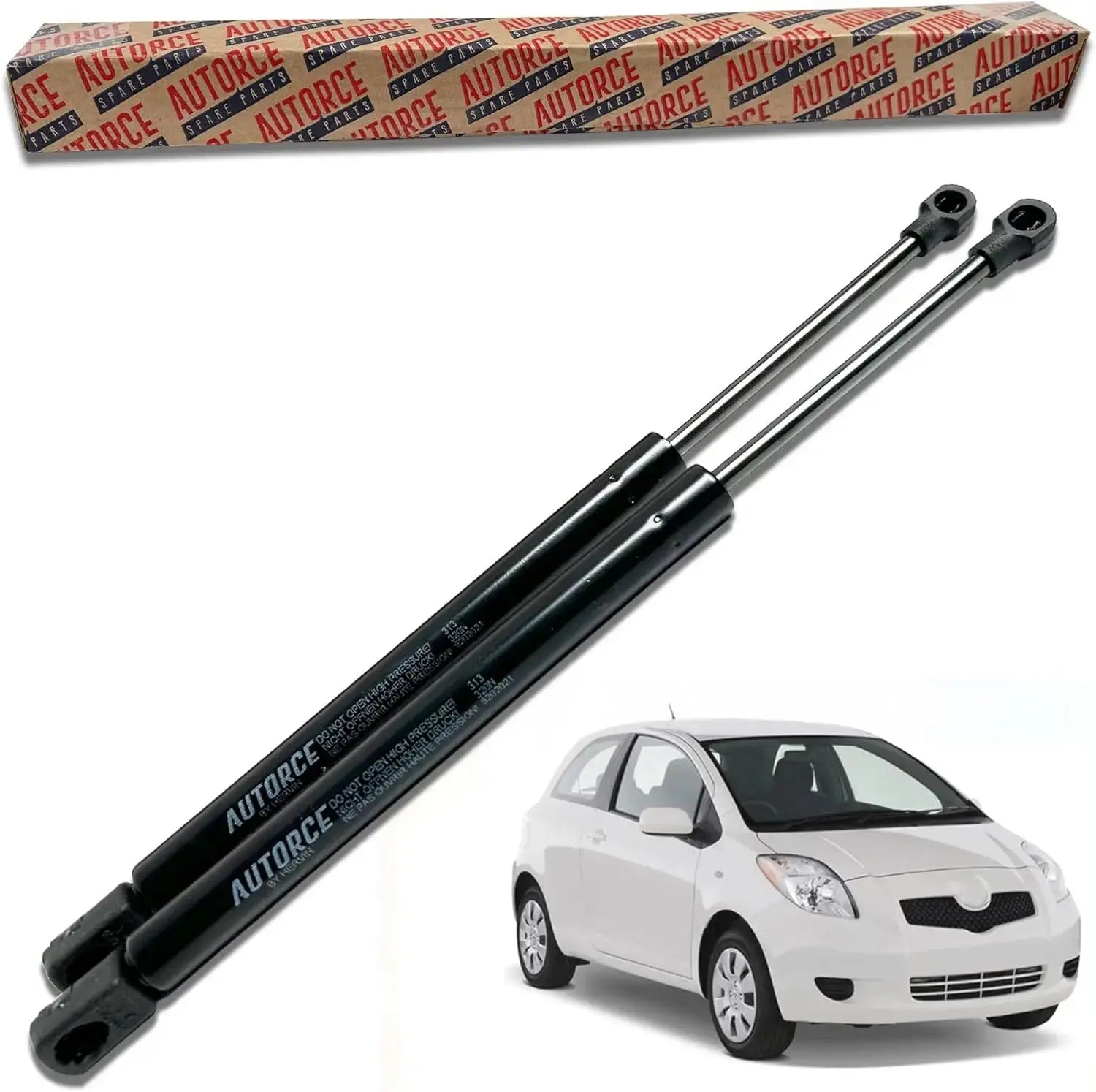


2 Pcs Rear Tailgate Boot Gas Struts For Toyota Yaris II XP9 (2005 - 2014) 390 (N) 430 MM - 68950-0D020, 68960-0D010
Sale price£16.90
Regular price£21.90
No reviews
In stock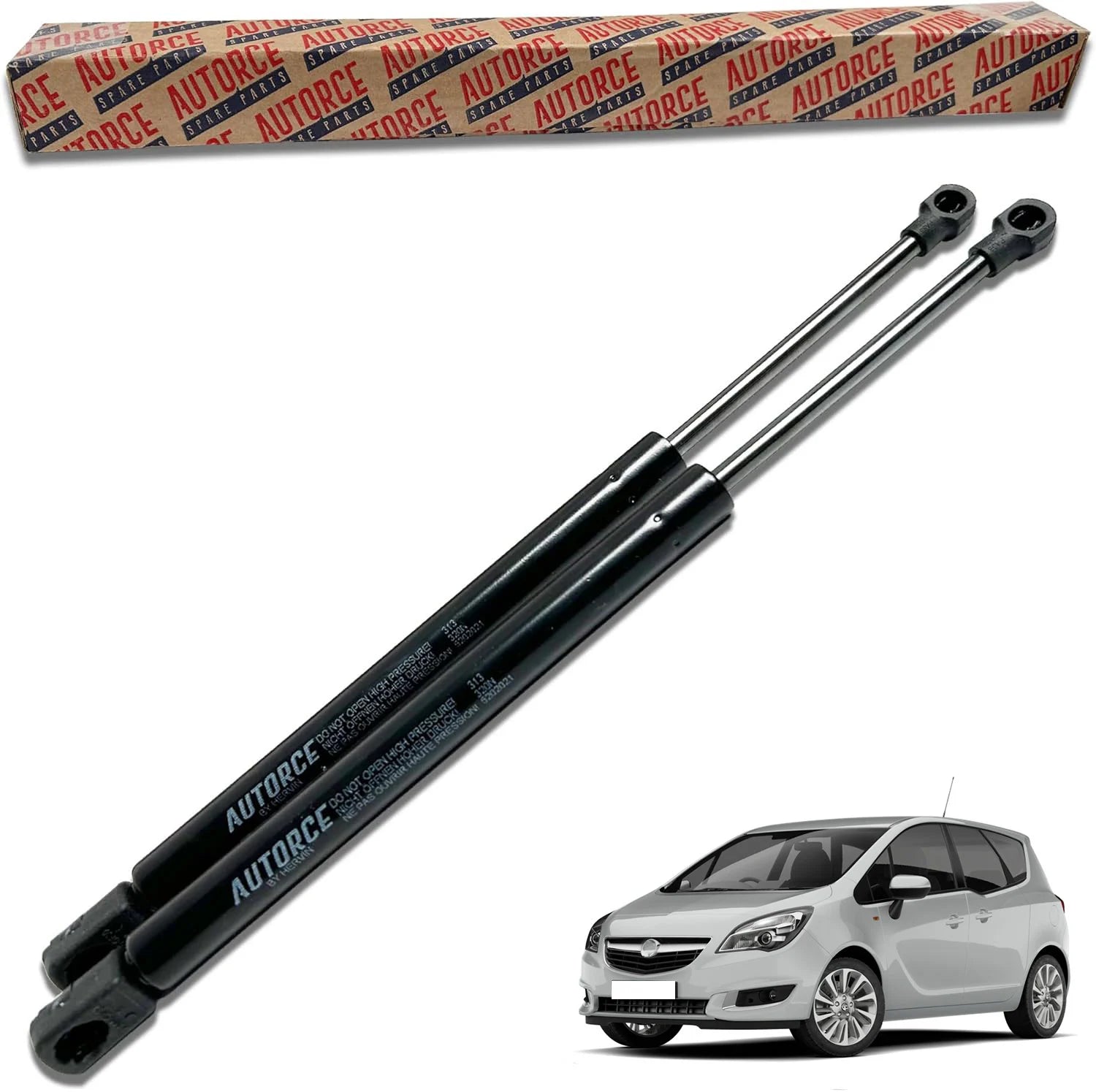

2 Pcs Rear Tailgate Boot Gas Struts For Vauxhall Meriva Mk2 (S10) 13268741,13338367
Sale price£14.90
1 review
In stock

2 Pcs Rear Tailgate Boot Gas Struts For Opel Meriva B (S10) 13338367, 13268741
Sale price£14.90
No reviews
In stock

2 Pcs Rear Tailgate Boot Gas Struts For Renault Megane III 844300009R, 7701057303
Sale price£14.90
No reviews
In stock

2 Pcs Rear Tailgate Boot Gas Struts For Toyota Avensis - 6896005060, 68960050
Sale price£15.90
No reviews
In stock
Filters (0)












